| title | thumbnail | authors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Run a Chatgpt-like Chatbot on a Single GPU with ROCm |
/blog/assets/chatbot-amd-gpu/thumbnail.png |
|
ChatGPT, OpenAI's groundbreaking language model, has become an influential force in the realm of artificial intelligence, paving the way for a multitude of AI applications across diverse sectors. With its staggering ability to comprehend and generate human-like text, ChatGPT has transformed industries, from customer support to creative writing, and has even served as an invaluable research tool.
Various efforts have been made to provide open-source large language models which demonstrate great capabilities but in smaller sizes, such as OPT, LLAMA, Alpaca and Vicuna.
In this blog, we will delve into the world of Vicuna, and explain how to run the Vicuna 13B model on a single AMD GPU with ROCm.
What is Vicuna?
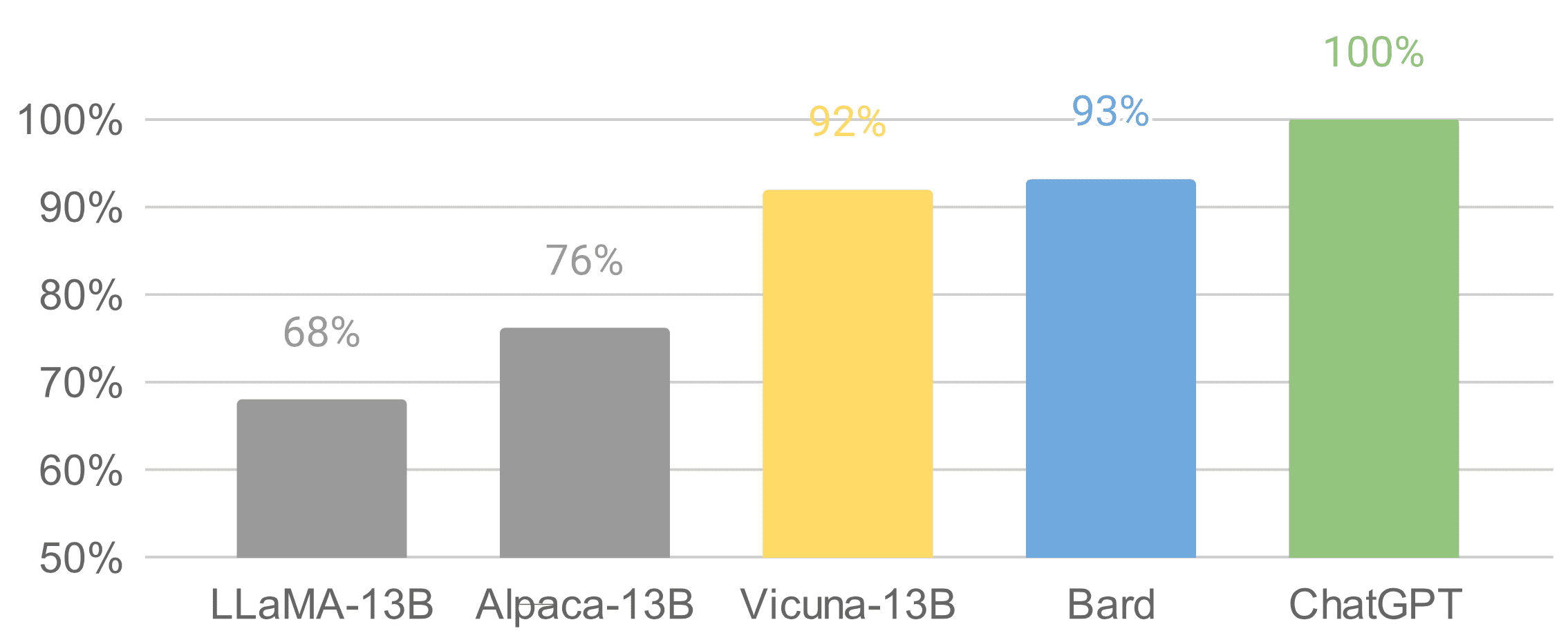
Vicuna is an open-source chatbot with 13 billion parameters, developed by a team from UC Berkeley, CMU, Stanford, and UC San Diego. To create Vicuna, a LLAMA base model was fine-tuned using about 70K user-shared conversations collected from ShareGPT.com via public APIs. According to initial assessments where GPT-4 is used as a reference, Vicuna-13B has achieved over 90%* quality compared to OpenAI ChatGPT.
It was released on Github on Apr 11, just a few weeks ago. It is worth mentioning that the data set, training code, evaluation metrics, training cost are known for Vicuna. Its total training cost was just around $300, making it a cost-effective solution for the general public.
