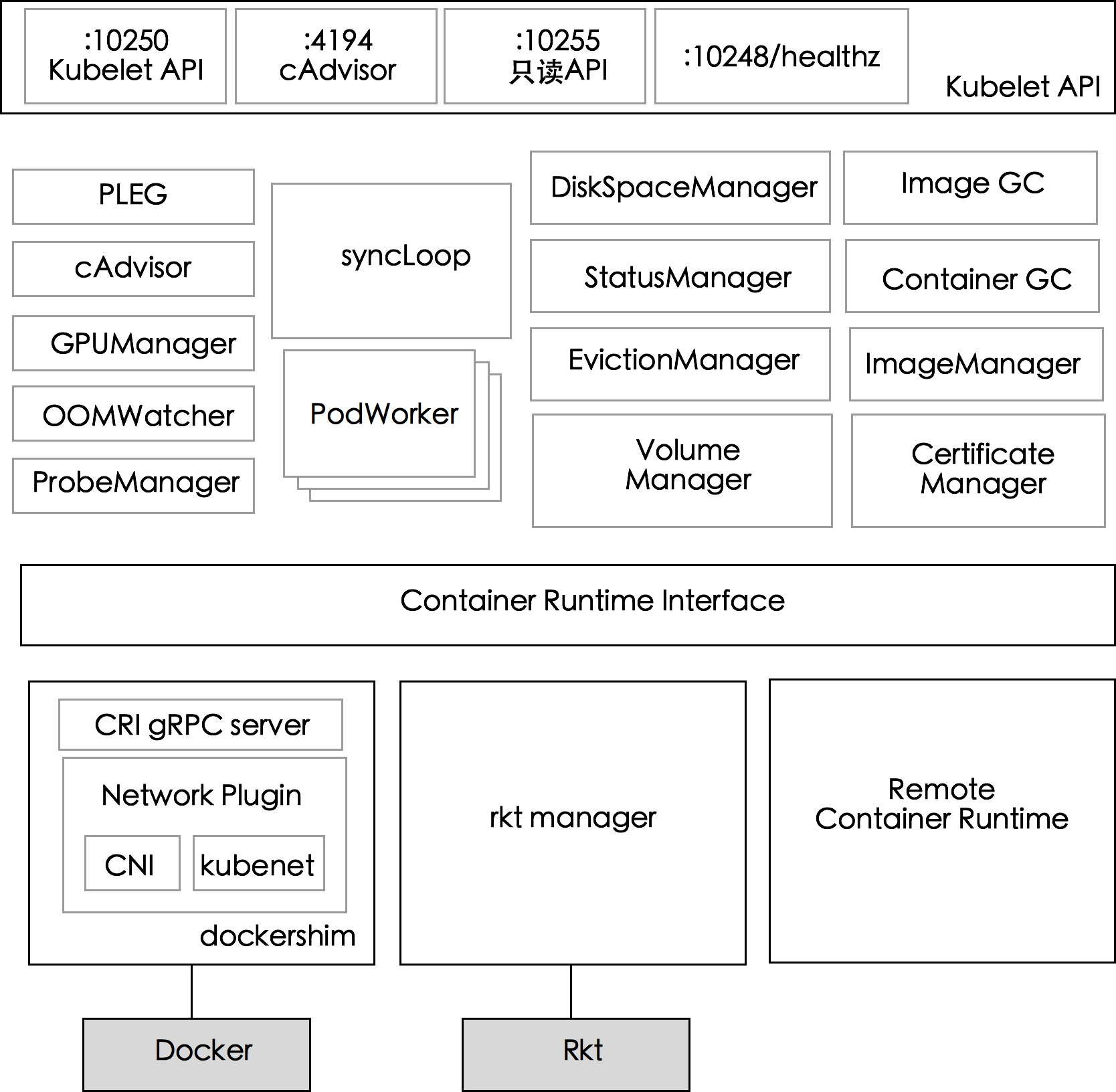
[TOC]
代码基于 1.6 版本
k8s.io/kubernetes/cmd/kubelet/kubelet.go
func main() {
// ...
if err := app.Run(s, nil); err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "error: %v\n", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
}k8s.io/kubernetes/cmd/kubelet/app/server.go
// Run runs the specified KubeletServer with the given KubeletDeps. This should never exit.
// The kubeDeps argument may be nil - if so, it is initialized from the settings on KubeletServer.
// Otherwise, the caller is assumed to have set up the KubeletDeps object and a default one will
// not be generated.
func Run(s *options.KubeletServer, kubeDeps *kubelet.KubeletDeps) error {
if err := run(s, kubeDeps); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to run Kubelet: %v", err)
}
return nil
}
func run(s *options.KubeletServer, kubeDeps *kubelet.KubeletDeps) (err error) {
/*kubeDeps = nil*/
// ...
done := make(chan struct{})
// ...
// Validate configuration.
if err := validateConfig(s); err != nil {
return err
}
nodeName, err := getNodeName(kubeDeps.Cloud, nodeutil.GetHostname(s.HostnameOverride))
// Setup event recorder if required.
makeEventRecorder(&s.KubeletConfiguration, kubeDeps, nodeName)
if kubeDeps.ContainerManager == nil {
// ...
kubeDeps.ContainerManager, err = cm.NewContainerManager(
kubeDeps.Mounter,
kubeDeps.CAdvisorInterface,
cm.NodeConfig{
RuntimeCgroupsName: s.RuntimeCgroups,
SystemCgroupsName: s.SystemCgroups,
KubeletCgroupsName: s.KubeletCgroups,
ContainerRuntime: s.ContainerRuntime,
CgroupsPerQOS: s.CgroupsPerQOS,
CgroupRoot: s.CgroupRoot,
CgroupDriver: s.CgroupDriver,
ProtectKernelDefaults: s.ProtectKernelDefaults,
NodeAllocatableConfig: cm.NodeAllocatableConfig{
KubeReservedCgroupName: s.KubeReservedCgroup,
SystemReservedCgroupName: s.SystemReservedCgroup,
EnforceNodeAllocatable: sets.NewString(s.EnforceNodeAllocatable...),
KubeReserved: kubeReserved,
SystemReserved: systemReserved,
HardEvictionThresholds: hardEvictionThresholds,
},
ExperimentalQOSReserved: *experimentalQOSReserved,
},
s.ExperimentalFailSwapOn,
kubeDeps.Recorder)
}
// ....
RunKubelet(&s.KubeletFlags, &s.KubeletConfiguration, kubeDeps, s.RunOnce, standaloneMode);
<-done
return nil
}func RunKubelet(kubeFlags *options.KubeletFlags, kubeCfg *componentconfig.KubeletConfiguration, kubeDeps *kubelet.KubeletDeps, runOnce bool, standaloneMode bool) error {
hostname := nodeutil.GetHostname(kubeFlags.HostnameOverride)
// Query the cloud provider for our node name, default to hostname if kcfg.Cloud == nil
nodeName, err := getNodeName(kubeDeps.Cloud, hostname)
// Setup event recorder if required.
makeEventRecorder(kubeCfg, kubeDeps, nodeName)
hostNetworkSources, err := kubetypes.GetValidatedSources(kubeCfg.HostNetworkSources)
hostPIDSources, err := kubetypes.GetValidatedSources(kubeCfg.HostPIDSources)
hostIPCSources, err := kubetypes.GetValidatedSources(kubeCfg.HostIPCSources)
privilegedSources := capabilities.PrivilegedSources{
HostNetworkSources: hostNetworkSources,
HostPIDSources: hostPIDSources,
HostIPCSources: hostIPCSources,
}
capabilities.Setup(kubeCfg.AllowPrivileged, privilegedSources, 0)
credentialprovider.SetPreferredDockercfgPath(kubeCfg.RootDirectory)
builder := kubeDeps.Builder
if builder == nil {
builder = CreateAndInitKubelet // 重点分析
}
if kubeDeps.OSInterface == nil {
kubeDeps.OSInterface = kubecontainer.RealOS{}
}
// 调用 CreateAndInitKubelet 完成 kubelet.KubeletBootstrap 的创建
k, err := builder(kubeCfg, kubeDeps, &kubeFlags.ContainerRuntimeOptions, standaloneMode, kubeFlags.HostnameOverride, kubeFlags.NodeIP, kubeFlags.ProviderID)
podCfg := kubeDeps.PodConfig
//...
startKubelet(k, podCfg, kubeCfg, kubeDeps)
}func startKubelet(k kubelet.KubeletBootstrap, podCfg *config.PodConfig, kubeCfg *componentconfig.KubeletConfiguration, kubeDeps *kubelet.KubeletDeps) {
// start the kubelet
go wait.Until(func() { k.Run(podCfg.Updates()) }, 0, wait.NeverStop)
// start the kubelet server, 主要提供给API Server 访问相关信息
if kubeCfg.EnableServer {
go wait.Until(func() {
k.ListenAndServe(net.ParseIP(kubeCfg.Address), uint(kubeCfg.Port), kubeDeps.TLSOptions, kubeDeps.Auth, kubeCfg.EnableDebuggingHandlers, kubeCfg.EnableContentionProfiling)
}, 0, wait.NeverStop)
}
if kubeCfg.ReadOnlyPort > 0 {
go wait.Until(func() {
k.ListenAndServeReadOnly(net.ParseIP(kubeCfg.Address), uint(kubeCfg.ReadOnlyPort))
}, 0, wait.NeverStop)
}
}创建kubelet并初始化相关工作
func CreateAndInitKubelet(kubeCfg *componentconfig.KubeletConfiguration, kubeDeps *kubelet.KubeletDeps, crOptions *options.ContainerRuntimeOptions, standaloneMode bool, hostnameOverride, nodeIP, providerID string) (k kubelet.KubeletBootstrap, err error) {
// TODO: block until all sources have delivered at least one update to the channel, or break the sync loop
// up into "per source" synchronizations
// NewMainKubelet 完成对象的创建,非常长的一个函数
k, err = kubelet.NewMainKubelet(kubeCfg, kubeDeps, crOptions, standaloneMode, hostnameOverride, nodeIP, providerID)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 事件通知
k.BirthCry()
// 启动垃圾回收相关工作
k.StartGarbageCollection()
return k, nil
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
// NewMainKubelet instantiates a new Kubelet object along with all the required internal modules.
// No initialization of Kubelet and its modules should happen here.
func NewMainKubelet(kubeCfg *componentconfig.KubeletConfiguration, kubeDeps *KubeletDeps, crOptions *options.ContainerRuntimeOptions, standaloneMode bool, hostnameOverride, nodeIP, providerID string) (*Kubelet, error){
if kubeDeps.PodConfig == nil {
var err error
kubeDeps.PodConfig, err = makePodSourceConfig(kubeCfg, kubeDeps, nodeName)
// ...
klet.statusManager = status.NewManager(klet.kubeClient, klet.podManager, klet)
// ...
klet.podWorkers = newPodWorkers(klet.syncPod, kubeDeps.Recorder, klet.workQueue, klet.resyncInterval, backOffPeriod, klet.podCache)
// ...
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
// makePodSourceConfig creates a config.PodConfig from the given
// KubeletConfiguration or returns an error.
func makePodSourceConfig(kubeCfg *componentconfig.KubeletConfiguration, kubeDeps *KubeletDeps, nodeName types.NodeName) (*config.PodConfig, error) {
// ...
// source of all configuration
cfg := config.NewPodConfig(config.PodConfigNotificationIncremental, kubeDeps.Recorder)
// define file config source
if kubeCfg.PodManifestPath != "" {
config.NewSourceFile(kubeCfg.PodManifestPath, nodeName, kubeCfg.FileCheckFrequency.Duration, cfg.Channel(kubetypes.FileSource))
}
// define url config source
if kubeCfg.ManifestURL != "" {
config.NewSourceURL(kubeCfg.ManifestURL, manifestURLHeader, nodeName, kubeCfg.HTTPCheckFrequency.Duration, cfg.Channel(kubetypes.HTTPSource))
}
if kubeDeps.KubeClient != nil {
config.NewSourceApiserver(kubeDeps.KubeClient, nodeName, cfg.Channel(kubetypes.ApiserverSource))
}
return cfg, nil
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/config/config.go
// PodConfig is a configuration mux that merges many sources of pod configuration into a single
// consistent structure, and then delivers incremental change notifications to listeners
// in order.
type PodConfig struct {
pods *podStorage
mux *config.Mux // 保存汇入的各个 channel
// the channel of denormalized changes passed to listeners
updates chan kubetypes.PodUpdate // 对外暴露的channel
// contains the list of all configured sources
sourcesLock sync.Mutex
sources sets.String
}
// Mux is a class for merging configuration from multiple sources. Changes are
// pushed via channels and sent to the merge function.
type Mux struct {
// Invoked when an update is sent to a source.
merger Merger
// Sources and their lock.
sourceLock sync.RWMutex
// Maps source names to channels
sources map[string]chan interface{}
}NewMainKubelet() 函数中主要就是根据配置设置好 kubelet 结构中的各字段。
// Kubelet is the main kubelet implementation.
type Kubelet struct {
kubeletConfiguration componentconfig.KubeletConfiguration
hostname string
nodeName types.NodeName
runtimeCache kubecontainer.RuntimeCache
kubeClient clientset.Interface
iptClient utilipt.Interface
rootDirectory string
// podWorkers handle syncing Pods in response to events.
podWorkers PodWorkers
// resyncInterval is the interval between periodic full reconciliations of
// pods on this node.
resyncInterval time.Duration
// sourcesReady records the sources seen by the kubelet, it is thread-safe.
sourcesReady config.SourcesReady
// podManager is a facade that abstracts away the various sources of pods
// this Kubelet services.
podManager kubepod.Manager
// Needed to observe and respond to situations that could impact node stability
evictionManager eviction.Manager
// Optional, defaults to /logs/ from /var/log
logServer http.Handler
// Optional, defaults to simple Docker implementation
runner kubecontainer.ContainerCommandRunner
// cAdvisor used for container information.
cadvisor cadvisor.Interface
// Set to true to have the node register itself with the apiserver.
registerNode bool
// Set to true to have the node register itself as schedulable.
registerSchedulable bool
// for internal book keeping; access only from within registerWithApiserver
registrationCompleted bool
// Set to true if the kubelet is in standalone mode (i.e. setup without an apiserver)
standaloneMode bool
// If non-empty, use this for container DNS search.
clusterDomain string
// If non-nil, use this for container DNS server.
clusterDNS []net.IP
// masterServiceNamespace is the namespace that the master service is exposed in.
masterServiceNamespace string
// serviceLister knows how to list services
serviceLister serviceLister
// nodeInfo knows how to get information about the node for this kubelet.
nodeInfo predicates.NodeInfo
// a list of node labels to register
nodeLabels map[string]string
// Last timestamp when runtime responded on ping.
// Mutex is used to protect this value.
runtimeState *runtimeState
// Volume plugins.
volumePluginMgr *volume.VolumePluginMgr
// Network plugin.
networkPlugin network.NetworkPlugin
// Handles container probing.
probeManager prober.Manager
// Manages container health check results.
livenessManager proberesults.Manager
// How long to keep idle streaming command execution/port forwarding
// connections open before terminating them
streamingConnectionIdleTimeout time.Duration
// The EventRecorder to use
recorder record.EventRecorder
// Policy for handling garbage collection of dead containers.
containerGC kubecontainer.ContainerGC
// Manager for image garbage collection.
imageManager images.ImageGCManager
// Diskspace manager.
diskSpaceManager diskSpaceManager
// Secret manager.
secretManager secret.Manager
// Cached MachineInfo returned by cadvisor.
machineInfo *cadvisorapi.MachineInfo
// Handles certificate rotations.
serverCertificateManager certificate.Manager
// Syncs pods statuses with apiserver; also used as a cache of statuses.
statusManager status.Manager
// VolumeManager runs a set of asynchronous loops that figure out which
// volumes need to be attached/mounted/unmounted/detached based on the pods
// scheduled on this node and makes it so.
volumeManager volumemanager.VolumeManager
// Cloud provider interface.
cloud cloudprovider.Interface
autoDetectCloudProvider bool
// Indicates that the node initialization happens in an external cloud controller
externalCloudProvider bool
// Reference to this node.
nodeRef *clientv1.ObjectReference
// Container runtime.
containerRuntime kubecontainer.Runtime
// reasonCache caches the failure reason of the last creation of all containers, which is
// used for generating ContainerStatus.
reasonCache *ReasonCache
// nodeStatusUpdateFrequency specifies how often kubelet posts node status to master.
// Note: be cautious when changing the constant, it must work with nodeMonitorGracePeriod
// in nodecontroller. There are several constraints:
// 1. nodeMonitorGracePeriod must be N times more than nodeStatusUpdateFrequency, where
// N means number of retries allowed for kubelet to post node status. It is pointless
// to make nodeMonitorGracePeriod be less than nodeStatusUpdateFrequency, since there
// will only be fresh values from Kubelet at an interval of nodeStatusUpdateFrequency.
// The constant must be less than podEvictionTimeout.
// 2. nodeStatusUpdateFrequency needs to be large enough for kubelet to generate node
// status. Kubelet may fail to update node status reliably if the value is too small,
// as it takes time to gather all necessary node information.
nodeStatusUpdateFrequency time.Duration
// Generates pod events.
pleg pleg.PodLifecycleEventGenerator
// Store kubecontainer.PodStatus for all pods.
podCache kubecontainer.Cache
// os is a facade for various syscalls that need to be mocked during testing.
os kubecontainer.OSInterface
// Watcher of out of memory events.
oomWatcher OOMWatcher
// Monitor resource usage
resourceAnalyzer stats.ResourceAnalyzer
// Whether or not we should have the QOS cgroup hierarchy for resource management
cgroupsPerQOS bool
// If non-empty, pass this to the container runtime as the root cgroup.
cgroupRoot string
// Mounter to use for volumes.
mounter mount.Interface
// Writer interface to use for volumes.
writer kubeio.Writer
// Manager of non-Runtime containers.
containerManager cm.ContainerManager
// Maximum Number of Pods which can be run by this Kubelet
maxPods int
// Monitor Kubelet's sync loop
syncLoopMonitor atomic.Value
// Container restart Backoff
backOff *flowcontrol.Backoff
// Channel for sending pods to kill.
podKillingCh chan *kubecontainer.PodPair
// The configuration file used as the base to generate the container's
// DNS resolver configuration file. This can be used in conjunction with
// clusterDomain and clusterDNS.
resolverConfig string
// Optionally shape the bandwidth of a pod
// TODO: remove when kubenet plugin is ready
shaper bandwidth.BandwidthShaper
// Information about the ports which are opened by daemons on Node running this Kubelet server.
daemonEndpoints *v1.NodeDaemonEndpoints
// A queue used to trigger pod workers.
workQueue queue.WorkQueue
// oneTimeInitializer is used to initialize modules that are dependent on the runtime to be up.
oneTimeInitializer sync.Once
// If non-nil, use this IP address for the node
nodeIP net.IP
// If non-nil, this is a unique identifier for the node in an external database, eg. cloudprovider
providerID string
// clock is an interface that provides time related functionality in a way that makes it
// easy to test the code.
clock clock.Clock
// outOfDiskTransitionFrequency specifies the amount of time the kubelet has to be actually
// not out of disk before it can transition the node condition status from out-of-disk to
// not-out-of-disk. This prevents a pod that causes out-of-disk condition from repeatedly
// getting rescheduled onto the node.
outOfDiskTransitionFrequency time.Duration
// handlers called during the tryUpdateNodeStatus cycle
setNodeStatusFuncs []func(*v1.Node) error
// TODO: think about moving this to be centralized in PodWorkers in follow-on.
// the list of handlers to call during pod admission.
admitHandlers lifecycle.PodAdmitHandlers
// softAdmithandlers are applied to the pod after it is admitted by the Kubelet, but before it is
// run. A pod rejected by a softAdmitHandler will be left in a Pending state indefinitely. If a
// rejected pod should not be recreated, or the scheduler is not aware of the rejection rule, the
// admission rule should be applied by a softAdmitHandler.
softAdmitHandlers lifecycle.PodAdmitHandlers
// the list of handlers to call during pod sync loop.
lifecycle.PodSyncLoopHandlers
// the list of handlers to call during pod sync.
lifecycle.PodSyncHandlers
// the number of allowed pods per core
podsPerCore int
// enableControllerAttachDetach indicates the Attach/Detach controller
// should manage attachment/detachment of volumes scheduled to this node,
// and disable kubelet from executing any attach/detach operations
enableControllerAttachDetach bool
// trigger deleting containers in a pod
containerDeletor *podContainerDeletor
// config iptables util rules
makeIPTablesUtilChains bool
// The bit of the fwmark space to mark packets for SNAT.
iptablesMasqueradeBit int
// The bit of the fwmark space to mark packets for dropping.
iptablesDropBit int
// The AppArmor validator for checking whether AppArmor is supported.
appArmorValidator apparmor.Validator
// The handler serving CRI streaming calls (exec/attach/port-forward).
criHandler http.Handler
// experimentalHostUserNamespaceDefaulting sets userns=true when users request host namespaces (pid, ipc, net),
// are using non-namespaced capabilities (mknod, sys_time, sys_module), the pod contains a privileged container,
// or using host path volumes.
// This should only be enabled when the container runtime is performing user remapping AND if the
// experimental behavior is desired.
experimentalHostUserNamespaceDefaulting bool
// GPU Manager
gpuManager gpu.GPUManager
// dockerLegacyService contains some legacy methods for backward compatibility.
// It should be set only when docker is using non json-file logging driver.
dockerLegacyService dockershim.DockerLegacyService
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
// Run starts the kubelet reacting to config updates
func (kl *Kubelet) Run(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate) {
if kl.logServer == nil {
kl.logServer = http.StripPrefix("/logs/", http.FileServer(http.Dir("/var/log/")))
}
if kl.kubeClient == nil {
glog.Warning("No api server defined - no node status update will be sent.")
}
if err := kl.initializeModules(); err != nil {
kl.recorder.Eventf(kl.nodeRef, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.KubeletSetupFailed, err.Error())
glog.Error(err)
kl.runtimeState.setInitError(err)
}
// Start volume manager
go kl.volumeManager.Run(kl.sourcesReady, wait.NeverStop)
if kl.kubeClient != nil {
// Start syncing node status immediately, this may set up things the runtime needs to run.
go wait.Until(kl.syncNodeStatus, kl.nodeStatusUpdateFrequency, wait.NeverStop)
}
go wait.Until(kl.syncNetworkStatus, 30*time.Second, wait.NeverStop)
go wait.Until(kl.updateRuntimeUp, 5*time.Second, wait.NeverStop)
// Start loop to sync iptables util rules
if kl.makeIPTablesUtilChains {
go wait.Until(kl.syncNetworkUtil, 1*time.Minute, wait.NeverStop)
}
// Start a goroutine responsible for killing pods (that are not properly
// handled by pod workers).
go wait.Until(kl.podKiller, 1*time.Second, wait.NeverStop)
// Start gorouting responsible for checking limits in resolv.conf
if kl.resolverConfig != "" {
go wait.Until(func() { kl.checkLimitsForResolvConf() }, 30*time.Second, wait.NeverStop)
}
// Start component sync loops.
kl.statusManager.Start()
kl.probeManager.Start()
// Start the pod lifecycle event generator.
kl.pleg.Start()
kl.syncLoop(updates, kl) // kubelet核心函数
}// syncLoop is the main loop for processing changes. It watches for changes from
// three channels (file, apiserver, and http) and creates a union of them. For
// any new change seen, will run a sync against desired state and running state. If
// no changes are seen to the configuration, will synchronize the last known desired
// state every sync-frequency seconds. Never returns.
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoop(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler) {
glog.Info("Starting kubelet main sync loop.")
// The resyncTicker wakes up kubelet to checks if there are any pod workers
// that need to be sync'd. A one-second period is sufficient because the
// sync interval is defaulted to 10s.
syncTicker := time.NewTicker(time.Second)
defer syncTicker.Stop()
housekeepingTicker := time.NewTicker(housekeepingPeriod)
defer housekeepingTicker.Stop()
plegCh := kl.pleg.Watch()
for {
if rs := kl.runtimeState.runtimeErrors(); len(rs) != 0 {
glog.Infof("skipping pod synchronization - %v", rs)
time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)
continue
}
if !kl.syncLoopIteration(updates, handler, syncTicker.C, housekeepingTicker.C, plegCh) {
break
}
}
}
// SyncHandler is an interface implemented by Kubelet, for testability
type SyncHandler interface {
HandlePodAdditions(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodUpdates(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodRemoves(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodReconcile(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodSyncs(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodCleanups() error
}// syncLoopIteration reads from various channels and dispatches pods to the
// given handler.
//
// Arguments:
// 1. configCh: a channel to read config events from // updates
// 2. handler: the SyncHandler to dispatch pods to // SyncHandler
// 3. syncCh: a channel to read periodic sync events from
// 4. houseKeepingCh: a channel to read housekeeping events from
// 5. plegCh: a channel to read PLEG updates from
//
// Events are also read from the kubelet liveness manager's update channel.
//
// The workflow is to read from one of the channels, handle that event, and
// update the timestamp in the sync loop monitor.
//
// Here is an appropriate place to note that despite the syntactical
// similarity to the switch statement, the case statements in a select are
// evaluated in a pseudorandom order if there are multiple channels ready to
// read from when the select is evaluated. In other words, case statements
// are evaluated in random order, and you can not assume that the case
// statements evaluate in order if multiple channels have events.
//
// With that in mind, in truly no particular order, the different channels
// are handled as follows:
//
// * configCh: dispatch the pods for the config change to the appropriate
// handler callback for the event type
// * plegCh: update the runtime cache; sync pod
// * syncCh: sync all pods waiting for sync
// * houseKeepingCh: trigger cleanup of pods
// * liveness manager: sync pods that have failed or in which one or more
// containers have failed liveness checks
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoopIteration(configCh <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler,
syncCh <-chan time.Time, housekeepingCh <-chan time.Time, plegCh <-chan *pleg.PodLifecycleEvent) bool {
kl.syncLoopMonitor.Store(kl.clock.Now())
select {
case u, open := <-configCh:
// Update from a config source; dispatch it to the right handler
// callback.
switch u.Op {
case kubetypes.ADD:
// After restarting, kubelet will get all existing pods through
// ADD as if they are new pods. These pods will then go through the
// admission process and *may* be rejected. This can be resolved
// once we have checkpointing.
handler.HandlePodAdditions(u.Pods) // 接着讲解流程
case kubetypes.UPDATE:
handler.HandlePodUpdates(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.REMOVE:
handler.HandlePodRemoves(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.RECONCILE:
handler.HandlePodReconcile(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.DELETE:
// DELETE is treated as a UPDATE because of graceful deletion.
handler.HandlePodUpdates(u.Pods)
}
// Mark the source ready after receiving at least one update from the
// source. Once all the sources are marked ready, various cleanup
// routines will start reclaiming resources. It is important that this
// takes place only after kubelet calls the update handler to process
// the update to ensure the internal pod cache is up-to-date.
kl.sourcesReady.AddSource(u.Source)
case e := <-plegCh:
if isSyncPodWorthy(e) {
// PLEG event for a pod; sync it.
if pod, ok := kl.podManager.GetPodByUID(e.ID); ok {
glog.V(2).Infof("SyncLoop (PLEG): %q, event: %#v", format.Pod(pod), e)
handler.HandlePodSyncs([]*v1.Pod{pod})
} else {
// If the pod no longer exists, ignore the event.
glog.V(4).Infof("SyncLoop (PLEG): ignore irrelevant event: %#v", e)
}
}
if e.Type == pleg.ContainerDied {
if containerID, ok := e.Data.(string); ok {
kl.cleanUpContainersInPod(e.ID, containerID)
}
}
case <-syncCh:
// Sync pods waiting for sync
podsToSync := kl.getPodsToSync()
if len(podsToSync) == 0 {
break
}
glog.V(4).Infof("SyncLoop (SYNC): %d pods; %s", len(podsToSync), format.Pods(podsToSync))
kl.HandlePodSyncs(podsToSync)
case update := <-kl.livenessManager.Updates():
if update.Result == proberesults.Failure {
// The liveness manager detected a failure; sync the pod.
// We should not use the pod from livenessManager, because it is never updated after
// initialization.
pod, ok := kl.podManager.GetPodByUID(update.PodUID)
if !ok {
// If the pod no longer exists, ignore the update.
break
}
handler.HandlePodSyncs([]*v1.Pod{pod})
}
case <-housekeepingCh:
if !kl.sourcesReady.AllReady() {
// If the sources aren't ready or volume manager has not yet synced the states,
// skip housekeeping, as we may accidentally delete pods from unready sources.
glog.V(4).Infof("SyncLoop (housekeeping, skipped): sources aren't ready yet.")
} else {
err := handler.HandlePodCleanups()
}
}
kl.syncLoopMonitor.Store(kl.clock.Now())
return true
}Kubelet automatically creates so-called mirror pod on Kubernetes API server for each static pod, so the pods are visible there, but they cannot be controlled from the API server.
// HandlePodAdditions is the callback in SyncHandler for pods being added from
// a config source.
func (kl *Kubelet) HandlePodAdditions(pods []*v1.Pod) {
start := kl.clock.Now()
sort.Sort(sliceutils.PodsByCreationTime(pods))
for _, pod := range pods {
// k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/pod/pod_manager.go
// NewBasicPodManager(client MirrorClient, secretManager secret.Manager) Manager
// basicManager
existingPods := kl.podManager.GetPods()
// Always add the pod to the pod manager. Kubelet relies on the pod
// manager as the source of truth for the desired state. If a pod does
// not exist in the pod manager, it means that it has been deleted in
// the apiserver and no action (other than cleanup) is required.
kl.podManager.AddPod(pod)
if kubepod.IsMirrorPod(pod) {
kl.handleMirrorPod(pod, start)
continue
}
if !kl.podIsTerminated(pod) {
// We failed pods that we rejected, so activePods include all admitted
// pods that are alive.
activePods := kl.filterOutTerminatedPods(existingPods)
// Check if we can admit the pod; if not, reject it.
if ok, reason, message := kl.canAdmitPod(activePods, pod); !ok {
kl.rejectPod(pod, reason, message)
continue
}
}
mirrorPod, _ := kl.podManager.GetMirrorPodByPod(pod)
kl.dispatchWork(pod, kubetypes.SyncPodCreate, mirrorPod, start) // 进行分发
// 处理probe相关的检测
kl.probeManager.AddPod(pod) // Handles container probing.
}
}// dispatchWork starts the asynchronous sync of the pod in a pod worker.
// If the pod is terminated, dispatchWork
func (kl *Kubelet) dispatchWork(pod *v1.Pod, syncType kubetypes.SyncPodType, mirrorPod *v1.Pod, start time.Time) {
// ...
// Run the sync in an async worker.
kl.podWorkers.UpdatePod(&UpdatePodOptions{
Pod: pod,
MirrorPod: mirrorPod,
UpdateType: syncType,
OnCompleteFunc: func(err error) {
if err != nil {
metrics.PodWorkerLatency.WithLabelValues(syncType.String()).Observe(metrics.SinceInMicroseconds(start))
}
},
})
// Note the number of containers for new pods.
if syncType == kubetypes.SyncPodCreate {
metrics.ContainersPerPodCount.Observe(float64(len(pod.Spec.Containers)))
}
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/pod_workers.go
type podWorkers struct {
// Protects all per worker fields.
podLock sync.Mutex
// Tracks all running per-pod goroutines - per-pod goroutine will be
// processing updates received through its corresponding channel.
podUpdates map[types.UID]chan UpdatePodOptions
// Track the current state of per-pod goroutines.
// Currently all update request for a given pod coming when another
// update of this pod is being processed are ignored.
isWorking map[types.UID]bool
// Tracks the last undelivered work item for this pod - a work item is
// undelivered if it comes in while the worker is working.
lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate map[types.UID]UpdatePodOptions
workQueue queue.WorkQueue
// This function is run to sync the desired stated of pod.
// NOTE: This function has to be thread-safe - it can be called for
// different pods at the same time.
syncPodFn syncPodFnType
// The EventRecorder to use
recorder record.EventRecorder
// backOffPeriod is the duration to back off when there is a sync error.
backOffPeriod time.Duration
// resyncInterval is the duration to wait until the next sync.
resyncInterval time.Duration
// podCache stores kubecontainer.PodStatus for all pods.
podCache kubecontainer.Cache
}// Apply the new setting to the specified pod.
// If the options provide an OnCompleteFunc, the function is invoked if the update is accepted.
// Update requests are ignored if a kill pod request is pending.
func (p *podWorkers) UpdatePod(options *UpdatePodOptions) {
pod := options.Pod
uid := pod.UID
var podUpdates chan UpdatePodOptions
var exists bool
p.podLock.Lock()
defer p.podLock.Unlock()
if podUpdates, exists = p.podUpdates[uid]; !exists {
// We need to have a buffer here, because checkForUpdates() method that
// puts an update into channel is called from the same goroutine where
// the channel is consumed. However, it is guaranteed that in such case
// the channel is empty, so buffer of size 1 is enough.
podUpdates = make(chan UpdatePodOptions, 1)
p.podUpdates[uid] = podUpdates
// Creating a new pod worker either means this is a new pod, or that the
// kubelet just restarted. In either case the kubelet is willing to believe
// the status of the pod for the first pod worker sync. See corresponding
// comment in syncPod.
go func() {
defer runtime.HandleCrash()
p.managePodLoop(podUpdates)
}()
}
if !p.isWorking[pod.UID] {
p.isWorking[pod.UID] = true
podUpdates <- *options
} else {
// if a request to kill a pod is pending, we do not let anything overwrite that request.
update, found := p.lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate[pod.UID]
if !found || update.UpdateType != kubetypes.SyncPodKill {
p.lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate[pod.UID] = *options
}
}
}
func (p *podWorkers) managePodLoop(podUpdates <-chan UpdatePodOptions) {
var lastSyncTime time.Time
for update := range podUpdates {
err := func() error {
podUID := update.Pod.UID
// This is a blocking call that would return only if the cache
// has an entry for the pod that is newer than minRuntimeCache
// Time. This ensures the worker doesn't start syncing until
// after the cache is at least newer than the finished time of
// the previous sync.
status, err := p.podCache.GetNewerThan(podUID, lastSyncTime)
if err != nil {
return err
}
err = p.syncPodFn(syncPodOptions{
mirrorPod: update.MirrorPod,
pod: update.Pod,
podStatus: status,
killPodOptions: update.KillPodOptions,
updateType: update.UpdateType,
})
lastSyncTime = time.Now()
return err
}()
// notify the call-back function if the operation succeeded or not
if update.OnCompleteFunc != nil {
update.OnCompleteFunc(err)
}
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Error syncing pod %s (%q), skipping: %v", update.Pod.UID, format.Pod(update.Pod), err)
p.recorder.Eventf(update.Pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedSync, "Error syncing pod, skipping: %v", err)
}
p.wrapUp(update.Pod.UID, err)
}
}
// klet.podWorkers = newPodWorkers(klet.syncPod, kubeDeps.Recorder, klet.workQueue, klet.resyncInterval, backOffPeriod, klet.podCache)
func newPodWorkers(syncPodFn syncPodFnType, recorder record.EventRecorder, workQueue queue.WorkQueue,
resyncInterval, backOffPeriod time.Duration, podCache kubecontainer.Cache) *podWorkers {
return &podWorkers{
podUpdates: map[types.UID]chan UpdatePodOptions{},
isWorking: map[types.UID]bool{},
lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate: map[types.UID]UpdatePodOptions{},
syncPodFn: syncPodFn, // kubelet.syncPod()
recorder: recorder,
workQueue: workQueue,
resyncInterval: resyncInterval,
backOffPeriod: backOffPeriod,
podCache: podCache,
}
}// syncPod is the transaction script for the sync of a single pod.
//
// Arguments:
//
// o - the SyncPodOptions for this invocation
//
// The workflow is:
// * If the pod is being created, record pod worker start latency
// * Call generateAPIPodStatus to prepare an v1.PodStatus for the pod
// * If the pod is being seen as running for the first time, record pod
// start latency
// * Update the status of the pod in the status manager
// * Kill the pod if it should not be running
// * Create a mirror pod if the pod is a static pod, and does not
// already have a mirror pod
// * Create the data directories for the pod if they do not exist
// * Wait for volumes to attach/mount
// * Fetch the pull secrets for the pod
// * Call the container runtime's SyncPod callback
// * Update the traffic shaping for the pod's ingress and egress limits
//
// If any step of this workflow errors, the error is returned, and is repeated
// on the next syncPod call.
func (kl *Kubelet) syncPod(o syncPodOptions) error {
// pull out the required options
pod := o.pod
mirrorPod := o.mirrorPod
podStatus := o.podStatus
updateType := o.updateType
// if we want to kill a pod, do it now!
// ...
// Latency measurements for the main workflow are relative to the
// first time the pod was seen by the API server.
var firstSeenTime time.Time
if firstSeenTimeStr, ok := pod.Annotations[kubetypes.ConfigFirstSeenAnnotationKey]; ok {
firstSeenTime = kubetypes.ConvertToTimestamp(firstSeenTimeStr).Get()
}
// Record pod worker start latency if being created
// ...
// Generate final API pod status with pod and status manager status
apiPodStatus := kl.generateAPIPodStatus(pod, podStatus)
// The pod IP may be changed in generateAPIPodStatus if the pod is using host network. (See #24576)
// TODO(random-liu): After writing pod spec into container labels, check whether pod is using host network, and
// set pod IP to hostIP directly in runtime.GetPodStatus
podStatus.IP = apiPodStatus.PodIP
// Record the time it takes for the pod to become running.
existingStatus, ok := kl.statusManager.GetPodStatus(pod.UID)
if !ok || existingStatus.Phase == v1.PodPending && apiPodStatus.Phase == v1.PodRunning &&
!firstSeenTime.IsZero() {
metrics.PodStartLatency.Observe(metrics.SinceInMicroseconds(firstSeenTime))
}
runnable := kl.canRunPod(pod)
// ...
// Update status in the status manager
// 将 pod 的变化状态信息放入到 statusManager, 用于同步到 API Server
kl.statusManager.SetPodStatus(pod, apiPodStatus)
// Kill pod if it should not be running
// ....
// If the network plugin is not ready, only start the pod if it uses the host network
// Create Cgroups for the pod and apply resource parameters
// to them if cgroups-per-qos flag is enabled.
pcm := kl.containerManager.NewPodContainerManager()
// If pod has already been terminated then we need not create
// or update the pod's cgroup
if !kl.podIsTerminated(pod) {
// When the kubelet is restarted with the cgroups-per-qos
// flag enabled, all the pod's running containers
// should be killed intermittently and brought back up
// under the qos cgroup hierarchy.
// Check if this is the pod's first sync
firstSync := true
for _, containerStatus := range apiPodStatus.ContainerStatuses {
if containerStatus.State.Running != nil {
firstSync = false
break
}
}
// Don't kill containers in pod if pod's cgroups already
// exists or the pod is running for the first time
podKilled := false
if !pcm.Exists(pod) && !firstSync {
if err := kl.killPod(pod, nil, podStatus, nil); err == nil {
podKilled = true
}
}
// Create and Update pod's Cgroups
// Don't create cgroups for run once pod if it was killed above
// The current policy is not to restart the run once pods when
// the kubelet is restarted with the new flag as run once pods are
// expected to run only once and if the kubelet is restarted then
// they are not expected to run again.
// We don't create and apply updates to cgroup if its a run once pod and was killed above
if !(podKilled && pod.Spec.RestartPolicy == v1.RestartPolicyNever) {
if !pcm.Exists(pod) {
if err := kl.containerManager.UpdateQOSCgroups(); err != nil {
glog.V(2).Infof("Failed to update QoS cgroups while syncing pod: %v", err)
}
if err := pcm.EnsureExists(pod); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to ensure that the pod: %v cgroups exist and are correctly applied: %v", pod.UID, err)
}
}
}
}
// Create Mirror Pod for Static Pod if it doesn't already exist
if kubepod.IsStaticPod(pod) {
// Create Mirror Pod for Static Pod if it doesn't already exist
}
// Make data directories for the pod
err := kl.makePodDataDirs(pod)
// Wait for volumes to attach/mount
kl.volumeManager.WaitForAttachAndMount(pod)
// Fetch the pull secrets for the pod
pullSecrets := kl.getPullSecretsForPod(pod)
// Call the container runtime's SyncPod callback
// kubeGenericRuntimeManager, 封装了 rkt和docker等多种支持
result := kl.containerRuntime.SyncPod(pod, apiPodStatus, podStatus, pullSecrets, kl.backOff)
kl.reasonCache.Update(pod.UID, result)
if err := result.Error(); err != nil {
return err
}
// early successful exit if pod is not bandwidth-constrained
// Update the traffic shaping for the pod's ingress and egress limits
ingress, egress, err := bandwidth.ExtractPodBandwidthResources(pod.Annotations)
// ...
return nil
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/kuberuntime/kuberuntime_manager.go
// SyncPod syncs the running pod into the desired pod by executing following steps:
//
// 1. Compute sandbox and container changes.
// 2. Kill pod sandbox if necessary.
// 3. Kill any containers that should not be running.
// 4. Create sandbox if necessary.
// 5. Create init containers.
// 6. Create normal containers.
func (m *kubeGenericRuntimeManager) SyncPod(pod *v1.Pod, _ v1.PodStatus, podStatus *kubecontainer.PodStatus, pullSecrets []v1.Secret, backOff *flowcontrol.Backoff) (result kubecontainer.PodSyncResult) {
// Step 1: Compute sandbox and container changes.
podContainerChanges := m.computePodContainerChanges(pod, podStatus)
if podContainerChanges.CreateSandbox {
ref, err := ref.GetReference(api.Scheme, pod)
if podContainerChanges.SandboxID != "" {
m.recorder.Eventf(ref, v1.EventTypeNormal, "SandboxChanged", "Pod sandbox changed, it will be killed and re-created.")
}
}
// Step 2: Kill the pod if the sandbox has changed.
killResult := m.killPodWithSyncResult(pod, kubecontainer.ConvertPodStatusToRunningPod(m.runtimeName, podStatus), nil)
result.AddPodSyncResult(killResult)
} else {
// Step 3: kill any running containers in this pod which are not to keep.
for containerID, containerInfo := range podContainerChanges.ContainersToKill {
killContainerResult := kubecontainer.NewSyncResult(kubecontainer.KillContainer, containerInfo.name)
result.AddSyncResult(killContainerResult)
if err := m.killContainer(pod, containerID, containerInfo.name, containerInfo.message, nil); err != nil {
killContainerResult.Fail(kubecontainer.ErrKillContainer, err.Error())
return
}
}
}
// Keep terminated init containers fairly aggressively controlled
m.pruneInitContainersBeforeStart(pod, podStatus, podContainerChanges.InitContainersToKeep)
// We pass the value of the podIP down to generatePodSandboxConfig and
// generateContainerConfig, which in turn passes it to various other
// functions, in order to facilitate functionality that requires this
// value (hosts file and downward API) and avoid races determining
// the pod IP in cases where a container requires restart but the
// podIP isn't in the status manager yet.
//
// We default to the IP in the passed-in pod status, and overwrite it if the
// sandbox needs to be (re)started.
// Step 4: Create a sandbox for the pod if necessary.
podSandboxID := podContainerChanges.SandboxID
if podContainerChanges.CreateSandbox && len(podContainerChanges.ContainersToStart) > 0 {
createSandboxResult := kubecontainer.NewSyncResult(kubecontainer.CreatePodSandbox, format.Pod(pod))
result.AddSyncResult(createSandboxResult)
podSandboxID, msg, err = m.createPodSandbox(pod, podContainerChanges.Attempt)
podSandboxStatus, err := m.runtimeService.PodSandboxStatus(podSandboxID)
// If we ever allow updating a pod from non-host-network to
// host-network, we may use a stale IP.
if !kubecontainer.IsHostNetworkPod(pod) {
// Overwrite the podIP passed in the pod status, since we just started the pod sandbox.
podIP = m.determinePodSandboxIP(pod.Namespace, pod.Name, podSandboxStatus
}
}
// Get podSandboxConfig for containers to start.
configPodSandboxResult := kubecontainer.NewSyncResult(kubecontainer.ConfigPodSandbox, podSandboxID)
result.AddSyncResult(configPodSandboxResult)
podSandboxConfig, err := m.generatePodSandboxConfig(pod, podContainerChanges.Attempt)
if err != nil {
configPodSandboxResult.Fail(kubecontainer.ErrConfigPodSandbox, message)
return
}
// Step 5: start init containers.
status, next, done := findNextInitContainerToRun(pod, podStatus)
if status != nil && status.ExitCode != 0 {
// container initialization has failed, flag the pod as failed
initContainerResult := kubecontainer.NewSyncResult(kubecontainer.InitContainer, status.Name)
initContainerResult.Fail(kubecontainer.ErrRunInitContainer, fmt.Sprintf("init container %q exited with %d", status.Name, status.ExitCode))
result.AddSyncResult(initContainerResult)
}
// If we need to start the next container, do so now then exit
container := next
startContainerResult := kubecontainer.NewSyncResult(kubecontainer.StartContainer, container.Name)
result.AddSyncResult(startContainerResult)
isInBackOff, msg, err := m.doBackOff(pod, container, podStatus, backOff)
m.startContainer(podSandboxID, podSandboxConfig, container, pod, podStatus, pullSecrets, podIP)
// Successfully started the container; clear the entry in the failure
return
}
// Step 6: start containers in podContainerChanges.ContainersToStart.
for idx := range podContainerChanges.ContainersToStart {
container := &pod.Spec.Containers[idx]
startContainerResult := kubecontainer.NewSyncResult(kubecontainer.StartContainer, container.Name)
result.AddSyncResult(startContainerResult)
isInBackOff, msg, err := m.doBackOff(pod, container, podStatus, backOff)
if isInBackOff {
startContainerResult.Fail(err, msg)
continue
}
if msg, err := m.startContainer(podSandboxID, podSandboxConfig, container, pod, podStatus, pullSecrets, podIP); err != nil {
startContainerResult.Fail(err, msg)
continue
}
}
return
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/status/status_manager.go
// klet.statusManager = status.NewManager(klet.kubeClient, klet.podManager, klet)
func NewManager(kubeClient clientset.Interface, podManager kubepod.Manager, podDeletionSafety PodDeletionSafetyProvider) Manager {
return &manager{
kubeClient: kubeClient,
podManager: podManager,
podStatuses: make(map[types.UID]versionedPodStatus),
podStatusChannel: make(chan podStatusSyncRequest, 1000), // Buffer up to 1000 statuses
apiStatusVersions: make(map[types.UID]uint64),
podDeletionSafety: podDeletionSafety,
}
}
func (kl *Kubelet) Run(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate) {
// ...
// Start component sync loops.
kl.statusManager.Start()
kl.probeManager.Start()
// ...
}
func (m *manager) SetPodStatus(pod *v1.Pod, status v1.PodStatus) {
m.podStatusesLock.Lock()
defer m.podStatusesLock.Unlock()
// Make sure we're caching a deep copy.
status, err := copyStatus(&status)
if err != nil {
return
}
// Force a status update if deletion timestamp is set. This is necessary
// because if the pod is in the non-running state, the pod worker still
// needs to be able to trigger an update and/or deletion.
m.updateStatusInternal(pod, status, pod.DeletionTimestamp != nil)
}
// updateStatusInternal updates the internal status cache, and queues an update to the api server if
// necessary. Returns whether an update was triggered.
// This method IS NOT THREAD SAFE and must be called from a locked function.
func (m *manager) updateStatusInternal(pod *v1.Pod, status v1.PodStatus, forceUpdate bool) bool{
// ... 生成一个 podStatusSyncRequest 请求放入到 channel 中
select {
case m.podStatusChannel <- podStatusSyncRequest{pod.UID, newStatus}:
return true
}
}
func (m *manager) Start() {
// Don't start the status manager if we don't have a client. This will happen
// on the master, where the kubelet is responsible for bootstrapping the pods
// of the master components.
glog.Info("Starting to sync pod status with apiserver")
syncTicker := time.Tick(syncPeriod)
// syncPod and syncBatch share the same go routine to avoid sync races.
go wait.Forever(func() {
select {
case syncRequest := <-m.podStatusChannel:
m.syncPod(syncRequest.podUID, syncRequest.status)
case <-syncTicker:
m.syncBatch()
}
}, 0)
}
// syncPod syncs the given status with the API server. The caller must not hold the lock.
func (m *manager) syncPod(uid types.UID, status versionedPodStatus) {
// ...
newPod, err := m.kubeClient.Core().Pods(pod.Namespace).UpdateStatus(pod)
// ...
}
// syncBatch syncs pods statuses with the apiserver.
func (m *manager) syncBatch() {
var updatedStatuses []podStatusSyncRequest
podToMirror, mirrorToPod := m.podManager.GetUIDTranslations()
func() { // Critical section
m.podStatusesLock.RLock()
defer m.podStatusesLock.RUnlock()
// Clean up orphaned versions.
for uid := range m.apiStatusVersions {
_, hasPod := m.podStatuses[uid]
_, hasMirror := mirrorToPod[uid]
if !hasPod && !hasMirror {
delete(m.apiStatusVersions, uid)
}
}
for uid, status := range m.podStatuses {
syncedUID := uid
if mirrorUID, ok := podToMirror[uid]; ok {
if mirrorUID == "" {
glog.V(5).Infof("Static pod %q (%s/%s) does not have a corresponding mirror pod; skipping", uid, status.podName, status.podNamespace)
continue
}
syncedUID = mirrorUID
}
if m.needsUpdate(syncedUID, status) {
updatedStatuses = append(updatedStatuses, podStatusSyncRequest{uid, status})
} else if m.needsReconcile(uid, status.status) {
// Delete the apiStatusVersions here to force an update on the pod status
// In most cases the deleted apiStatusVersions here should be filled
// soon after the following syncPod() [If the syncPod() sync an update
// successfully].
delete(m.apiStatusVersions, syncedUID)
updatedStatuses = append(updatedStatuses, podStatusSyncRequest{uid, status})
}
}
}()
for _, update := range updatedStatuses {
glog.V(5).Infof("Status Manager: syncPod in syncbatch. pod UID: %q", update.podUID)
m.syncPod(update.podUID, update.status)
}
}// Kubelet is the main kubelet implementation.
type Kubelet struct {
// ...
// Handles container probing.
probeManager prober.Manager
// Manages container health check results.
livenessManager proberesults.Manager
// ...
}
func NewMainKubelet() {
// ...
klet.livenessManager = proberesults.NewManager()
// ...
klet.probeManager = prober.NewManager(
klet.statusManager,
klet.livenessManager,
klet.runner,
containerRefManager,
kubeDeps.Recorder)
// ...
}
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoopIteration(){
// ...
case update := <-kl.livenessManager.Updates():
if update.Result == proberesults.Failure {
// The liveness manager detected a failure; sync the pod.
// We should not use the pod from livenessManager, because it is never updated after
// initialization.
pod, ok := kl.podManager.GetPodByUID(update.PodUID)
handler.HandlePodSyncs([]*v1.Pod{pod})
}
// ...
}
// Run starts the kubelet reacting to config updates
func (kl *Kubelet) Run(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate) {
// ...
// Start component sync loops.
kl.statusManager.Start()
kl.probeManager.Start()
// ...
}
func (kl *Kubelet) HandlePodAdditions(pods []*v1.Pod) {
for _, pod := range pods {
kl.probeManager.AddPod(pod) // Handles container probing.
}
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/prober/prober_manager.go
// Start syncing probe status. This should only be called once.
func (m *manager) Start() {
// Start syncing readiness.
go wait.Forever(m.updateReadiness, 0)
}
func (m *manager) updateReadiness() {
update := <-m.readinessManager.Updates()
ready := update.Result == results.Success
m.statusManager.SetContainerReadiness(update.PodUID, update.ContainerID, ready)
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/status/status_manager.go
func (m *manager) SetContainerReadiness(podUID types.UID, containerID kubecontainer.ContainerID, ready bool) {
pod, ok := m.podManager.GetPodByUID(podUID)
oldStatus, found := m.podStatuses[pod.UID]
// Find the container to update.
containerStatus, _, ok := findContainerStatus(&oldStatus.status, containerID.String())
if containerStatus.Ready == ready {
format.Pod(pod), containerID.String())
return
}
// Make sure we're not updating the cached version.
status, err := copyStatus(&oldStatus.status)
containerStatus, _, _ = findContainerStatus(&status, containerID.String())
containerStatus.Ready = ready
// Update pod condition.
readyConditionIndex := -1
for i, condition := range status.Conditions {
if condition.Type == v1.PodReady {
readyConditionIndex = i
break
}
}
readyCondition := GeneratePodReadyCondition(&pod.Spec, status.ContainerStatuses, status.Phase)
status.Conditions = append(status.Conditions, readyCondition)
// 放入到内部更新的channel中
m.updateStatusInternal(pod, status, false)
}代码基于 1.9.2
func startKubelet(k kubelet.Bootstrap, podCfg *config.PodConfig, kubeCfg *kubeletconfiginternal.KubeletConfiguration, kubeDeps *kubelet.Dependencies) {
// start the kubelet
go wait.Until(func() { k.Run(podCfg.Updates()) }, 0, wait.NeverStop)
// start the kubelet server 默认端口 10250
if kubeCfg.EnableServer {
go wait.Until(func() {
k.ListenAndServe(
net.ParseIP(kubeCfg.Address),
uint(kubeCfg.Port),
kubeDeps.TLSOptions,
kubeDeps.Auth,
kubeCfg.EnableDebuggingHandlers,
kubeCfg.EnableContentionProfiling)
}, 0, wait.NeverStop)
}
// 默认端口 10255
if kubeCfg.ReadOnlyPort > 0 {
go wait.Until(func() {
k.ListenAndServeReadOnly(net.ParseIP(kubeCfg.Address), uint(kubeCfg.ReadOnlyPort))
}, 0, wait.NeverStop)
}
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
// Bootstrap is a bootstrapping interface for kubelet, targets the initialization protocol
type Bootstrap interface {
// ...
ListenAndServe(address net.IP, port uint, tlsOptions *server.TLSOptions, auth server.AuthInterface, enableDebuggingHandlers, enableContentionProfiling bool)
ListenAndServeReadOnly(address net.IP, port uint)
// ...
}总览:
// ListenAndServeKubeletServer initializes a server to respond to HTTP network requests on the Kubelet.
func ListenAndServeKubeletServer(
host HostInterface,
resourceAnalyzer stats.ResourceAnalyzer,
address net.IP,
port uint,
tlsOptions *TLSOptions,
auth AuthInterface,
enableDebuggingHandlers,
enableContentionProfiling bool,
runtime kubecontainer.Runtime,
criHandler http.Handler) {
handler := NewServer(host, resourceAnalyzer, auth, enableDebuggingHandlers, enableContentionProfiling, runtime, criHandler)
s := &http.Server{
Addr: net.JoinHostPort(address.String(),
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(port), 10)),
Handler: &handler,
MaxHeaderBytes: 1 << 20,
}
s.ListenAndServe())
}
// ListenAndServeKubeletReadOnlyServer initializes a server to respond to HTTP network requests on the Kubelet.
func ListenAndServeKubeletReadOnlyServer(host HostInterface,
resourceAnalyzer stats.ResourceAnalyzer,
address net.IP,
port uint,
runtime kubecontainer.Runtime) {
s := NewServer(host, resourceAnalyzer, nil, false, false, runtime, nil)
server := &http.Server{
Addr: net.JoinHostPort(address.String(),
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(port), 10)),
Handler: &s,
MaxHeaderBytes: 1 << 20,
}
server.ListenAndServe()
}通过以上对比可以发现, 10250 与 10255(ReadyOnly)最终调用的是用同一个对象,但是传入的参数不同
func ListenAndServeKubeletServer() ... {
// ...
handler := NewServer(host, resourceAnalyzer, auth, enableDebuggingHandlers, enableContentionProfiling, runtime, criHandler)
// ...
}
func ListenAndServeKubeletReadOnlyServer() ... {
// ...
s := NewServer(host, resourceAnalyzer, /*auth*/ nil, /*enableDebuggingHandlers*/ false, /*enableContentionProfiling*/ false, runtime, /*criHandler*/ nil)
// ...
}
// NewServer 函数的原型声明如下:
func NewServer(
host HostInterface,
resourceAnalyzer stats.ResourceAnalyzer,
auth AuthInterface,
enableDebuggingHandlers,
enableContentionProfiling bool,
runtime kubecontainer.Runtime,
criHandler http.Handler)(){
// ...
