| layout | title |
|---|---|
default |
Pre-course |
{::options parse_block_html="true" /}
The course will be taught using both R and Python depending on the tools available. While you will be able to follow all lectures and exercises conceptually, you should be familiar with basic usage of both programming languages as these are requirements for the course:
You should also be familiar with basic command line input (mkdir, cd, ls, cp, mv).
Before the course, you should go through the data preprocessing notebook.
For additional information on some of the topics that we will discuss, refer to the reading materials.
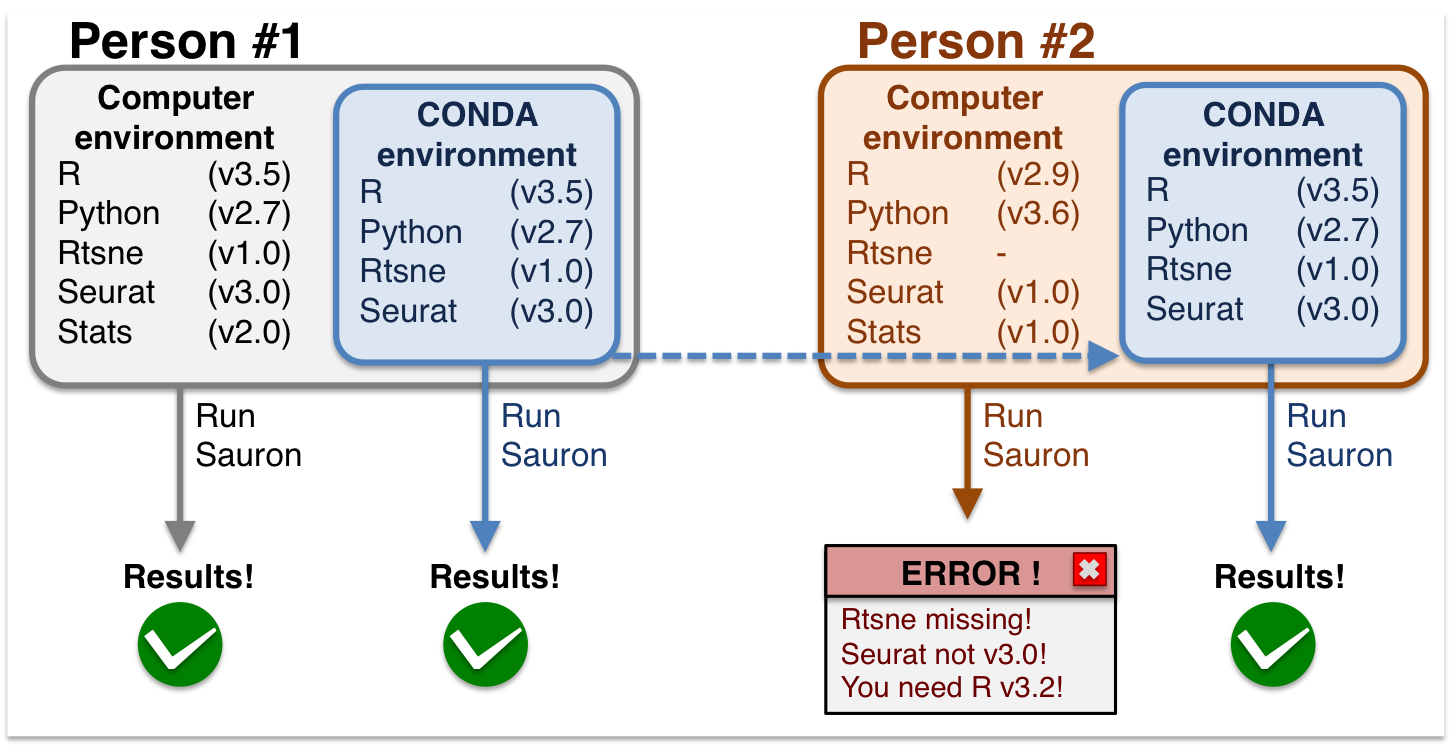
During this workshop, you will use conda environments to run the exercises. This is because conda environments allow all users to have the same computing environment, i.e. package versions. This enforces reproducibility for you to run this material without the need to re-install or change your local versions. See and graphical example below:
Conda environments are a self-contained directory that you can use in order to reproduce all your results.
Briefly, you need to:
1. Install Conda and Mamba
2. Install git and clone the repository
3. Create and activate the environment
4. Launch RStudio or Jupyter
5. Deactivate the environment after running your analyses
You can read more about Conda environments and other important concepts to help you make your research reproducible.
Start by installing Conda. We suggest installing Miniconda3 and NOT Anaconda. After installing Conda.
**On Mac OS X**
First, make sure you have Xcode and CommandLineTools installed and updated to latest version (in AppStore). If you have not already installed CommadLineTools, go to a terminal window and run:
xcode-select --install
First download the latest version of Miniconda3 and run it to install.
curl -o Miniconda3-latest-MacOSX-x86_64.sh https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-MacOSX-x86_64.sh
sh Miniconda3-latest-MacOSX-x86_64.sh
Follow the instructions on screen, scrolling down, pressing ENTER and replying yes when necessary. Install it in the default directory. Restart your terminal window to apply modifications. After restarting, you can type the command below to install Mamba:
conda init
conda install -n base -c conda-forge mamba
**On Ubuntu**
First download the latest version of Miniconda3 and run it to install.
