### Code Examples
- Basic Sorting Algorithms
- Advanced Sorting Algorithms - Quick Sort
- Advanced Sorting Algorithms - Merge Sort
- Module
- Implentation
- Import Module
Sorting is the most heavily studied concept in Computer Science. A sorting algorithm takes a list of items and sorts them in a particular order, most commonly alphabetically or numerical. Though every major programming language has built-in sorting libraries, it comes in handy if you know how they work. Depending upon requirement you may want to use any of these.
Bubble Sort
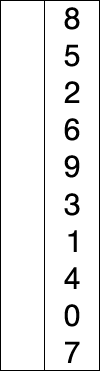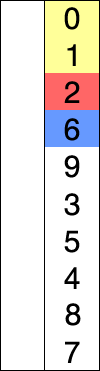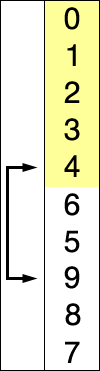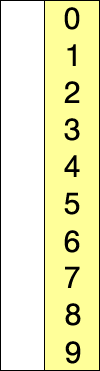
The bubble sort is one of the slowest sorting algorithms, but it is also one of the easiest sorts to implement.
Selection Sort
This sort works by starting at the beginning of the array and comparing the first element with the remaining elements. After examining all the elements, the smallest element is placed in the first position of the array, and the algorithm moves to the second position. This process continues until the data is sorted.
Insertion Sort
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that builds the final sorted array (or list) one item at a time. It is much less efficient on large lists than more advanced algorithms such as quicksort, heapsort, or merge sort. However, insertion sort provides several advantages.
Quick Sort
The Quicksort algorithm is one of the fastest sorting algorithms for large data sets. Quicksort is a divide-and-conquer algorithm that recursively breaks a list of data into successively smaller sublists consisting of the smaller elements and the larger elements. The algorithm continues this process until all the data in the list is sorted. The algorithm divides the list into sublists by selecting one element of the list as a pivot. Data is sorted around the pivot by moving elements less than the pivot to the bottom of the list and elements that are greater than the pivot to the top of the list.
Merge Sort
MergeSort is a Divide and Conquer algorithm. It divides input array in two halves, calls itself for the two halves and then merges the two sorted halves. The merge() function is used for merging two halves. The merge(arr, l, m, r) is key process that assumes that arr[l..m] and arr[m+1..r] are sorted and merges the two sorted sub-arrays into one.
Bucket and Heap sort makes use of insertion sort function help, to sort the elements. But this methods are usefull and import anyway.
In addition to the time and space complexity of sorting algorithms, the below properties help define sorting algorithms.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Adaptability | An adaptive sort’s performance improves the more sorted the list is initially. |
| In-place | An in-place sort requires a constant amount of additional space. |
| Parallelism | A parallel sort can split its workload between multiple workers. |
| Stability | A stable sort preserves the order of items in the list that evaluate to the same value. |
More importantly one should know when and where to use them. Some examples where you can find direct application of sorting techniques include:
Sorting by price, popularity etc in e-commerce websites
- Images from wikipedia
- More information about Sorting Algorithms