}此处先分析 ListenAndServeReadOnly:
// ListenAndServeReadOnly runs the kubelet HTTP server in read-only mode.
func (kl *Kubelet) ListenAndServeReadOnly(address net.IP, port uint) {
server.ListenAndServeKubeletReadOnlyServer(kl, kl.resourceAnalyzer, address, port, kl.containerRuntime)
}文件 k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/server/server.go
ListenAndServeKubeletReadOnlyServer(...)
// ListenAndServeKubeletReadOnlyServer initializes a server to respond to HTTP network requests on the Kubelet.
func ListenAndServeKubeletReadOnlyServer(host HostInterface, resourceAnalyzer stats.ResourceAnalyzer, address net.IP, port uint, runtime kubecontainer.Runtime) {
glog.V(1).Infof("Starting to listen read-only on %s:%d", address, port)
s := NewServer(host, resourceAnalyzer, nil, false, false, runtime, nil)
server := &http.Server{
Addr: net.JoinHostPort(address.String(), strconv.FormatUint(uint64(port), 10)),
Handler: &s, // 设置成了 NewServer 返回值
MaxHeaderBytes: 1 << 20,
}
glog.Fatal(server.ListenAndServe())
}
// 因为是 Http 服务,这里重点分析 NewServer(...) 返回的结果, 因为 http.Server 中的 Handler 为返回值。
func NewServer(...) Server {
server := Server{
host: host,
resourceAnalyzer: resourceAnalyzer,
auth: auth,
restfulCont: &filteringContainer{Container: restful.NewContainer()},
runtime: runtime,
}
if auth != nil {
// 安装Auth Filter
server.InstallAuthFilter()
}
// 安装 Default Handlers
server.InstallDefaultHandlers()
// 根据debug flag来确定是否启动调试handler
if enableDebuggingHandlers {
server.InstallDebuggingHandlers(criHandler)
if enableContentionProfiling {
goruntime.SetBlockProfileRate(1)
}
} else {
server.InstallDebuggingDisabledHandlers()
}
return server
}
// ServeHTTP responds to HTTP requests on the Kubelet.
func (s *Server) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
// ...
s.restfulCont.ServeHTTP(w, req)
}type Server struct {
auth AuthInterface
host HostInterface
restfulCont containerInterface // 真正的 Http Server 服务对象
resourceAnalyzer stats.ResourceAnalyzer
runtime kubecontainer.Runtime
}
// containerInterface defines the restful.Container functions used on the root container
type containerInterface interface {
Add(service *restful.WebService) *restful.Container
Handle(path string, handler http.Handler)
Filter(filter restful.FilterFunction)
ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request)
RegisteredWebServices() []*restful.WebService
// RegisteredHandlePaths returns the paths of handlers registered directly with the container (non-web-services)
// Used to test filters are being applied on non-web-service handlers
RegisteredHandlePaths() []string
}真正处理 默认 Restful 的函数:
const (
metricsPath = "/metrics"
cadvisorMetricsPath = "/metrics/cadvisor"
specPath = "/spec/"
statsPath = "/stats/"
logsPath = "/logs/"
)
// InstallDefaultHandlers registers the default set of supported HTTP request
// patterns with the restful Container.
func (s *Server) InstallDefaultHandlers() {
healthz.InstallHandler(s.restfulCont,
healthz.PingHealthz,
healthz.NamedCheck("syncloop", s.syncLoopHealthCheck),
)
ws := new(restful.WebService)
// http://xxx:10250/pods
ws.Path("/pods").Produces(restful.MIME_JSON)
ws.Route(ws.GET("").To(s.getPods).Operation("getPods"))
s.restfulCont.Add(ws)
s.restfulCont.Add(stats.CreateHandlers(statsPath /*/stats/*/, s.host, s.resourceAnalyzer))
s.restfulCont.Handle(metricsPath/*/metrics*/, prometheus.Handler())
// cAdvisor metrics are exposed under the secured handler as well
r := prometheus.NewRegistry()
r.MustRegister(metrics.NewPrometheusCollector(prometheusHostAdapter{s.host}, containerPrometheusLabels))
s.restfulCont.Handle(cadvisorMetricsPath, /*/metrics/cadvisor*/
promhttp.HandlerFor(r, promhttp.HandlerOpts{ErrorHandling: promhttp.ContinueOnError}),
)
ws = new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path(specPath/*spec*/).Produces(restful.MIME_JSON)
ws.Route(ws.GET("").To(s.getSpec).Operation("getSpec").Writes(cadvisorapi.MachineInfo{}))
s.restfulCont.Add(ws)
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
// ListenAndServe runs the kubelet HTTP server.
func (kl *Kubelet) ListenAndServe(
address net.IP,
port uint,
tlsOptions *server.TLSOptions,
auth server.AuthInterface,
enableDebuggingHandlers,
enableContentionProfiling bool) {
server.ListenAndServeKubeletServer(kl,
kl.resourceAnalyzer,
address,
port,
tlsOptions,
auth,
enableDebuggingHandlers,
enableContentionProfiling,
// kuberuntime.NewKubeGenericRuntimeManager
// ==> KubeGenericRuntime
// k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/
// kuberuntime/kuberuntime_manager.go
kl.containerRuntime,
// dockershim.NewDockerService
kl.criHandler)
// type KubeGenericRuntime interface {
// kubecontainer.Runtime
// kubecontainer.IndirectStreamingRuntime
// kubecontainer.ContainerCommandRunner
//}
}
// 其中 kl.criHandler 在 NewMainKubelet() 函数中被设置成了 dockershim.NewDockerService 对象
func NewMainKubelet(){
// ...
// rktnetes cannot be run with CRI.
if containerRuntime != kubetypes.RktContainerRuntime {
// ...
switch containerRuntime {
case kubetypes.DockerContainerRuntime:
// Create and start the CRI shim running as a grpc server.
streamingConfig := getStreamingConfig(kubeCfg, kubeDeps)
ds, err := dockershim.NewDockerService(kubeDeps.DockerClientConfig,
crOptions.PodSandboxImage,
streamingConfig,
&pluginSettings,
runtimeCgroups,
kubeCfg.CgroupDriver,
crOptions.DockershimRootDirectory,
crOptions.DockerDisableSharedPID)
if err := ds.Start(); err != nil {
// ds.Start() 内部调用 ds.containerManager.Start()
}
// For now, the CRI shim redirects the streaming requests to the
// kubelet, which handles the requests using DockerService..
klet.criHandler = ds // 调用dockershim.NewDockerService
// ...
// The unix socket for kubelet <-> dockershim communication.
server := dockerremote.NewDockerServer(remoteRuntimeEndpoint, ds)
if err := server.Start(); err != nil {
// server.Start() 的调用, 默认启动 gRPC server unix:///var/run/dockershim.sock
// Start starts the dockershim grpc server.
// func (s *DockerServer) Start() error {
// l, err := util.CreateListener(s.endpoint)
//
// // Create the grpc server and register runtime and image services.
// s.server = grpc.NewServer()
// runtimeapi.RegisterRuntimeServiceServer(s.server, s.service)
// runtimeapi.RegisterImageServiceServer(s.server, s.service)
// }
}
// Create dockerLegacyService when the logging driver is not supported.
supported, err := ds.IsCRISupportedLogDriver()
// ...
}
// ...
// kl.containerRuntime 相关对象
runtimeService, imageService, err := getRuntimeAndImageServices(remoteRuntimeEndpoint, remoteImageEndpoint, kubeCfg.RuntimeRequestTimeout)
klet.runtimeService = runtimeService
runtime, err := kuberuntime.NewKubeGenericRuntimeManager(
kubecontainer.FilterEventRecorder(kubeDeps.Recorder),
klet.livenessManager,
seccompProfileRoot,
containerRefManager,
machineInfo,
klet,
kubeDeps.OSInterface,
klet,
httpClient,
imageBackOff,
kubeCfg.SerializeImagePulls,
float32(kubeCfg.RegistryPullQPS),
int(kubeCfg.RegistryBurst),
kubeCfg.CPUCFSQuota,
runtimeService,
imageService,
kubeDeps.ContainerManager.InternalContainerLifecycle(),
legacyLogProvider,
)
// 设置对应的 containerRuntime 字段对象
klet.containerRuntime = runtime
klet.runner = runtime
// 设置 cAdvisor
if cadvisor.UsingLegacyCadvisorStats(containerRuntime, remoteRuntimeEndpoint) {
klet.StatsProvider = stats.NewCadvisorStatsProvider(
klet.cadvisor,
klet.resourceAnalyzer,
klet.podManager,
klet.runtimeCache,
klet.containerRuntime)
} else {
klet.StatsProvider = stats.NewCRIStatsProvider(
klet.cadvisor,
klet.resourceAnalyzer,
klet.podManager,
klet.runtimeCache,
runtimeService,
imageService)
}
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/dockershim/docker_service.go
// NOTE: Anything passed to DockerService should be eventually handled in another way when we switch to running the shim as a different process.
func NewDockerService(config *ClientConfig,
podSandboxImage string,
streamingConfig *streaming.Config,
pluginSettings *NetworkPluginSettings,
cgroupsName string,
kubeCgroupDriver string,
dockershimRootDir string,
disableSharedPID bool) (DockerService, error) {
client := NewDockerClientFromConfig(config)
c := libdocker.NewInstrumentedInterface(client)
checkpointHandler, err := NewPersistentCheckpointHandler(dockershimRootDir)
ds := &dockerService{
client: c,
os: kubecontainer.RealOS{},
podSandboxImage: podSandboxImage,
streamingRuntime: &streamingRuntime{
client: client,
execHandler: &NativeExecHandler{},
},
containerManager: cm.NewContainerManager(cgroupsName, client),
checkpointHandler: checkpointHandler,
disableSharedPID: disableSharedPID,
networkReady: make(map[string]bool),
}
// check docker version compatibility.