For more details about Vicuna, please check out https://vicuna.lmsys.org.
Why do we need a quantized GPT model?
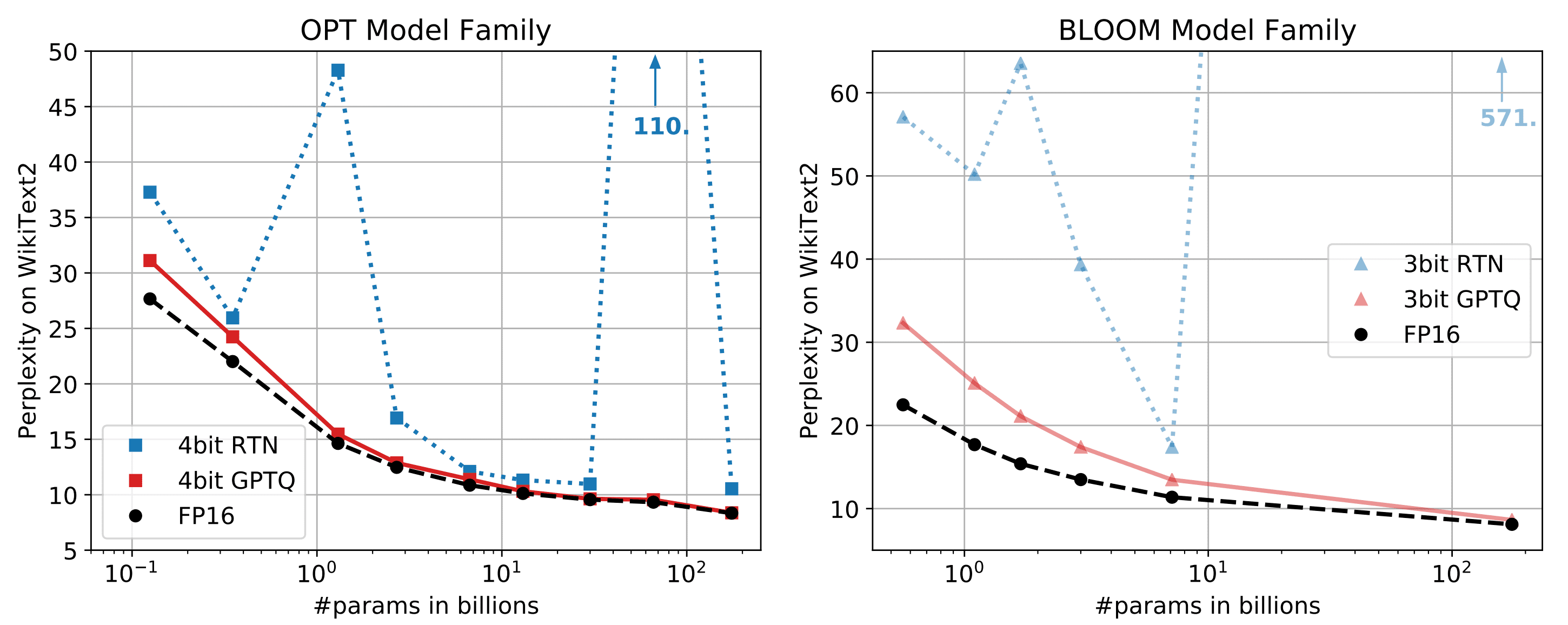
Running Vicuna-13B model in fp16 requires around 28GB GPU RAM. To further reduce the memory footprint, optimization techniques are required. There is a recent research paper GPTQ published, which proposed accurate post-training quantization for GPT models with lower bit precision. As illustrated below, for models with parameters larger than 10B, the 4-bit or 3-bit GPTQ can achieve comparable accuracy with fp16.
Moreover, large parameters of these models also have a severely negative effect on GPT latency because GPT token generation is more limited by memory bandwidth (GB/s) than computation (TFLOPs or TOPs) itself. For this reason, a quantized model does not degrade token generation latency when the GPU is under a memory bound situation. Refer to the GPTQ quantization papers and github repo.
By leveraging this technique, several 4-bit quantized Vicuna models are available from Hugging Face as follows,
To run the Vicuna 13B model on an AMD GPU, we need to leverage the power of ROCm (Radeon Open Compute), an open-source software platform that provides AMD GPU acceleration for deep learning and high-performance computing applications.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to set up and run the Vicuna 13B model on an AMD GPU with ROCm:
System Requirements
Before diving into the installation process, ensure that your system meets the following requirements:
-
An AMD GPU that supports ROCm (check the compatibility list on docs.amd.com page)
-
A Linux-based operating system, preferably Ubuntu 18.04 or 20.04
-
Conda or Docker environment
-
Python 3.6 or higher
For more information, please check out https://docs.amd.com/bundle/ROCm-Installation-Guide-v5.4.3/page/Prerequisites.html.
This example has been tested on Instinct MI210 and Radeon RX6900XT GPUs with ROCm5.4.3 and Pytorch2.0.
Quick Start
1 ROCm installation and Docker container setup (Host machine)
1.1 ROCm installation
The following is for ROCm5.4.3 and Ubuntu 22.04. Please modify according to your target ROCm and Ubuntu version from: https://docs.amd.com/bundle/ROCm-Installation-Guide-v5.4.3/page/How_to_Install_ROCm.html
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
wget https://repo.radeon.com/amdgpu-install/5.4.3/ubuntu/jammy/amdgpu-install_5.4.50403-1_all.deb
sudo apt-get install ./amdgpu-install_5.4.50403-1_all.deb
sudo amdgpu-install --usecase=hiplibsdk,rocm,dkms
sudo amdgpu-install --list-usecase
sudo reboot
1.2 ROCm installation verification
rocm-smi
sudo rocminfo
1.3 Docker image pull and run a Docker container
The following uses Pytorch2.0 on ROCm5.4.2. Please use the appropriate docker image according to your target ROCm and Pytorch version: https://hub.docker.com/r/rocm/pytorch/tags
docker pull rocm/pytorch:rocm5.4.2_ubuntu20.04_py3.8_pytorch_2.0.0_preview
sudo docker run --device=/dev/kfd --device=/dev/dri --group-add video \
--shm-size=8g --cap-add=SYS_PTRACE --security-opt seccomp=unconfined \
--ipc=host -it --name vicuna_test -v ${PWD}:/workspace -e USER=${USER} \
rocm/pytorch:rocm5.4.2_ubuntu20.04_py3.8_pytorch_2.0.0_preview
2 Model quantization and Model inference (Inside the docker)
You can either download quantized Vicuna-13b model from Huggingface or quantize the floating-point model. Please check out Appendix - GPTQ model quantization if you want to quantize the floating-point model.
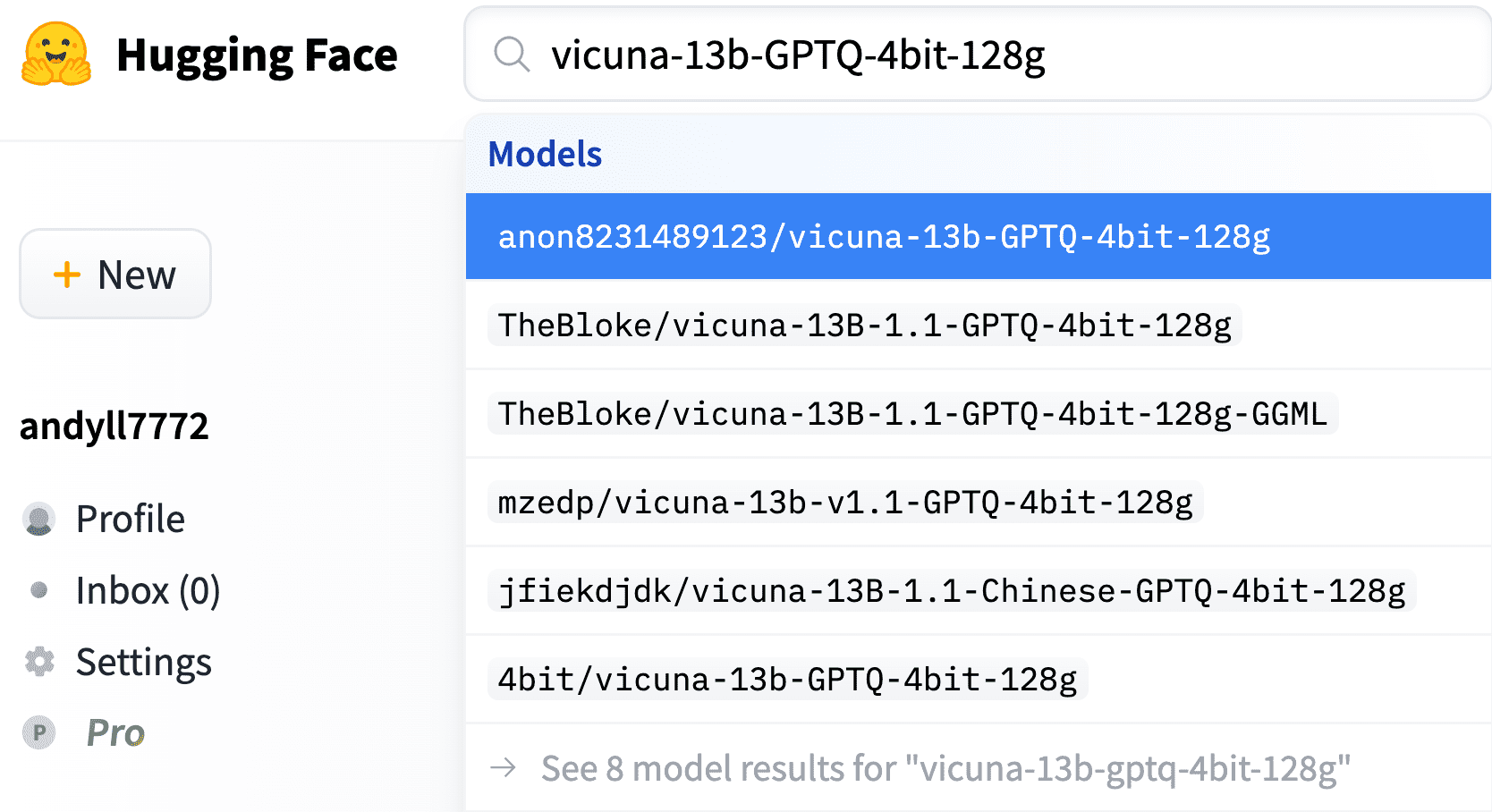
2.1 Download the quantized Vicuna-13b model
Use download-model.py script from the following git repo.
git clone https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui.git
cd text-generation-webui
python download-model.py anon8231489123/vicuna-13b-GPTQ-4bit-128g
- Running the Vicuna 13B GPTQ Model on AMD GPU
git clone https://github.com/oobabooga/GPTQ-for-LLaMa.git -b cuda
cd GPTQ-for-LLaMa
python setup_cuda.py install
These commands will compile and link HIPIFIED CUDA-equivalent kernel binaries to
python as C extensions. The kernels of this implementation are composed of dequantization + FP32 Matmul. If you want to use dequantization + FP16 Matmul for additional speed-up, please check out Appendix - GPTQ Dequantization + FP16 Mamul kernel for AMD GPUs
git clone https://github.com/oobabooga/GPTQ-for-LLaMa.git -b cuda
cd GPTQ-for-LLaMa/
python setup_cuda.py install
# model inference
python llama_inference.py ../../models/vicuna-13b --wbits 4 --load \
../../models/vicuna-13b/vicuna-13b_4_actorder.safetensors --groupsize 128 --text “You input text here”
Now that you have everything set up, it's time to run the Vicuna 13B model on your AMD GPU. Use the commands above to run the model. Replace "Your input text here" with the text you want to use as input for the model. If everything is set up correctly, you should see the model generating output text based on your input.
3. Expose the quantized Vicuna model to the Web API server
Change the path of GPTQ python modules (GPTQ-for-LLaMa) in the following line:
To launch Web UXUI from the gradio library, you need to set up the controller, worker (Vicunal model worker), web_server by running them as background jobs.
nohup python0 -W ignore::UserWarning -m fastchat.serve.controller &
nohup python0 -W ignore::UserWarning -m fastchat.serve.model_worker --model-path /path/to/quantized_vicuna_weights \
--model-name vicuna-13b-quantization --wbits 4 --groupsize 128 &
nohup python0 -W ignore::UserWarning -m fastchat.serve.gradio_web_server &
Now the 4-bit quantized Vicuna-13B model can be fitted in RX6900XT GPU DDR memory, which has 16GB DDR. Only 7.52GB of DDR (46% of 16GB) is needed to run 13B models whereas the model needs more than 28GB of DDR space in fp16 datatype. The latency penalty and accuracy penalty are also very minimal and the related metrics are provided at the end of this article.
