- Go to the Notebook folder of this repo.
- Upload the Bi_LSTM.ipynb notebook on the Google Colab notebooks (https://colab.research.google.com/)
- (Optional) We recommend changing the runtime type to utilize a TPU or GPU Hardware accelerator (if available). This step will substantially decrease the training time of the model.
- Just execute the notebook's cells serially. The notebook fetches the data directly from this repo with a URL link.
If you find the repo useful, please consider citing the following publications/datasets produced by this work:.
- ML-based Traffic Steering for Heterogeneous Ultra-dense beyond-5G Networks (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10118923)
- Which ML Model to Choose? Experimental Evaluation for a Beyond-5G Traffic Steering Case (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10279485)
- The data are published in the IEEE Dataport: https://ieee-dataport.org/documents/ue-statistics-time-series-cqi-lte-networks#
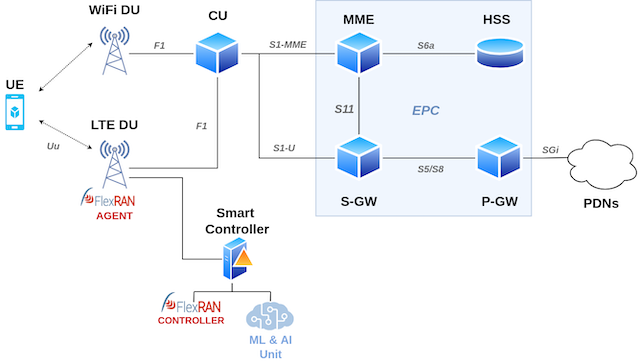
This repo contains the data and code that are used to develop intelligent smart steering in heterogeneous ultra-dense beyond-5G networks. We use the following network topology:
It is a 5G disaggregated network supporting heterogeneous wireless connection to a single UE (multi-homed UE). It is based on the 3GPP Option-2 split of the Radio Access Network (RAN) disaggregating the latter into one Central Unit (CU) and multiple Distributed Units (DUs). 3GPP (LTE) and Non-3GPP (WIFI) DUs are exploited to enforce the heterogeneous UE connection, being guided by the CU. The CU and DU units are connected over an ethernet-based fronthaul exchanging traffic through the F1 interface employing the F1 Application Protocol (F1AP). As core and RAN, we use the LTE versions of the OpenAirInterface (OAI). We rely on the FlexRAN slicing communication between the Controller and the Agent to develop a dynamic DU steering mechanism that optimally steers the downlink traffic via the DUs. Therefore, we construct a smart controller by inserting an AI unit at the side of the FlexRAN Controller.
This unit predicts the LTE link’s quality and then optimally steers the traffic to ensure the best end-user Quality of Experience (QoE). The unit analyzes the Channel Quality Indicator (CQI); a metric posted by the UEs to the base station (BS). It is linked with the allocation of the UE’s modulation and coding schemes and ranges from 0 to 15 in values. This is from no to 64 QAM modulation, from zero to 0.93 code rate, from zero to 5.6 bits per symbol, from less than 1.25 to 20.31 SINR (dB) and from zero to 3840 Transport Block Size bits.
For the forecasting, we implement a Bidirectional Long short-term Memory (Bi-LSTM) Neural Network (NN) to forecast the CQI values and infer on the quality of the LTE link.
-
Data Folder: In this foler, we have the CQI data collected from real cars in a route in city Volos, Greece. There are two files, the train.csv which contains CQI data from 73 cars and used as training data. The other file is the test.txt which contains the CQI data from the experiment in our experimental environment, as described in the paper.
-
Figures Folder: In this folder, we have several important figures that are used by the notebook.
-
Notebook Folder: In this folder, we have the notebook that includes part of the utilized machine learning pipeline used to develop the Bi-LSTM model in the paper. It is a reproducable notebook that is easily executed in Google Colab or locally. In the notebook, you can find useful functions and information on the pre-processing, deep learning model development, evaluation and extra stuff.
-
utils.py file: This file includes the functions developed in the notebook for easier usage.