Read or watch:
man or help:
openclosereadwritedprintf
At the end of this project, you are expected to be able to explain to anyone, without the help of Google:
- Look for the right source of information online
- How to create, open, close, read and write files
- What are file descriptors
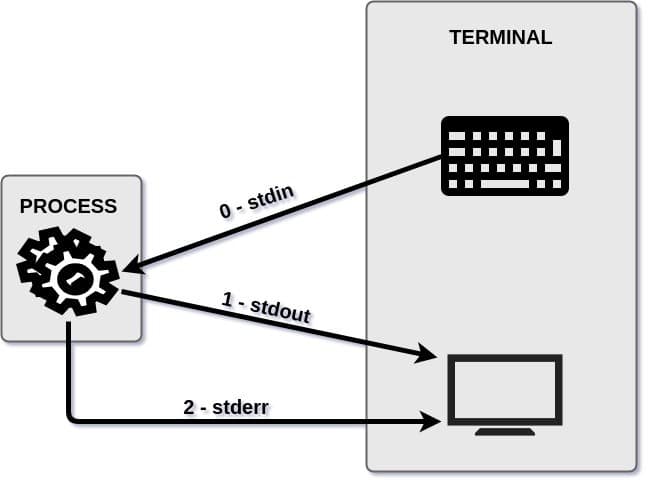
- What are the 3 standard file descriptors, what are their purpose and what are their
POSIXnames - How to use the I/O system calls
open,close,readandwrite - What are and how to use the flags
O_RDONLY,O_WRONLY,O_RDWR - What are file permissions, and how to set them when creating a file with the
opensystem call - What is a system call
- What is the difference between a function and a system call
- Allowed editors:
vi,vim,emacs - All your files will be compiled on Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
- Your programs and functions will be compiled with
gcc 4.8.4using the flags-Wall-Werror-Wextraand -pedantic - All your files should end with a new line
- A
README.mdfile, at the root of the folder of the project is mandatory - Your code should use the
Bettystyle. It will be checked using betty-style.pl and betty-doc.pl - You are not allowed to use global variables
- No more than 5 functions per file
- The only C standard library functions allowed are
malloc,freeandexit. Any use of functions likeprintf,puts,calloc,reallocetc… is forbidden - Allowed syscalls:
read,write,open,close - You are allowed to use _putchar
- You don’t have to push
_putchar.c, we will use our file. If you do it won’t be taken into account - In the following examples, the
main.cfiles are shown as examples. You can use them to test your functions, but you don’t have to push them to your repo (if you do we won’t take them into account). We will use our ownmain.cfiles at compilation. Ourmain.cfiles might be different from the one shown in the examples - The prototypes of all your functions and the prototype of the function
_putcharshould be included in your header file calledholberton.h - Don’t forget to push your header file
- All your header files should be include guarded
- Tip: always prefer using symbolic constants (
POSIX) vs numbers when it makes sense. For instanceread(STDIN_FILENO, ...vsread(0, ...
Write a function that reads a text file and prints it to the POSIX standard output.
Create a function that creates a file.
Write a function that appends text at the end of a file.
Write a program that copies the content of a file to another file.