Test the quantized Vicuna model in the Web API server
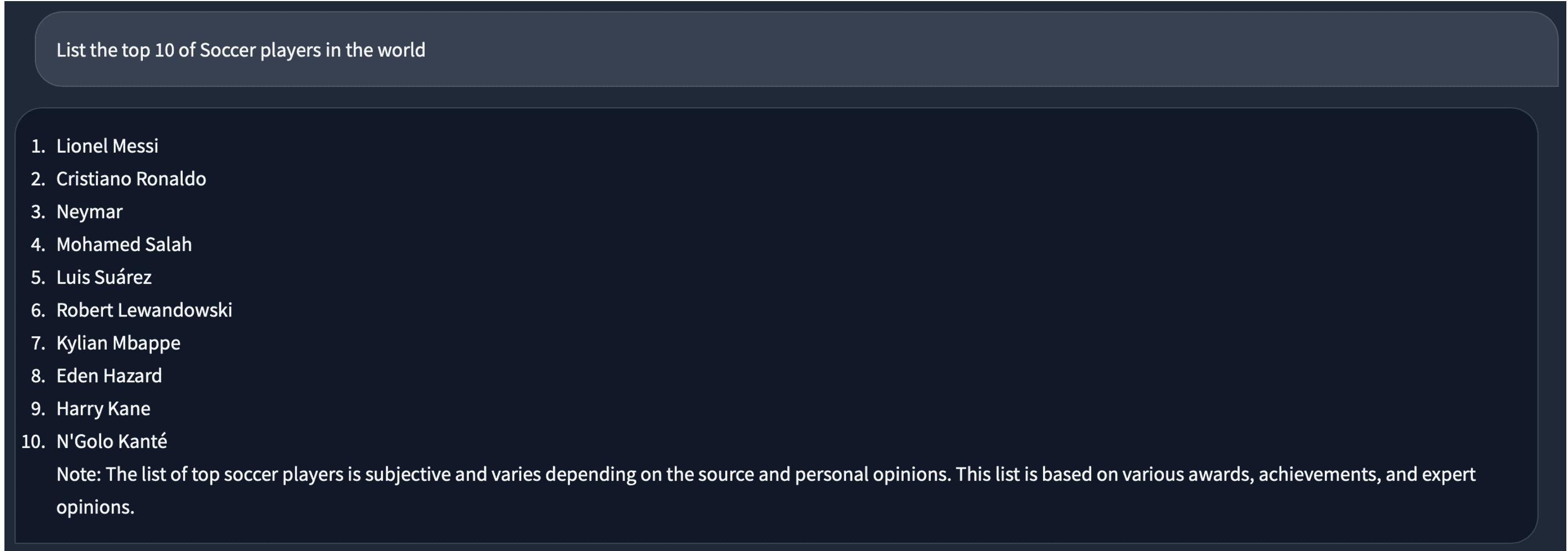
Let us give it a try. First, let us use fp16 Vicuna model for language translation.
It does a better job than me. Next, let us ask something about soccer. The answer looks good to me.
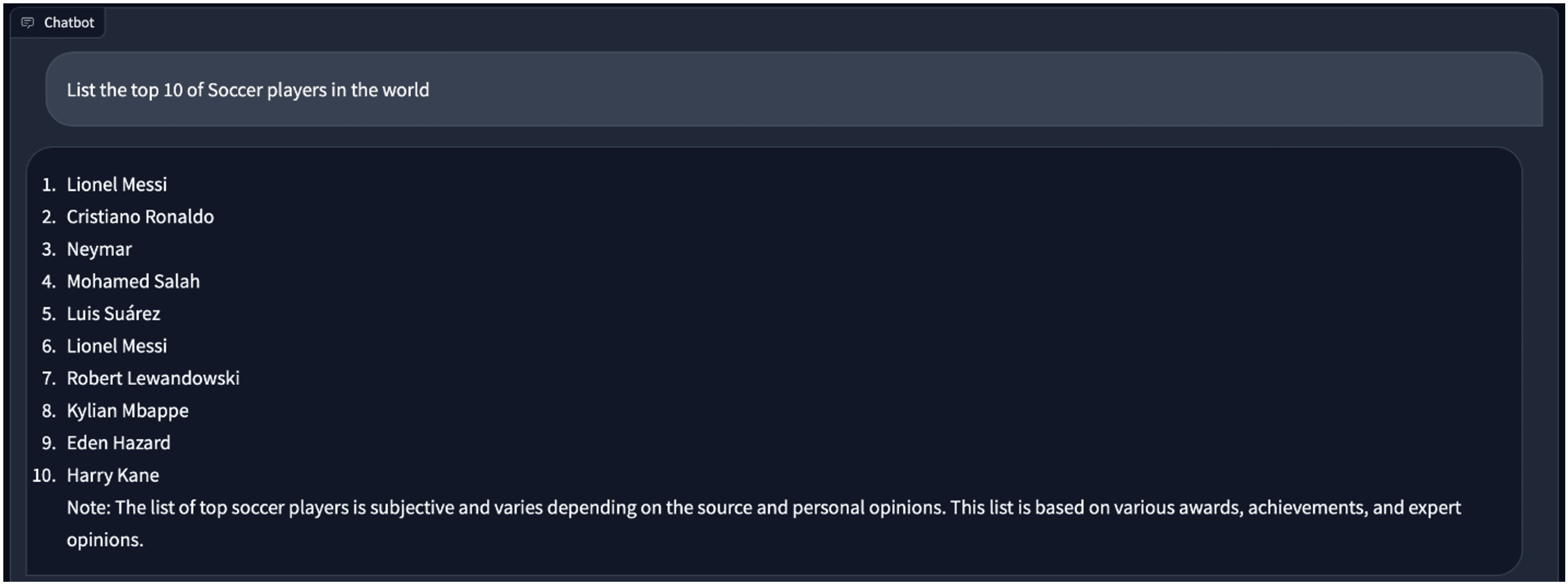
When we switch to the 4-bit model, for the same question, the answer is a bit different. There is a duplicated “Lionel Messi” in it.
Vicuna fp16 and 4bit quantized model comparison
Test environment:
- GPU: Instinct MI210, RX6900XT
- python: 3.10
- pytorch: 2.1.0a0+gitfa08e54
- rocm: 5.4.3
Metrics - Model size (GB)
- Model parameter size. When the models are preloaded to GPU DDR, the actual DDR size consumption is larger than model itself due to caching for Input and output token spaces.
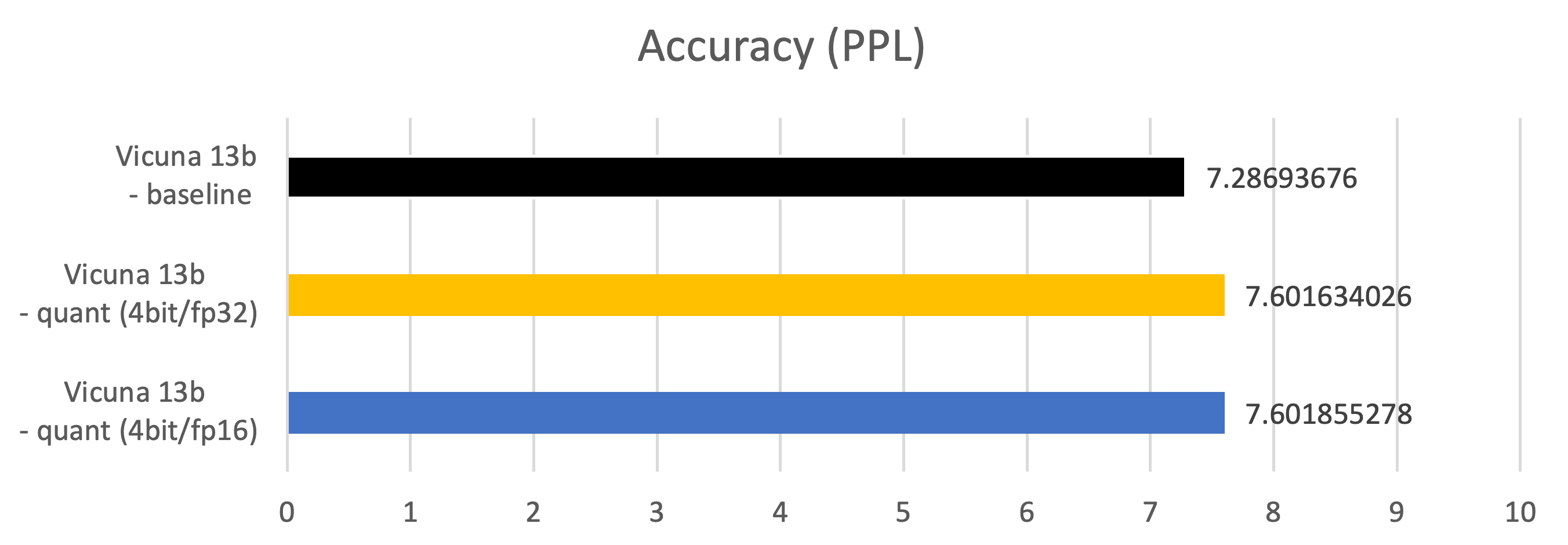
Metrics – Accuracy (PPL: Perplexity)
-
Measured on 2048 examples of C4 (https://paperswithcode.com/dataset/c4) dataset
-
Vicuna 13b – baseline: fp16 datatype parameter, fp16 Matmul
-
Vicuna 13b – quant (4bit/fp32): 4bits datatype parameter, fp32 Matmul
-
Vicuna 13b – quant (4bit/fp16): 4bits datatype parameter, fp16 Matmul
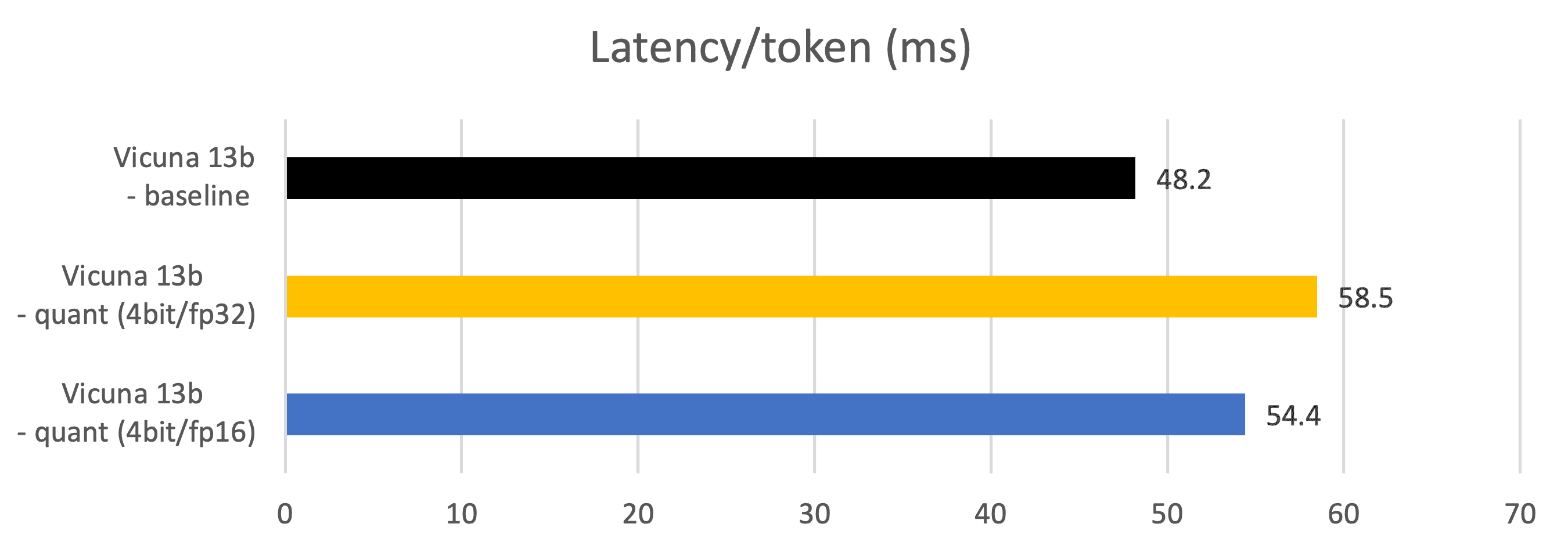
Metrics – Latency (Token generation latency, ms)
-
Measured during token generation phases.
-
Vicuna 13b – baseline: fp16 datatype parameter, fp16 Matmul
-
Vicuna 13b – quant (4bit/fp32): 4bits datatype parameter, fp32 Matmul
-
