Using Module Federation to federate Wasm modules across independent applications. In this demo, we will use Conways Game of Life to illustrate how Wasm can be shared.
- Make sure you have node.js installed locally
- From the root of the project run:
yarn && pnpm run start.
This will start the Host and Remote applications in dev mode.
- The
Hostapp is hosted on port8080 - The
Remoteapp is hosted on port8081
Navigate to your browser and open the Host app running on http://localhost:8080. You should see a few buttons. Click the "Play" button to start the app. Click the "Stop" button (same button) to pause the execution. Press the "Tick" button to step through the execution frame-by-frame, and lastly click the "Reset" button to reset the app.
To run tests in interactive mode, run npm run cypress:debug from the root directory of the project. It will open Cypress Test Runner and allow to run tests in interactive mode. More info about "How to run tests"
To build app and run test in headless mode, run yarn e2e:ci. It will build app and run tests for this workspace in headless mode. If tets failed cypress will create cypress directory in sample root folder with screenshots and videos.
"Best Practices, Rules amd more interesting information here
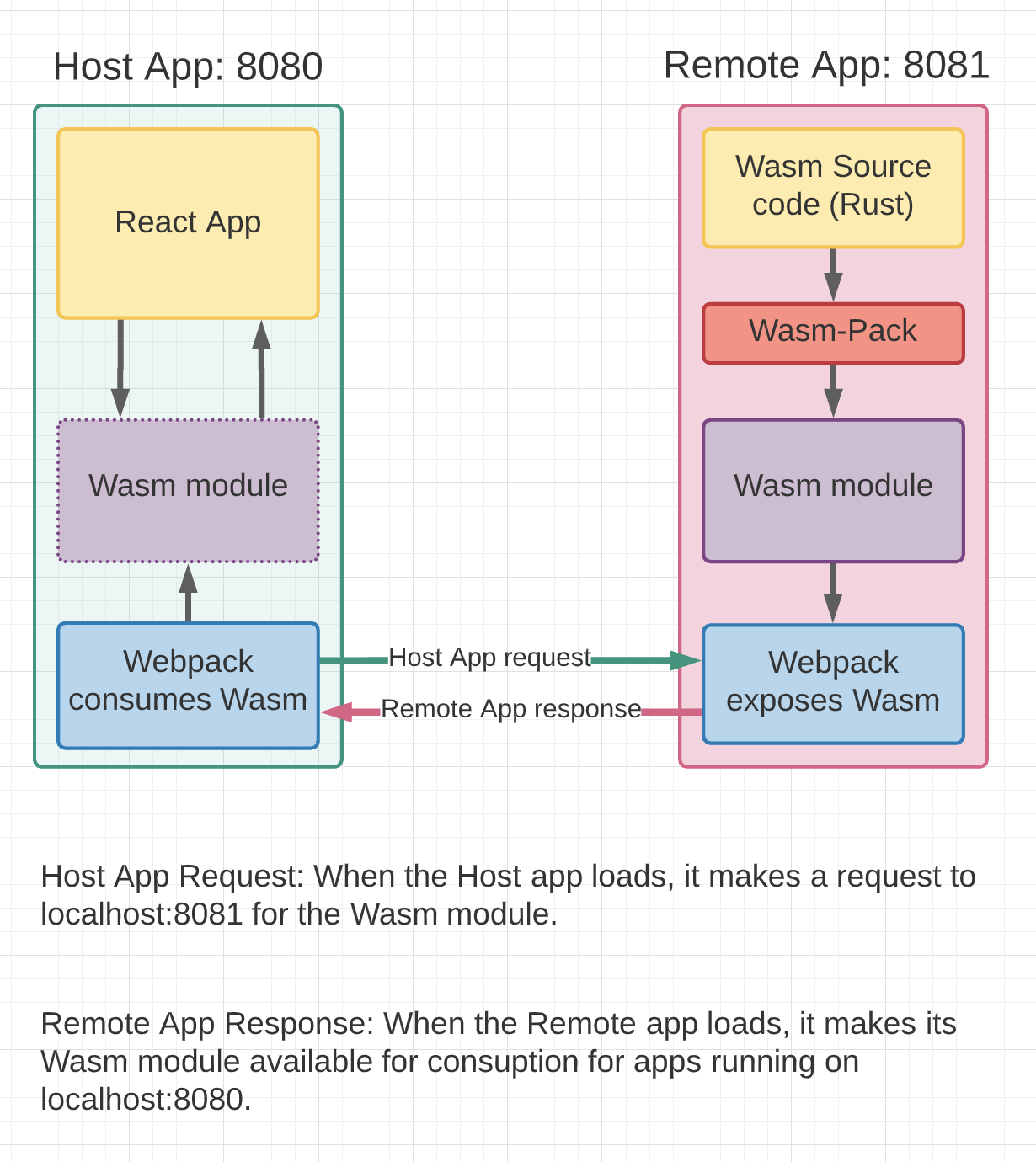
Webpack's Module Federation Plugin powers the sharing of the Wasm module between our two apps at runtime. Below is a low-fidelity diagram illustrating how webpack is used to share code.
