Query a count of the number of cities in CITY having a Population larger than 100 000.
Input Format
The CITY table is described as follows:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM city WHERE population > 100000;
Query the total population of all cities in CITY where District is California.
SELECT SUM(population) FROM city WHERE district = 'California';
Query the average population of all cities in CITY where District is California.
SELECT AVG(population) FROM city WHERE district = 'California';
Query the average population for all cities in CITY, rounded down to the nearest integer.
SELECT ROUND(AVG(population)) FROM city;
Query the sum of the populations for all Japanese cities in CITY. The COUNTRYCODE for Japan is JPN.
SELECT SUM(population) FROM city WHERE countrycode = 'JPN';
Query the difference between the maximum and minimum populations in CITY.
SELECT (MAX(population) - MIN(population)) FROM city;
Samantha was tasked with calculating the average monthly salaries for all employees in the EMPLOYEES table, but did not realize her keyboard's 0 key was broken until after completing the calculation. She wants your help finding the difference between her miscalculation (using salaries with any zeroes removed), and the actual average salary.
Write a query calculating the amount of error (i.e.: actual - miscalculated average monthly salaries), and round it up to the next integer.
Input Format
The EMPLOYEES table is described as follows:
Note: Salary is measured in dollars per month and its value is < 10^5.
SELECT CEIL(AVG(salary) - AVG(REPLACE(salary, '0', ''))) FROM employees;
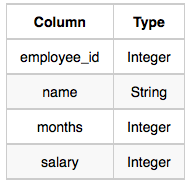
We define an employee's total earnings to be their monthly salary*months worked, and the maximum total earnings to be the maximum total earnings for any employee in the Employee table. Write a query to find the maximum total earnings for all employees as well as the total number of employees who have maximum total earnings. Then print these values as 2-space-separated integers.
Input Format
The Employee table containing employee data for a company is described as follows:
where employee_id is an employee's ID number, name is their name, months is the total number of months they've been working for the company, and salary is the their monthly salary.
SELECT * FROM (SELECT months*salary, COUNT(*) FROM employee GROUP BY months*salary ORDER BY months*salary DESC) WHERE ROWNUM = 1;
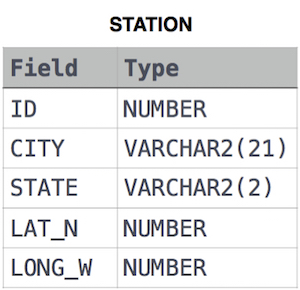
Query the following two values from the STATION table:
The sum of all values in LAT_N rounded to a scale of 2 decimal places.
The sum of all values in LONG_W rounded to a scale of 2 decimal places.
Input Format
The STATION table is described as follows:
where LAT_N is the northern latitude and LONG_W is the western longitude.
SELECT (ROUND(SUM(lat_n), 2) || ' ' || ROUND(SUM(long_w), 2)) FROM station;
Query the sum of Northern Latitudes (LAT_N) from STATION having values greater than 38.7880 and less than 137.2345. Truncate your answer to 4 decimal places.
SELECT ROUND(SUM(lat_n), 4) FROM station WHERE lat_n > 38.7880 AND lat_n < 137.2345;
Query the greatest value of the Northern Latitudes (LAT_N) from STATION that is less than 137.2345. Truncate your answer to 4 decimal places.
SELECT ROUND(MAX(lat_n), 4) FROM station WHERE lat_n < 137.2345;
Query the Western Longitude (LONG_W) for the largest Northern Latitude (LAT_N) in STATION that is less than 137.2345. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.
SELECT ROUND(long_w, 4) FROM station WHERE lat_n = (SELECT MAX(lat_n) FROM station WHERE lat_n < 137.2345);
Query the smallest Northern Latitude (LAT_N) from STATION that is greater than 38.7780. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.
SELECT ROUND(MIN(lat_n), 4) FROM station WHERE lat_n > 38.7780;
Query the Western Longitude (LONG_W)where the smallest Northern Latitude (LAT_N) in STATION is greater than 38.7780. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.
SELECT ROUND(long_w, 4) FROM station WHERE lat_n = (SELECT MIN(lat_n) FROM station WHERE lat_n > 38.7780);
Consider P1(a,b) and P2(c,d) to be two points on a 2D plane.
a happens to equal the minimum value in Northern Latitude (LAT_N in STATION).
b happens to equal the minimum value in Western Longitude (LONG_W in STATION).
c happens to equal the maximum value in Northern Latitude (LAT_N in STATION).
d happens to equal the maximum value in Western Longitude (LONG_W in STATION).
Query the Manhattan Distance between points P1 and P2 and round it to a scale of 4 decimal places.
SELECT ROUND(ABS(a - c) + ABS(b - d), 4) FROM (
SELECT MIN(lat_n) AS a, MIN(long_w) AS b, MAX(lat_n) AS c, MAX(long_w) AS d FROM station);
Consider P1(a,c) and P2(b,d) to be two points on a 2D plane.
(a,b) - the respective minimum and maximum values of Northern Latitude (LAT_N)
(c,d) - the respective minimum and maximum values of Western Longitude (LONG_W) in STATION.
Query the Euclidean Distance between points P1 and P2 and format your answer to display 4 decimal digits.
SELECT ROUND (SQRT((a - b) * (a - b) + (c - d) * (c - d)), 4) FROM (
SELECT MIN(lat_n) AS a, MAX(lat_n) AS b, MIN(long_w) AS c, MAX(long_w) AS d FROM station);