We are going to create a Kubernetes cluster with a Jenkins X platform deployed using the Jenkins X CLI. You will see that having a ready CI/CD Cloud Native platform from scratch is just a matter of minutes by executing some easy commands from the CLI.
Note: In case you want to use the Jenkins X Boot feature to create the cluster using GitOps, use this lab. If not, you can continue reading and create the cluster and deploy Jenkins X using the
jx create clustercommand from the CLI.
Make sure the Google Cloud project you're working on is the one selected in the Cloud Web Console. This should be the case if you opened Cloud Shell with the right project selected:
gcloud config list projectOutput (do not copy)
[core]
project = <your-project-id>
Your active configuration is: [cloudshell-30655]
If the output is not showing the proper project id, get it from the Google Console top menu and set it up with the following command:
gcloud config set project <your-project-id>Now that your project ID is set, export the value to a shell variable for later use:
export PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)Let's create a GKE cluster to host Jenkins X. To create the cluster, run the jx tool with the following options, substituting the zone for one that's more suitable to you depending on your physical location:
jx create cluster gke --no-tiller --skip-login --default-admin-password=admin --project-id=${PROJECT_ID} --cluster-name=jenkins-x-lab --zone=europe-west1-d --version=2.0.330This command is interactive; it will guide you through creating a cluster on GKE by prompting you to answer some questions. Read on to know how to continue.
The jx command will attempt to locate any required dependencies first (particularly, Helm), if it discovers that some are missing (it will ask you to install helm, for example) it will prompt to install them for you in the ~/.jx/bin folder. Just answer yes for jx to install whatever dependencies are required.
Follow the prompt to provide the following answers:
- Google Cloud Machine Type: n1-standard-2
- Minimum number of Nodes: 4
- Maximum number of Nodes: 6
- Would you like use preemptible VMs: N
- Would you like to access Google Cloud Storage / Google Container Registry: Y
- Would you like to enable Cloud Build, Container Registry & Container Analysis APIs: Y
- Would you like to enable Kaniko for building container images: Y
Now jx is using the Google Cloud SDK to create a GKE cluster with the provided parameters. It will take some time before continuing with the configuration (up to five minutes), and will output something like this:
Output (do not copy)
INFO[0244] Creating cluster...
Once the cluster is created, the jx execution continues and you will be prompted for some configuration options. There will be some delays between prompts when the jx command proceeds with different installation actions; just follow these answers for the different steps and you should be good to go:
- Select Jenkins installation type: Serverless Jenkins X Pipelines with Tekton
- Please enter the name you wish to use with git: enter your GitHub user as Git user
- Please enter the email address you wish to use with git: enter your GitHub email as Git email address
- No existing ingress controller found in the kube-system namespace, shall we install one? Y
- Domain .nip.io Accept the proposed domain by pressing Enter
- Would you like to enable Long Term Storage? A bucket for provider gke will be created (Y/n) Y
- GitHub user name: enter your GitHub username
- API Token: copy here the API Token generated in the GitHub page presented to you when you followed the suggested URL link in the terminal
- Do you wish to use GitHub as the pipelines Git server: Yes
- API Token: copy here the API Token generated in the GitHub page presented to you when you followed the suggested URL link in the terminal. Be careful, this is a new API token, different from the previous one. Now the installer will take a bit of time before continuing with the next steps.
- Pick default workload build pack: select the option Kubernetes Workloads: Automated CI+CD with GitOps Promotion
- Select the organization where you want to create the environment repository: select here the GitHub organization you have already configured
Note: the nip.io service you just used is just a way to have a static domain based on your IP.
The jx command should exit successfully showing an output similar to this:
(Output)
Jenkins X installation completed successfully
********************************************************
NOTE: Your admin password is: admin
********************************************************
Your Kubernetes context is now set to the namespace: jx
To switch back to your original namespace use: jx namespace default
Or to use this context/namespace in just one terminal use: jx shell
For help on switching contexts see: https://jenkins-x.io/developing/kube-context/
To import existing projects into Jenkins: jx import
To create a new microservice from a quickstart: jx create quickstart
Fetching cluster endpoint and auth data.
kubeconfig entry generated for jenkins-x-lab.
Context "gke_javiercm-jx_europe-west1-d_jenkins-x-lab" modified.
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
chartmuseum chartmuseum.jx.104.155.99.229.nip.io 104.155.99.229 80 3m40s
deck deck.jx.104.155.99.229.nip.io 104.155.99.229 80 3m40s
hook hook.jx.104.155.99.229.nip.io 104.155.99.229 80 3m39s
monocular monocular.jx.104.155.99.229.nip.io 104.155.99.229 80 3m41s
nexus nexus.jx.104.155.99.229.nip.io 104.155.99.229 80 3m40s
tide tide.jx.104.155.99.229.nip.io 104.155.99.229 80 3m40s
Note the admin password shown by the end of the installation as you'll be using it afterwards (it should be admin).