💡 For more on Module federation, see the docs and checkout this write-up.
As seen in the diagram above, the Host application imports a Wasm module from the Remote application. Under the hood, this import happens in an async boundary, which is created by webpack and wraps around the react app, giving webpack the opportunity to make an async HTTP call for the Wasm module.
The Wasm module on the left (purple) has a dotted line to represent that the Wasm code does not exist in the Host app until it is federated in at runtime.
Let's see how this is implemented in our webpack configs.
Host configs: packages/host/webpack.config.js
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: "Host",
remotes: {
GameOfLifeModule: `GameOfLifeModule@http://localhost:8081/remoteEntry.js`,
},
}),Remote configs: packages/remote/webpack.config.js
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: "GameOfLifeModule",
filename: "remoteEntry.js",
exposes: {
"./GameOfLifeModule": "./pkg/",
},
}),The Remote app uses Webpack Module Federation to expose the Wasm module for consumption by the Host app. As pictured in the code snipet above, the ./pkg code will be made available through the http://localhost:8081/remoteEntry.js file.
The GameOfLife Wasm module, pictured above as GameOfLifeModule, contains the logic for Conways Game of Life. The source code for this particular implementation was borrowed from The Offical Rust Wasm Docs.
The consumption and usage of our Wasm module can be found in the packages/host/app.jsx file on lines 2 and 12.
On line 2 we are importing the federated Wasm module:
import * as GameOfLife from "GameOfLifeModule/GameOfLifeModule";and on line 12 we are consuming the module:
GameOfLife.then(({ Universe }) => {
if (!cells) {
setCells(Universe.new());
}
});In the example above, the Wasm Module exports a class Universe which we use to initialize a new Game Of Life. We then set the instance of the new Universe in a slice of react state on the same line, and reference the Universe as cells throughout the rest of the component. This allows us to use react to control a Wasm module that is being federated into react from a completely stand-alonle remote app.
In order to run the Rust->Wasm toolchain, please make sure you have the project dependencies in the next section installed.
Once those are installed, go to packages/remote/webpack.config.js and uncomment the code that has been commented out.
you can start developing on the Remote app or the Host app with pnpm run start.
💡 For local development of Host app, make sure that the Remote app is also running so that the import of the Wasm module does not fail. You can start both apps by running pnpm run start in the top-level dir.
Install Rust
$ curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | shvSource your bash profile after the step above (source $HOME/.cargo/env)
Install wasm-pack
$ curl https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-pack/installer/init.sh -sSf | shThis mini monorepo consists of two packages. Here is a bit more about each.
Consumer of federated Wasm module. Uses React to interact with the federated Wasm module but could also be written in plain JavaScript like the Remote.
Exposes Wasm module. Wasm module is built with Rust, compiled by webpack wasm-pack loader.
This package was bootstrapped with the Rust Webpack Template project. For more, visit their repo as well as the fabulous docs at the Rust Wasm webiste.
This demo is built upon many OSS projects including:
- Rust Webpack Template -> Template Used to bootsrap the
Remoteapp - Webpack Module Federation -> Used to share the Wasm module across apps
- The Offical Rust Wasm Docs -> Provided starter Game Of Life Code
- wasm-pack -> Webpack loader for compiling Rust to Wasm
To run tests in interactive mode, run npm run cypress:debug from the root directory of the project. It will open Cypress Test Runner and allow to run tests in interactive mode. More info about "How to run tests"
To build app and run test in headless mode, run yarn e2e:ci. It will build app and run tests for this workspace in headless mode. If tets failed cypress will create cypress directory in sample root folder with screenshots and videos.
"Best Practices, Rules amd more interesting information here