Read or watch:
At the end of this project, you are expected to be able to explain to anyone, without the help of Google:
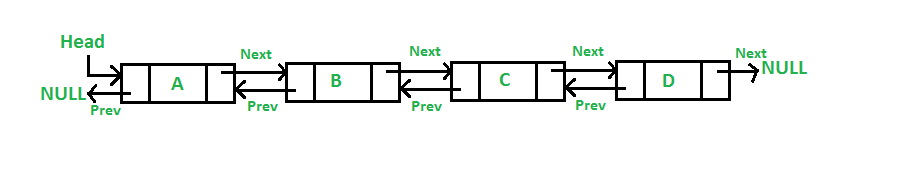
- What is a doubly linked list
- How to use doubly linked lists
- Start to look for the right source of information without too much help
- Allowed editors:
vi,vim,emacs - All your files will be compiled on Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
- Your programs and functions will be compiled with
gcc 4.8.4using the flags-Wall-Werror-Wextraand -pedantic - All your files should end with a new line
- A
README.mdfile, at the root of the folder of the project is mandatory - Your code should use the
Bettystyle. It will be checked using betty-style.pl and betty-doc.pl - You are not allowed to use global variables
- No more than 5 functions per file
- The only C standard library functions allowed are
malloc,free,printfandexit - In the following examples, the
main.cfiles are shown as examples. You can use them to test your functions, but you don’t have to push them to your repo (if you do we won’t take them into account). We will use our ownmain.cfiles at compilation. Ourmain.cfiles might be different from the one shown in the examples - The prototypes of all your functions should be included in your header file called
lists.h - Don’t forget to push your header file
- All your header files should be include guarded
This must be the data strcuture for this project:
/**
* struct dlistint_s - doubly linked list
* @n: integer
* @prev: points to the previous node
* @next: points to the next node
*
* Description: doubly linked list node structure
* for Holberton project
*/
typedef struct dlistint_s
{
int n;
struct dlistint_s *prev;
struct dlistint_s *next;
} dlistint_t;
Write a function that prints all the elements of a dlistint_t list.
- Prototype:
size_t print_dlistint(const dlistint_t *h); - Return: the number of nodes
Write a function that returns the number of elements in a linked dlistint_t list.
- Prototype:
size_t dlistint_len(const dlistint_t *h);
Write a function that adds a new node at the beginning of a dlistint_t list.
- Prototype:
dlistint_t *add_dnodeint(dlistint_t **head, const int n); - Return: the address of the new element, or
NULLif it failed
Write a function that adds a new node at the end of a dlistint_t list.
- Prototype:
dlistint_t *add_dnodeint_end(dlistint_t **head, const int n); - Return: the address of the new element, or
NULLif it failed
Write a function that free a dlistint_t list.
- Prototype:
void free_dlistint(dlistint_t *head);
Write a function that returns the nth node of a dlistint_t linked list.
- Prototype:
dlistint_t *get_dnodeint_at_index(dlistint_t *head, unsigned int index); - where
indexis the index of the node, starting from0 - if the node does not exist, return
NULL
Write a function that returns the sum of all the data (n) of a dlistint_t linked list.
- Prototype:
int sum_dlistint(dlistint_t *head); - if the list is empty, return
0
Write a function that inserts a new node at a given position.
- Prototype:
dlistint_t *insert_dnodeint_at_index(dlistint_t **h, unsigned int idx, int n); - where
idxis the index of the list where the new node should be added. Index starts at0 - Returns: the address of the new node, or
NULLif it failed - if it is not possible to add the new node at index
idx, do not add the new node and returnNULL
Files 2-add_dnodeint.c and 3-add_dnodeint_end.c will be compiled during the correction
Write a function that deletes the node at index index of a dlistint_t linked list.
- Prototype:
int delete_dnodeint_at_index(dlistint_t **head, unsigned int index); - where
indexis the index of the node that should be deleted. Index starts at0 - Returns:
1if it succeeded,-1if it failed