A python package of Zeroth-Order Optimization (ZOOpt).
Zeroth-order optimization (a.k.a. derivative-free optimization/black-box optimization) does not rely on the gradient of the objective function, but instead, learns from samples of the search space. It is suitable for optimizing functions that are nondifferentiable, with many local minima, or even unknown but only testable.
ZOOpt has a single-thread version and a light-weighted distribution version. Please find the details in the documents.
Documents: Wiki of ZOOpt
Citation:
Yu-Ren Liu, Yi-Qi Hu, Hong Qian, Yang Yu, Chao Qian. ZOOpt: Toolbox for Derivative-Free Optimization. CORR abs/1801.00329
(Features in this article are from version 0.2)
To use the single thread version, the easiest way to get ZOOpt is to type pip install zoopt in the terminal/command line.
Alternatively, to install ZOOpt by source code, download this project and sequentially run following commands in your terminal/command line.
$ python setup.py build
$ python setup.py install
We define the Ackley function for minimization (note that this function is for arbitrary dimensions, determined by the solution)
import numpy as np
def ackley(solution):
x = solution.get_x()
bias = 0.2
value = -20 * np.exp(-0.2 * np.sqrt(sum([(i - bias) * (i - bias) for i in x]) / len(x))) - \
np.exp(sum([np.cos(2.0*np.pi*(i-bias)) for i in x]) / len(x)) + 20.0 + np.e
return valueAckley function is a classical function with many local minima. In 2-dimension, it looks like (from wikipedia)
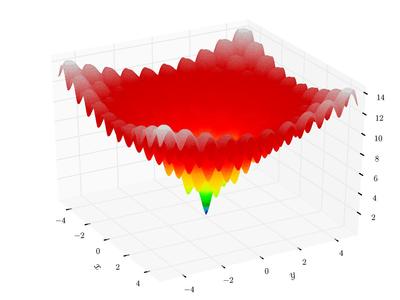 |
Then, use ZOOpt to optimize a 100-dimension Ackley function:
from zoopt import Dimension, Objective, Parameter, Opt
dim = 100 # dimension
obj = Objective(ackley, Dimension(dim, [[-1, 1]] * dim, [True] * dim))
# perform optimization
solution = Opt.min(obj, Parameter(budget=100 * dim))
# print result
solution.print_solution()For a few seconds, the optimization is done. Then, we can visualize the optimization progress
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(obj.get_history_bestsofar())
plt.savefig('figure.png')which looks like
 |
More examples are available in the example fold.
- Add the noise handling strategies Re-sampling and Value Suppression (AAAI'18), and the subset selection method with noise handling PONSS (NIPS'17)
- Add high-dimensionality handling method Sequential Random Embedding (IJCAI'16)
- Rewrite Pareto optimization method. Bugs fixed.
- Include the general optimization method RACOS (AAAI'16) and Sequential RACOS (AAAI'17), and the subset selection method POSS (NIPS'15).
- The algorithm selection is automatic. See examples in the
examplefold.- Default parameters work well on many problems, while parameters are fully controllable - Running speed optmized for Python
The distributed version of ZOOpt is consisted of the server project and the client project. Details can be found in the tutorial of the distributed ZOOpt