Note: You can check the passwords of the installation process in the file ádminsecrets.yaml’ that is saved in the Jenkins X local configuration directory ‘$HOME/.jx’. Check the secrets by:
cat ~/.jx/adminSecrets.yaml
Jenkins X installs different components in order to orchestrate Cloud Native CI/CD. These can be summarized conceptually as:
- Prow (Serverless Jenkins X): A webhook handler that listens to GitHub events and that uses ChatOps to trigger jobs to execute your pipeline
- Tekton: Using tekton pipelines and Jenkins X controller a pipeline is decoupled into tasks and pipeline resources that are Kubernetes native objects
- Chartmuseum: Helm chart repository to publish different charts to be used during pipeline execution
- Nexus: Artifact cache management that can be required by some applications during the building or deployment
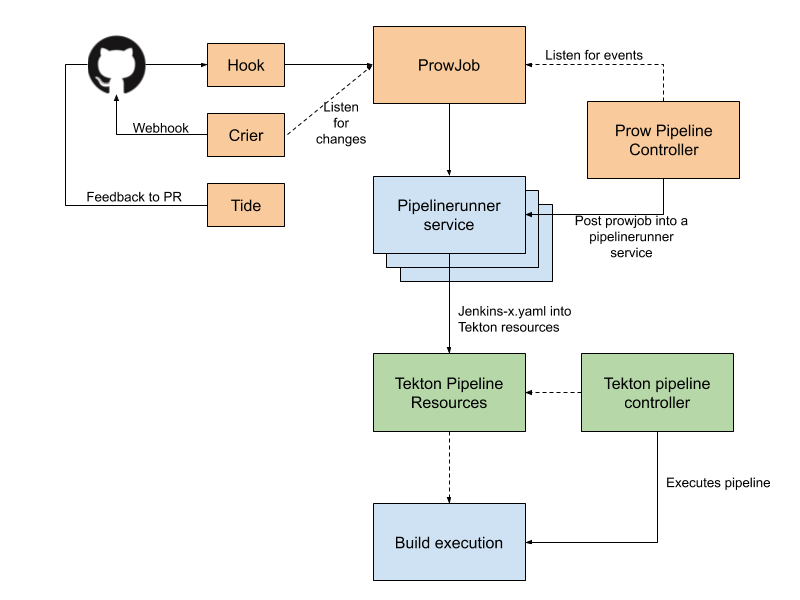
- Monocular: UI used for discovering and running Helm charts The more detailed architecture of Jenkins X using Tekton (Serverless Jenkins X) can be described below:
This is deployed to different pods and services in our development ‘jx’ namespace. So, let's take a look at what got installed based on the previous architecture diagram:
kubectl -n jx get podsOutput (do not copy)
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
crier-749f96fb4d-h8lgr 1/1 Running 0 10m
deck-696f77d746-mgxzm 1/1 Running 0 10m
deck-696f77d746-tk2ml 1/1 Running 0 10m
hook-6d9859bb47-562hx 1/1 Running 0 10m
hook-6d9859bb47-wzl95 1/1 Running 0 10m
horologium-6bc57b5f9-m2nsp 1/1 Running 0 10m
jenkins-x-chartmuseum-75d45b6d7f-k2rb9 1/1 Running 0 9m12s
jenkins-x-controllerbuild-5d957488fc-4nxz5 1/1 Running 0 9m10s
jenkins-x-controllerrole-567d98bcdb-rhbbs 1/1 Running 0 9m11s
jenkins-x-controllerteam-865b78fc69-jr6k8 1/1 Running 0 9m11s
jenkins-x-heapster-6586795784-7f2hz 2/2 Running 0 7m51s
jenkins-x-mongodb-696fdf64fc-768mp 1/1 Running 1 9m10s
jenkins-x-monocular-api-6b676d869-rv58f 1/1 Running 3 9m10s
jenkins-x-monocular-prerender-77f6cd8449-2dpv6 1/1 Running 0 9m10s
jenkins-x-monocular-ui-7b98595f74-bgvnb 1/1 Running 0 9m9s
jenkins-x-nexus-6ccd45c57c-5mnqh 1/1 Running 0 9m9s
pipeline-5f85b8df5b-59d7c 1/1 Running 0 10m
pipelinerunner-744d857549-dg8vr 1/1 Running 0 10m
plank-8849d9d67-d7nl9 1/1 Running 0 10m
sinker-85ff54bd9b-pmrlv 1/1 Running 0 10m
tekton-pipelines-controller-77cd668ddc-5vnjc 1/1 Running 0 10m
tekton-pipelines-webhook-5c6f475d75-twtdb 1/1 Running 0 10m
tide-5f8fb5964c-bgjn4 1/1 Running 0 10m
Jenkins X also created several secrets that it's using to authenticate to different services. You can have a look at them by running kubectl get secrets and observing how, for instance, there's a kaniko-secret stored to be used with Kaniko. The jx command can also give you entry URLs for different services deployed by Jenkins X:
jx get urlsOutput (do not copy)
deck http://deck.jx.35.187.61.201.nip.io
hook http://hook.jx.35.187.61.201.nip.io
jenkins-x-chartmuseum http://chartmuseum.jx.35.187.61.201.nip.io
jenkins-x-monocular-api http://monocular.jx.35.187.61.201.nip.io
jenkins-x-monocular-ui http://monocular.jx.35.187.61.201.nip.io
nexus http://nexus.jx.35.187.61.201.nip.io
tide http://tide.jx.35.187.61.201.nip.io
Note the deck URL that corresponds to Prow as we'll be using it to check that we're properly triggering pipelines from GitHub events. It is also now a good moment to have a look at how Jenkins X has created the environments and corresponding GitOps git repos, as well as a default promotion strategy:
jx get environmentsOutput (do not copy)
NAME LABEL KIND PROMOTE NAMESPACE ORDER CLUSTER SOURCE REF PR
dev Development Development Never jx 0
staging Staging Permanent Auto jx-staging 100 https://github.com/dcanadillas-kube/environment-jenkins-x-lab-staging.git
production Production Permanent Manual jx-production 200 https://github.com/dcanadillas-kube/environment-jenkins-x-lab-production.git
Note the following details in the PROMOTE column:
- Development follows a Never promotion strategy, because we're not actually deploying anything and you're working locally.
- Staging follows a default Auto promotion strategy, meaning that any merge performed on the application's repo master branch will automatically deployed as a new version to staging.
- Production follows a Manual promotion strategy, meaning that you will use a jx promotion command to promote your staging application version into production.
SOURCE column reflects the corresponding environment configuration git repo.
Now you can go to the next section: