An implementation of Jacobi-Davidson in Julia. This method can be used as an alternative to Julia's eigs to find a few eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a large sparse matrix.
We generate two random complex matrices A and B and use JDQZ to find the eigenvalues λ of the generalized eigenvalue problem Ax = λBx.
using JacobiDavidson, LinearAlgebra, SparseArrays, Plots
function run(n = 1000)
A = 2I + sprand(ComplexF64, n, n, 1 / n)
B = 2I + sprand(ComplexF64, n, n, 1 / n)
# Find all eigenvalues with a direct method
values = eigvals(Matrix(A), Matrix(B))
target = Near(1.5 - 0.7im)
pschur, residuals = jdqz(
A, B,
solver = GMRES(n, iterations = 7),
target = target,
pairs = 7,
subspace_dimensions = 10:15,
max_iter = 300,
verbosity = 1
)
# The eigenvalues found by Jacobi-Davidson
found = pschur.alphas ./ pschur.betas
#
p1 = scatter(real(values), imag(values), label = "eig")
scatter!(real(found), imag(found), marker = :+, label = "jdqz")
scatter!([real(target.τ)], [imag(target.τ)], marker = :star, label = "Target")
p2 = plot(residuals, yscale = :log10, marker = :auto, label = "Residual norm")
p1, p2
endThe first plot shows the full spectrum, together with the target we have set and the seven converged eigenvalues:
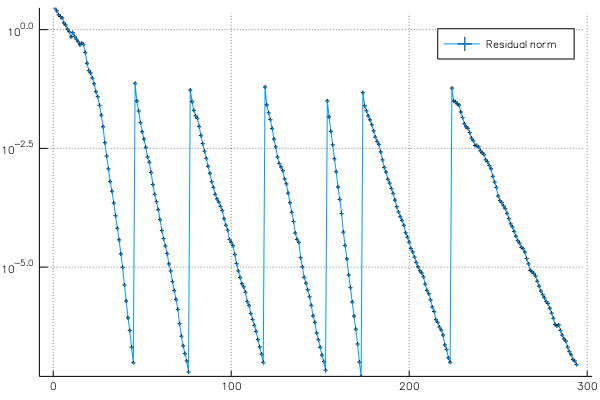
The second plot shows the residual norm of Ax - λBx during the iterations: