想象一下你是个城市基建规划者,地图上有 n 座城市,它们按以 1 到 n 的次序编号。
给你整数 n 和一个数组 conections,其中 connections[i] = [xi, yi, costi] 表示将城市 xi 和城市 yi 连接所要的costi(连接是双向的)。
返回连接所有城市的最低成本,每对城市之间至少有一条路径。如果无法连接所有 n 个城市,返回 -1
该 最小成本 应该是所用全部连接成本的总和。
示例 1:
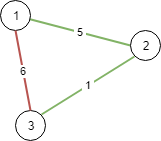
输入:n = 3, conections = [[1,2,5],[1,3,6],[2,3,1]] 输出:6 解释:选出任意 2 条边都可以连接所有城市,我们从中选取成本最小的 2 条。
示例 2:
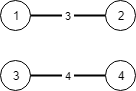
输入:n = 4, conections = [[1,2,3],[3,4,4]] 输出:-1 解释:即使连通所有的边,也无法连接所有城市。
提示:
1 <= n <= 1041 <= connections.length <= 104connections[i].length == 31 <= xi, yi <= nxi != yi0 <= costi <= 105
方法一:Kruskal 算法
Kruskal 算法是一种贪心算法,用于计算最小生成树。
Kruskal 算法的基本思想是,每次从边集中选择一条最小的边,如果这条边连接的两个顶点不在同一个连通分量中,则将这条边加入到最小生成树中,否则舍弃这条边。
对于本题,我们可以将边按照连通成本从小到大排序,用并查集维护连通分量,每次选择一条最小的边,如果这条边连接的两个顶点不在同一个连通分量中,则合并这两个顶点,然后累加连通成本。如果出现连通份量为
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def minimumCost(self, n: int, connections: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def find(x):
if p[x] != x:
p[x] = find(p[x])
return p[x]
connections.sort(key=lambda x: x[2])
p = list(range(n))
ans = 0
for x, y, cost in connections:
x, y = x - 1, y - 1
if find(x) == find(y):
continue
p[find(x)] = find(y)
ans += cost
n -= 1
if n == 1:
return ans
return -1class Solution {
private int[] p;
public int minimumCost(int n, int[][] connections) {
Arrays.sort(connections, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[2]));
p = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int[] e : connections) {
int x = e[0] - 1, y = e[1] - 1, cost = e[2];
if (find(x) == find(y)) {
continue;
}
p[find(x)] = find(y);
ans += cost;
if (--n == 1) {
return ans;
}
}
return -1;
}
private int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
}class Solution {
public:
int minimumCost(int n, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
vector<int> p(n);
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
sort(connections.begin(), connections.end(), [](auto& a, auto& b) { return a[2] < b[2]; });
int ans = 0;
function<int(int)> find = [&](int x) -> int {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
};
for (auto& e : connections) {
int x = e[0] - 1, y = e[1] - 1, cost = e[2];
if (find(x) == find(y)) {
continue;
}
p[find(x)] = find(y);
ans += cost;
if (--n == 1) {
return ans;
}
}
return -1;
}
};func minimumCost(n int, connections [][]int) (ans int) {
p := make([]int, n)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
}
sort.Slice(connections, func(i, j int) bool { return connections[i][2] < connections[j][2] })
var find func(int) int
find = func(x int) int {
if p[x] != x {
p[x] = find(p[x])
}
return p[x]
}
for _, e := range connections {
x, y, cost := e[0]-1, e[1]-1, e[2]
if find(x) == find(y) {
continue
}
p[find(x)] = find(y)
ans += cost
n--
if n == 1 {
return
}
}
return -1
}function minimumCost(n: number, connections: number[][]): number {
const p = new Array(n);
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
}
const find = (x: number): number => {
if (p[x] !== x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
};
connections.sort((a, b) => a[2] - b[2]);
let ans = 0;
for (const [x, y, cost] of connections) {
if (find(x - 1) == find(y - 1)) {
continue;
}
p[find(x - 1)] = find(y - 1);
ans += cost;
if (--n == 1) {
return ans;
}
}
return -1;
}