Esync removes wineserver overhead for synchronization objects. This can increase performance for some games, especially ones that rely heavily on the CPU. A more detailed explanation can be found here.
First step is to run the ulimit -Hn command. If the value printed is equal or greater to 524288 then you're all set, your system is ready to use Esync! If you are running Systemd 240 or later, this should already be the case.
There are 2 methods for increasing the maximum number of files open. Which method is preferable depends on the distribution currently in use. Applying both methods should have no negative side effect.
Modifying Systemd configuration
This method applies to Ubuntu and other systems using systemd (some systemd distros can also use the limits.conf method below). You (with root privileges or sudo) need to edit both /etc/systemd/system.conf and /etc/systemd/user.conf by adding DefaultLimitNOFILE=524288. If DefaultLimitNOFILE= already exist in both system.conf and user.conf, add 524288 after = and make sure to uncomment the line (remove the #) to make it functional.
Once the files are edited, restart your computer for the changes to take effect. To verify if the limits were applied, run ulimit -Hn to see open files limit (it should report 524288).
If the value printed still says something like 4096, try the ulimits method below.
Modifying ulimits.conf
On Linux distributions not using Systemd or distributions using pam-limits.conf (Arch Linux, Fedora, Solus,... ), you (with root privileges or sudo) need to edit /etc/security/limits.conf.
Change username to your actual username. Once the file is edited, reboot for the changes to take effect, and verify by running ulimit -Hn to see the new limit (524288).
username hard nofile 524288
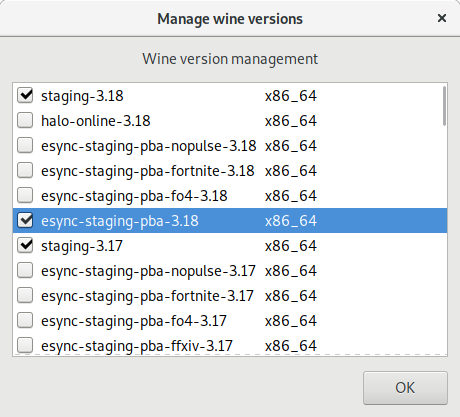
Using Esync Wine builds
Use our esync or tkg wine versions (it's recommended to use latest versions):
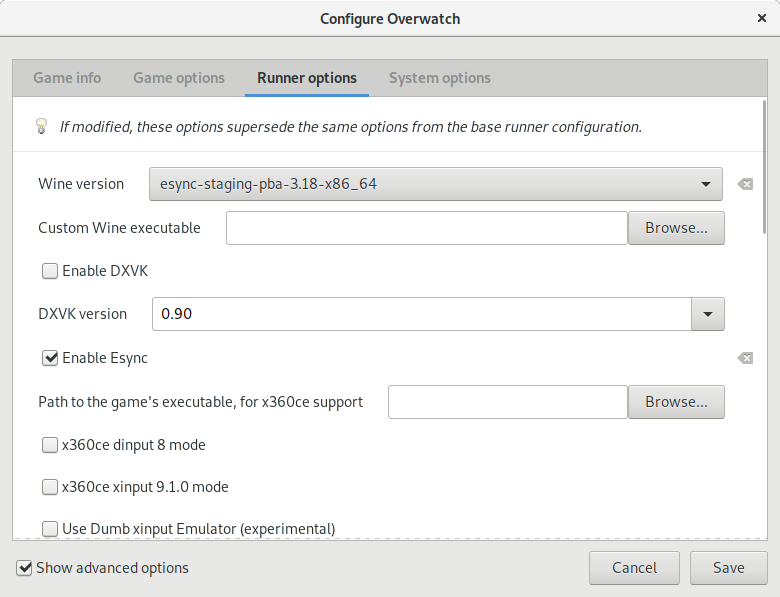
Enable Esync through the toggle in configuration: