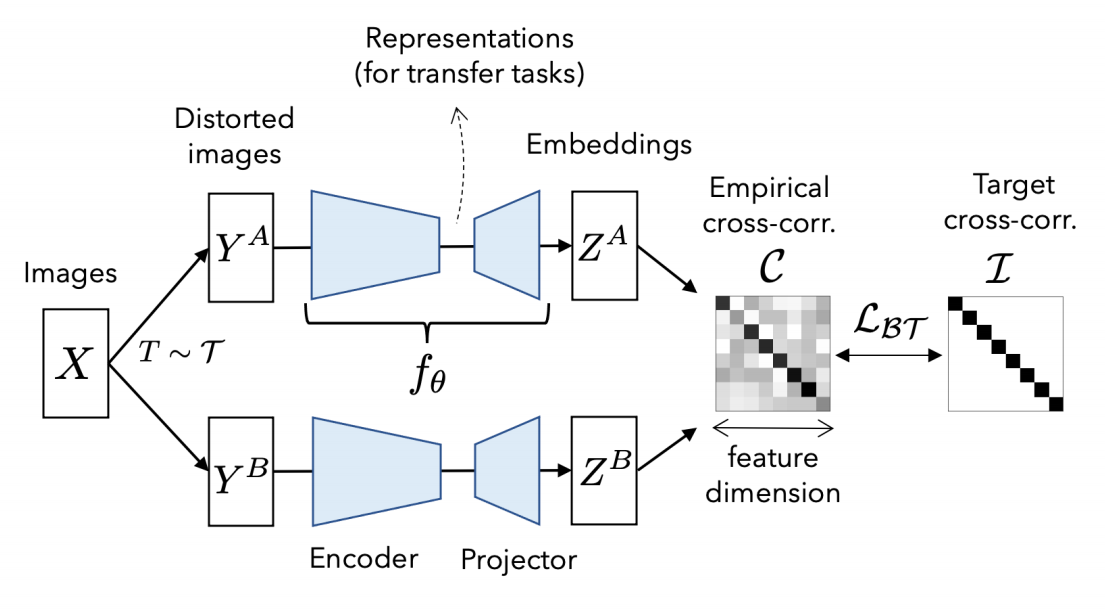
Barlow Twins: Self-Supervised Learning via Redundancy Reduction
Self-supervised learning (SSL) is rapidly closing the gap with supervised methods on large computer vision benchmarks. A successful approach to SSL is to learn embeddings which are invariant to distortions of the input sample. However, a recurring issue with this approach is the existence of trivial constant solutions. Most current methods avoid such solutions by careful implementation details. We propose an objective function that naturally avoids collapse by measuring the cross-correlation matrix between the outputs of two identical networks fed with distorted versions of a sample, and making it as close to the identity matrix as possible. This causes the embedding vectors of distorted versions of a sample to be similar, while minimizing the redundancy between the components of these vectors. The method is called Barlow Twins, owing to neuroscientist H. Barlow's redundancy-reduction principle applied to a pair of identical networks. Barlow Twins does not require large batches nor asymmetry between the network twins such as a predictor network, gradient stopping, or a moving average on the weight updates. Intriguingly it benefits from very high-dimensional output vectors. Barlow Twins outperforms previous methods on ImageNet for semi-supervised classification in the low-data regime, and is on par with current state of the art for ImageNet classification with a linear classifier head, and for transfer tasks of classification and object detection.
Predict image
from mmpretrain import inference_model
predict = inference_model('resnet50_barlowtwins-pre_8xb32-linear-coslr-100e_in1k', 'demo/bird.JPEG')
print(predict['pred_class'])
print(predict['pred_score'])Use the model
import torch
from mmpretrain import get_model
model = get_model('barlowtwins_resnet50_8xb256-coslr-300e_in1k', pretrained=True)
inputs = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
out = model(inputs)
print(type(out))
# To extract features.
feats = model.extract_feat(inputs)
print(type(feats))Train/Test Command
Prepare your dataset according to the docs.
Train:
python tools/train.py configs/barlowtwins/barlowtwins_resnet50_8xb256-coslr-300e_in1k.pyTest:
python tools/test.py configs/barlowtwins/benchmarks/resnet50_8xb32-linear-coslr-100e_in1k.py https://download.openmmlab.com/mmselfsup/1.x/barlowtwins/barlowtwins_resnet50_8xb256-coslr-300e_in1k/resnet50_linear-8xb32-coslr-100e_in1k/resnet50_linear-8xb32-coslr-100e_in1k_20220825-52fde35f.pth| Model | Params (M) | Flops (G) | Config | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|
barlowtwins_resnet50_8xb256-coslr-300e_in1k |
174.54 | 4.11 | config | model | log |
| Model | Pretrain | Params (M) | Flops (G) | Top-1 (%) | Config | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
resnet50_barlowtwins-pre_8xb32-linear-coslr-100e_in1k |
BARLOWTWINS | 25.56 | 4.11 | 71.80 | config | model | log |
@inproceedings{zbontar2021barlow,
title={Barlow twins: Self-supervised learning via redundancy reduction},
author={Zbontar, Jure and Jing, Li and Misra, Ishan and LeCun, Yann and Deny, St{\'e}phane},
booktitle={International Conference on Machine Learning},
year={2021},
}