Vicuna 13b – quant (4bit/fp16): 4bits datatype parameter, fp16 Matmul
Large language models (LLMs) have made significant advancements in chatbot systems, as seen in OpenAI’s ChatGPT. Vicuna-13B, an open-source LLM model has been developed and demonstrated excellent capability and quality.
By following this guide, you should now have a better understanding of how to set up and run the Vicuna 13B model on an AMD GPU with ROCm. This will enable you to unlock the full potential of this cutting-edge language model for your research and personal projects.
Thanks for reading!
Building Vicuna quantized model from the floating-point LLaMA model
a. Download LLaMA and Vicuna delta models from Huggingface
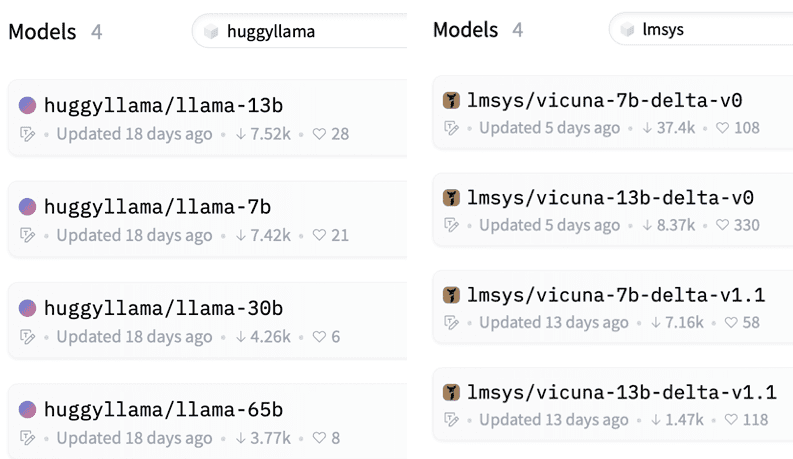
The developers of Vicuna (lmsys) provide only delta-models that can be applied to the LLaMA model. Download LLaMA in huggingface format and Vicuna delta parameters from Huggingface individually. Currently, 7b and 13b delta models of Vicuna are available.
https://huggingface.co/models?sort=downloads&search=huggyllama
https://huggingface.co/models?sort=downloads&search=lmsys
b. Convert LLaMA to Vicuna by using Vicuna-delta model
git clone https://github.com/lm-sys/FastChat
cd FastChat
Convert the LLaMA parameters by using this command:
(Note: do not use vicuna-{7b, 13b}-*delta-v0 because it’s vocab_size is different from that of LLaMA and the model cannot be converted)
python -m fastchat.model.apply_delta --base /path/to/llama-13b --delta lmsys/vicuna-13b-delta-v1.1 \
--target ./vicuna-13b
Now Vicuna-13b model is ready.
c. Quantize Vicuna to 2/3/4 bits
To apply the GPTQ to LLaMA and Vicuna,
git clone https://github.com/oobabooga/GPTQ-for-LLaMa -b cuda
cd GPTQ-for-LLaMa
(Note, do not use https://github.com/qwopqwop200/GPTQ-for-LLaMa for now. Because 2,3,4bit quantization + MatMul kernels implemented in this repo does not parallelize the dequant+matmul and hence shows lower token generation performance)
Quantize Vicuna-13b model with this command. QAT is done based on c4 data-set but you can also use other data-sets, such as wikitext2
(Note. Change group size with different combinations as long as the model accuracy increases significantly. Under some combination of wbit and groupsize, model accuracy can be increased significantly.)
python llama.py ./Vicuna-13b c4 --wbits 4 --true-sequential --act-order \
--save_safetensors Vicuna-13b-4bit-act-order.safetensors
Now the model is ready and saved as Vicuna-13b-4bit-act-order.safetensors.
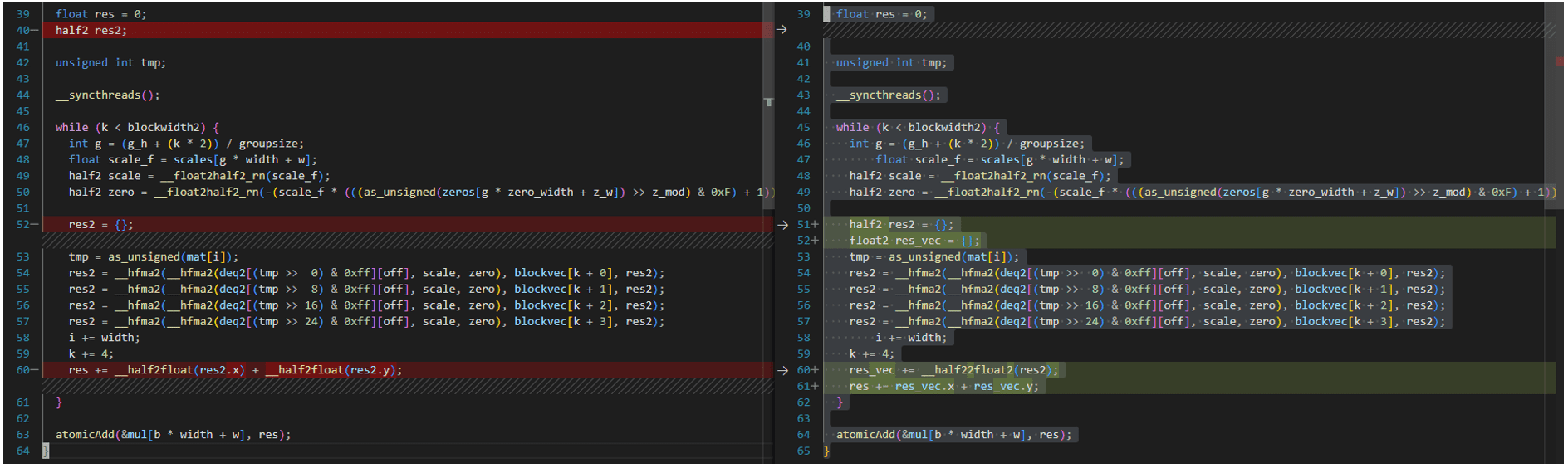
GPTQ Dequantization + FP16 Mamul kernel for AMD GPUs
The more optimized kernel implementation in https://github.com/oobabooga/GPTQ-for-LLaMa/blob/57a26292ed583528d9941e79915824c5af012279/quant_cuda_kernel.cu#L891
targets at A100 GPU and not compatible with ROCM5.4.3 HIPIFY toolkits. It needs to be modified as follows. The same for VecQuant2MatMulKernelFaster, VecQuant3MatMulKernelFaster, VecQuant4MatMulKernelFaster kernels.
For convenience, All the modified codes are available in Github Gist.