- Rolling Updates
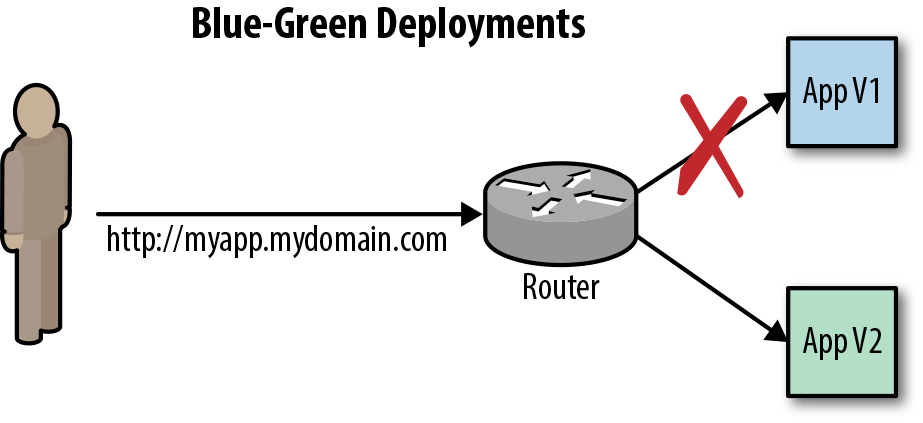
- Blue/Green Deployments
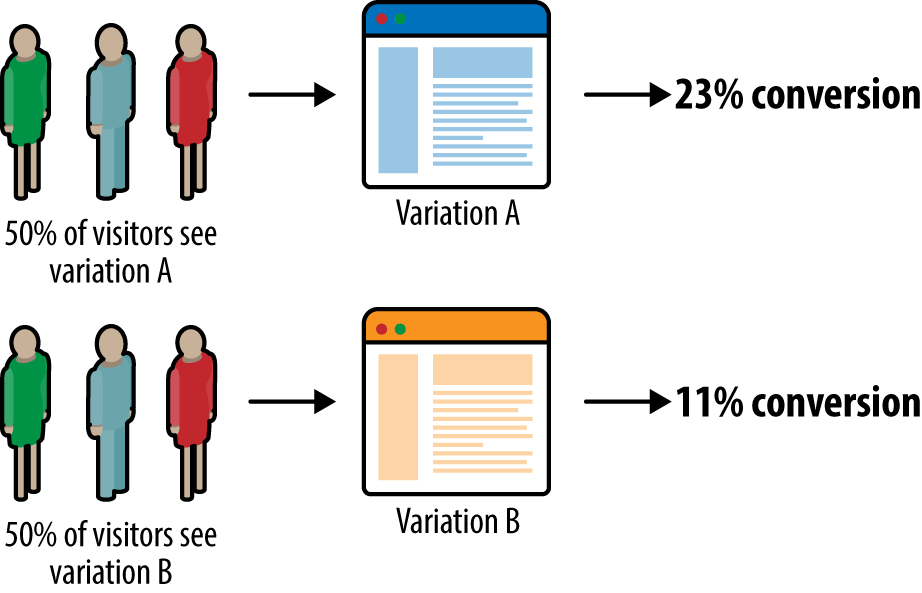
- A/B Deployments This will display the pod hostname which is servicing the web request
This is a fork of the below github repository https://github.com/openshift/django-ex.git
$ oc new-project demoproject --display-name="Demo Project" --description="Project for demo purpose"
$ oc project demoproject
$ oc new-app python:3.6~https://github.com/dineshsadasivam/demoapp --name=demoapp
$ oc expose svc demoapp --name=demoapp
$ oc get pods -o wide -l app=demoapp
Change the route loadbalacing algorith from the default Source IP to roundrobin and disable cookies for testing.
This will enabled testing of application loadbalacing from single workstation.
$ oc annotate route/demoapp haproxy.router.openshift.io/balance=roundrobin
$ oc annotate route/demoapp haproxy.router.openshift.io/disable_cookies=true
$ while true ; do curl http://demoapp-demoproject.router.default.svc.cluster.local 2>/dev/null |grep Hello ; done
Modify the application (https://github.com/dineshsadasivam/demoapp/tree/master/templates/hello.html) and trigger a new build for rolling update
$ oc start-build demoapp
$ oc rollback demoapp
The blue-green deployment strategy minimizes the time it takes to perform a deployment cutover by ensuring you have two versions of your application stacks available during the deployment. We can make use of the service and routing tiers to easily switch between the two running application stacks, hence it is very simple and fast to perform a rollback.
A/B deployments get their name from the ability to test the new application features as part of the deployment. This way you can create a hypothesis, perform an A/B deployment, test whether your hypothesis is true or false, and either roll back to your initial application state (A) or proceed with your new application state (B).