// ...
// create streaming server if configured.
if streamingConfig != nil {
// 真正处理的 ServerHttp 的对象为 streaming.NewServer
ds.streamingServer, err = streaming.NewServer(*streamingConfig, ds.streamingRuntime)
// ...
}
// dockershim currently only supports CNI plugins.
cniPlugins := cni.ProbeNetworkPlugins(
pluginSettings.PluginConfDir,
pluginSettings.PluginBinDir)
cniPlugins = append(cniPlugins, kubenet.NewPlugin(pluginSettings.PluginBinDir))
// set cni plugins .....
ds.network = network.NewPluginManager(plug)
// NOTE: cgroup driver is only detectable in docker 1.11+
cgroupDriver := defaultCgroupDriver
dockerInfo, err := ds.client.Info()
cgroupDriver = dockerInfo.CgroupDriver)
ds.cgroupDriver = cgroupDriver
// ...
// Register prometheus metrics.
metrics.Register()
return ds, nil
}
func (ds *dockerService) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if ds.streamingServer != nil {
ds.streamingServer.ServeHTTP(w, r)
} else {
http.NotFound(w, r)
}
}k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/server/streaming/server.go
streaming.server 对象最终调用 restful.WebService来生成对相应的处理,主要提供 exec/attach/portforward 等操作
// TODO(tallclair): Add auth(n/z) interface & handling.
func NewServer(config Config, runtime Runtime) (Server, error) {
s := &server{
config: config,
runtime: &criAdapter{runtime},
cache: newRequestCache(),
}
if s.config.BaseURL == nil {
s.config.BaseURL = &url.URL{
Scheme: "http",
Host: s.config.Addr,
}
if s.config.TLSConfig != nil {
s.config.BaseURL.Scheme = "https"
}
}
ws := &restful.WebService{}
endpoints := []struct {
path string
handler restful.RouteFunction
}{
{"/exec/{token}", s.serveExec},
{"/attach/{token}", s.serveAttach},
{"/portforward/{token}", s.servePortForward},
}
// If serving relative to a base path, set that here.
pathPrefix := path.Dir(s.config.BaseURL.Path)
for _, e := range endpoints {
for _, method := range []string{"GET", "POST"} {
ws.Route(ws.
Method(method).
Path(path.Join(pathPrefix, e.path)).
To(e.handler))
}
}
handler := restful.NewContainer()
handler.Add(ws)
s.handler = handler
s.server = &http.Server{
Addr: s.config.Addr,
Handler: s.handler,
TLSConfig: s.config.TLSConfig,
}
return s, nil
}分析完 kl.criHandler 以后,我们再接着看 10250 端口的服务监听的主要流程:
k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/server/server.go
// ListenAndServeKubeletServer initializes a server to respond to HTTP network requests on the Kubelet.
func ListenAndServeKubeletServer(
host HostInterface,
resourceAnalyzer stats.ResourceAnalyzer,
address net.IP,
port uint,
tlsOptions *TLSOptions,
auth AuthInterface,
enableDebuggingHandlers,
enableContentionProfiling bool,
runtime kubecontainer.Runtime,
criHandler http.Handler) {
handler := NewServer(host, resourceAnalyzer, auth, enableDebuggingHandlers, enableContentionProfiling, runtime, criHandler)
s := &http.Server{
Addr: net.JoinHostPort(address.String(),
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(port), 10)),
Handler: &handler,
MaxHeaderBytes: 1 << 20,
}
// 开始启动服务
glog.Fatal(s.ListenAndServe())
}
// NewServer initializes and configures a kubelet.Server object to handle HTTP requests.
func NewServer(
host HostInterface,
resourceAnalyzer stats.ResourceAnalyzer,
auth AuthInterface,
enableDebuggingHandlers,
enableContentionProfiling bool,
runtime kubecontainer.Runtime,
criHandler http.Handler) Server {
server := Server{
host: host,
resourceAnalyzer: resourceAnalyzer,
auth: auth,
restfulCont: &filteringContainer{Container: restful.NewContainer()},
runtime: runtime,
}
if auth != nil {
server.InstallAuthFilter()
}
// 设置了主要的工作
server.InstallDefaultHandlers()
if enableDebuggingHandlers {
server.InstallDebuggingHandlers(criHandler)
if enableContentionProfiling {
goruntime.SetBlockProfileRate(1)
}
} else {
server.InstallDebuggingDisabledHandlers()
}
return server
}
// InstallDefaultHandlers registers the default set of supported HTTP request
// patterns with the restful Container.
func (s *Server) InstallDefaultHandlers() {
healthz.InstallHandler(s.restfulCont,
healthz.PingHealthz,
healthz.NamedCheck("syncloop", s.syncLoopHealthCheck),
)
ws := new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path("/pods").Produces(restful.MIME_JSON)
ws.Route(ws.GET("").To(s.getPods).Operation("getPods"))
s.restfulCont.Add(ws)
s.restfulCont.Add(stats.CreateHandlers(statsPath, s.host, s.resourceAnalyzer))
s.restfulCont.Handle(metricsPath, prometheus.Handler())
// cAdvisor metrics are exposed under the secured handler as well
r := prometheus.NewRegistry()
r.MustRegister(metrics.NewPrometheusCollector(prometheusHostAdapter{s.host}, containerPrometheusLabels))
s.restfulCont.Handle(cadvisorMetricsPath,
promhttp.HandlerFor(r, promhttp.HandlerOpts{ErrorHandling: promhttp.ContinueOnError}),
)
ws = new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path(specPath).Produces(restful.MIME_JSON)
ws.Route(ws.GET("").To(s.getSpec).Operation("getSpec").Writes(cadvisorapi.MachineInfo{}))
s.restfulCont.Add(ws)
}
// InstallDebuggingHandlers registers the HTTP request patterns that serve logs or run commands/containers
func (s *Server) InstallDebuggingHandlers(criHandler http.Handler) {
glog.Infof("Adding debug handlers to kubelet server.")
ws := new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path("/run")
ws.Route(ws.POST("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{containerName}").
To(s.getRun).
Operation("getRun"))
ws.Route(ws.POST("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{uid}/{containerName}").
To(s.getRun).
Operation("getRun"))
s.restfulCont.Add(ws)
ws = new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path("/exec")
ws.Route(ws.GET("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{containerName}").
To(s.getExec).
Operation("getExec"))
ws.Route(ws.POST("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{containerName}").
To(s.getExec).
Operation("getExec"))
ws.Route(ws.GET("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{uid}/{containerName}").
To(s.getExec).
Operation("getExec"))
ws.Route(ws.POST("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{uid}/{containerName}").
To(s.getExec).
Operation("getExec"))
s.restfulCont.Add(ws)
ws = new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path("/attach")
ws.Route(ws.GET("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{containerName}").
To(s.getAttach).
Operation("getAttach"))
ws.Route(ws.POST("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{containerName}").
To(s.getAttach).
Operation("getAttach"))
ws.Route(ws.GET("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{uid}/{containerName}").
To(s.getAttach).
Operation("getAttach"))
ws.Route(ws.POST("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{uid}/{containerName}").
To(s.getAttach).
Operation("getAttach"))
s.restfulCont.Add(ws)
ws = new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path("/portForward")
ws.Route(ws.GET("/{podNamespace}/{podID}").To(s.getPortForward).
Operation("getPortForward"))
ws.Route(ws.POST("/{podNamespace}/{podID}").
To(s.getPortForward).
Operation("getPortForward"))
ws.Route(ws.GET("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{uid}").
To(s.getPortForward).
Operation("getPortForward"))
ws.Route(ws.POST("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{uid}").
To(s.getPortForward).
Operation("getPortForward"))
s.restfulCont.Add(ws)
ws = new(restful.WebService)
ws.
Path(logsPath)
ws.Route(ws.GET("").To(s.getLogs).Operation("getLogs"))
ws.Route(ws.GET("/{logpath:*}").To(s.getLogs).Operation("getLogs").
Param(ws.PathParameter("logpath", "path to the log").DataType("string")))
s.restfulCont.Add(ws)
ws = new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path("/containerLogs")
ws.Route(ws.GET("/{podNamespace}/{podID}/{containerName}").To(s.getContainerLogs).
Operation("getContainerLogs"))
s.restfulCont.Add(ws)
configz.InstallHandler(s.restfulCont)
handlePprofEndpoint := func(req *restful.Request, resp *restful.Response) {
name := strings.TrimPrefix(req.Request.URL.Path, pprofBasePath)
switch name {
case "profile":
pprof.Profile(resp, req.Request)
case "symbol":
pprof.Symbol(resp, req.Request)
case "cmdline":
pprof.Cmdline(resp, req.Request)
case "trace":
pprof.Trace(resp, req.Request)
default:
pprof.Index(resp, req.Request)
}
}
// Setup pprof handlers.
ws = new(restful.WebService).Path(pprofBasePath)
ws.Route(ws.GET("/{subpath:*}").To(func(req *restful.Request, resp *restful.Response) {
handlePprofEndpoint(req, resp)
})).Doc("pprof endpoint")
s.restfulCont.Add(ws)
// The /runningpods endpoint is used for testing only.
ws = new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path("/runningpods/").Produces(restful.MIME_JSON)
ws.Route(ws.GET("").To(s.getRunningPods).Operation("getRunningPods"))
s.restfulCont.Add(ws)
if criHandler != nil {
s.restfulCont.Handle("/cri/", criHandler)
}
}