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
sh Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
Follow the instructions on screen replying yes when necessary. Restart your terminal window to apply modifications. After restarting, you can type the command below to install Mamba:
conda init
conda install -n base -c conda-forge mamba
**On Windows 10**
Unfortunately, not all packages available on conda are compatible with windows machines. The good news is that Windows 10 offers native linux support via the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL2). This allows you to run linux/bash commands from within windows without the need of a virtual machine nor a dual-boot setup (i.e. having 2 operating systems). However, WSL does not offer a complete support for graphical interfaces (such as RStudio in our case), so we need additional steps to make that happen.
-
On Windows 10, install the WSL if you don't have it. Follow the instructions here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10
-
Once you have that installed, you can download and install MobaXterm (which is the enhanced terminal with graphical capacity): https://mobaxterm.mobatek.net
It is recommended that you INSTALL the program and not use the portable version. -
Inside MobaXterm, you will probably will see that your WSL is already listed on the left panel as an available connection. Just double-click it and you will be accessing it via MobaXterm. If by any chance you don't see it there, close MobaXterm and go to the WSL terminal, because probably the WSL is not allowing SSH connections. You can follow this link for the instructions on how to do it. You need to complete until the step
Start or restart the SSH service, while the further steps are optional, but might be useful. -
Inside MobaXterm, download Conda with the command:
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
- Inside MobaXterm, type the commands below to install Conda. Follow the instructions for the installation there.
cd ~/Downloads
sh Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
- Inside MobaXterm, Follow the instructions on screen replying
yeswhen necessary. Restart your terminal window to apply modifications. After restarting, you can type the command below to install Mamba:
conda init
conda install -n base -c conda-forge mamba
- Inside MobaXterm, type the commands below to install the X-server graphical packages that will be used to launch RStudio. https://docs.anaconda.com/anaconda/install/linux/
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install libgl1-mesa-glx libegl1-mesa libxrandr2 libxrandr2 libxss1 libxcursor1 libxcomposite1 libasound2 libxi6 libxtst6
- Close and open all application and Inside MobaXterm, you will probably will see that your WSL is already listed on the left panel as an available connection. Just double-click it and you will be accessing it via MobaXterm.
**On VirtualBox**
If by any means you see that the installations are not working as it should on your computer, you can try to create a virtual machine to run UBUNTU and install everything there. But please keep this alternative as the last temporary resourse, as we recommend troubleshooting the installation o the up-mentioned methods.
-
Download and install on your machine VIRTUALBOX https://www.virtualbox.org
-
Download the ISO disk of UBUNTU https://ubuntu.com/download/desktop
-
On VIRTUALBOX, click on
Settings(yellow engine) >General>Advancedand make sure that both settings Shared Clipboard and Drag'n'Drop are set toBidirectional. -
Completely close VIRTUALBOX and start it again to apply changes.
-
On VIRTUALBOX, create a machine called Ubuntu and add the image above
- set the memory to the maximum allowed in the GREEN bar
- set the hard disk to be dynamic allocated
- all other things can be default
-
Proceed with the Ubuntu installation as recommended. You can set to do "Minimal Installation" and deactivate to get updates during installation.
-
Inside Ubuntu, open TERMINAL and type the commands below to install the X-server graphical packages that will be used to launch RStudio. https://docs.anaconda.com/anaconda/install/linux/
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install libgl1-mesa-glx libegl1-mesa libxrandr2 libxrandr2 libxss1 libxcursor1 libxcomposite1 libasound2 libxi6 libxtst6
- Inside UBUNTU, Download conda:
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
- Inside UBUNTU, open the TERMINAL and type the commands below. Follow the instructions for the installation there.
cd ~/Downloads
sh Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
- Close Terminal to apply the CONDA updates.
Throughout the course we'll be using scripts and environments found in our github repository. After installing mamba, install git and clone the repository:
mamba install -c anaconda git #install
mkdir ~/Desktop/course
cd ~/Desktop/course
git clone https://github.com/NBISweden/workshop_omics_integration.git .
All environments are contained inside the folder /environments/
For each day you will have to create a different environment as not all programs are compatible with each other:
Before the course
#Linux
mamba env create -f environments/env-preprocessing_linux.yaml -n envprep
#MacOSX
mamba env create -f environments/env-preprocessing.yaml -n envprep
Day 1
#Linux
mamba env create -f environments/env-ml_linux.yaml -n envday1
#MacOSX
mamba env create -f environments/env-ml.yaml -n envday1
Day 2
#Linux
mamba env create -f environments/env-ml_day2_linux.yaml -n envday2
#MacOSX
mamba env create -f environments/env-ml_day2.yaml -n envday2
Days 3-5
#Linux
mamba env create -f environments/env-merged_nets_linux.yaml -n envdays35
#MacOSX
mamba env create -f environments/env-merged_nets.yaml -n envdays35
Activate the environments with mamba activate [environment name]. For instance
conda activate envday1
Depending on the exercise, you'll have to run scripts in either RStudio or Jupyter. You can launch these with
rstudio &
or
jupyter-notebook &
After you've ran all your analyses, you can deactivate the environment by typing:
conda deactivate