diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 32303b4a..b2b018c9 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
TensorHive
===
-
-
+
+



@@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ tensorhive test
```
(optional) If you want to allow your UNIX users to set up their TensorHive accounts on their own and run distributed
-programs through `Task nursery` plugin, use the `key` command to generate the SSH key for TensorHive:
+programs through `Task execution` plugin, use the `key` command to generate the SSH key for TensorHive:
```
tensorhive key
```
@@ -135,15 +135,22 @@ Terminal warning | Email warning
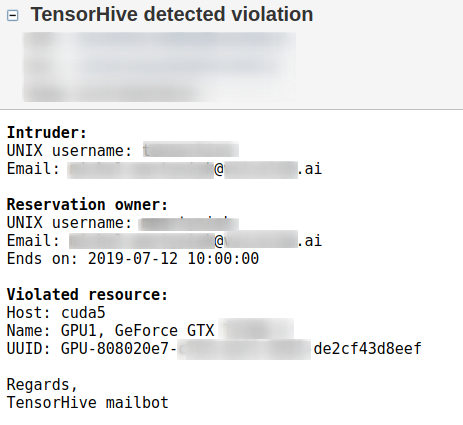
-#### Task nursery
+#### Task execution
-Here you can define commands for tasks you want to run on any configured nodes. You can manage them manually or set spawn/terminate date.
+Thanks to the `Task execution` module, you can define commands for tasks you want to run on any configured nodes.
+You can manage them manually or set spawn/terminate date.
Commands are run within `screen` session, so attaching to it while they are running is a piece of cake.
-
-It provides quite simple, but flexible (**framework-agnostic**) command templating mechanism that will help you automate multi-node trainings.
+It provides a simple, but flexible (**framework-agnostic**) command templating mechanism that will help you automate multi-node trainings.
+Additionally, specialized templates help to conveniently set proper parameters for chosen well known frameworks:
+
+
+
+In the [examples](https://github.com/roscisz/TensorHive/tree/master/examples)
+directory, you will find sample scenarios of using the `Task execution` module for various
+frameworks and computing environments.
+
TensorHive requires that users who want to use this feature must append TensorHive's public key to their `~/.ssh/authorized_keys` on all nodes they want to connect to.
-
Features
----------------------
@@ -156,7 +163,7 @@ Features
- [x] :warning: Send warning messages to terminal of users who violate the rules
- [x] :mailbox_with_no_mail: Send e-mail warnings
- [ ] :bomb: Kill unwanted processes
-- [X] :rocket: Task nursery and scheduling
+- [X] :rocket: Task execution and scheduling
- [x] :old_key: Execute any command in the name of a user
- [x] :alarm_clock: Schedule spawn and termination
- [x] :repeat: Synchronize process status
@@ -178,7 +185,7 @@ Features
- [x] Edit reservations
- [x] Cancel reservations
- [x] Attach jobs to reservation
-- [x] :baby_symbol: Task nursery
+- [x] :baby_symbol: Task execution
- [x] Create parametrized tasks and assign to hosts, automatically set `CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES`
- [x] Buttons for task spawning/scheduling/termination/killing actions
- [x] Fetch log produced by running task
@@ -204,16 +211,11 @@ TensorHive is currently being used in production in the following environments:
| Organization | Hardware | No. users |
| ------ | -------- | --------- |
-|  [Gdansk University of Technology](https://eti.pg.edu.pl/en) | NVIDIA DGX Station (4x Tesla V100 16GB | 30+ |
-|  [Lab at GUT](https://eti.pg.edu.pl/katedra-architektury-systemow-komputerowych/main) | 18x machines with GTX 1060 6GB | 20+ |
-| [Gradient PG](http://gradient.eti.pg.gda.pl/en/) | TITAN X 12GB | 10+ |
-|  [VoiceLab - Conversational Intelligence](https://www.voicelab.ai) | 30+ GTX and RTX cards | 10+
-
-Application examples and benchmarks
---------
-Along with TensorHive, we are developing a set of [**sample deep neural network training applications**](https://github.com/roscisz/TensorHive/tree/master/examples) in Distributed TensorFlow which will be used as test applications for the system. They can also serve as benchmarks for single GPU, distributed multi-GPU and distributed multi-node architectures. For each example, a full set of instructions to reproduce is provided.
+|  [Gdansk University of Technology](https://eti.pg.edu.pl/en) | NVIDIA DGX Station (4x Tesla V100) + NVIDIA DGX-1 (8x Tesla V100) | 30+ |
+|  [Lab at GUT](https://eti.pg.edu.pl/katedra-architektury-systemow-komputerowych/main) | 20 machines with GTX 1060 each | 20+ |
+|  [Gradient PG](http://gradient.eti.pg.gda.pl/en/) | A server with two GPUs shared by the Gradient science club at GUT. | 30+ |
+|  [VoiceLab - Conversational Intelligence](https://www.voicelab.ai) | 30+ GTX and RTX GPUs | 10+
-
[Gradient PG](http://gradient.eti.pg.gda.pl/en/) | A server with two GPUs shared by the Gradient science club at GUT. | 30+ |
+|  [VoiceLab - Conversational Intelligence](https://www.voicelab.ai) | 30+ GTX and RTX GPUs | 10+
-
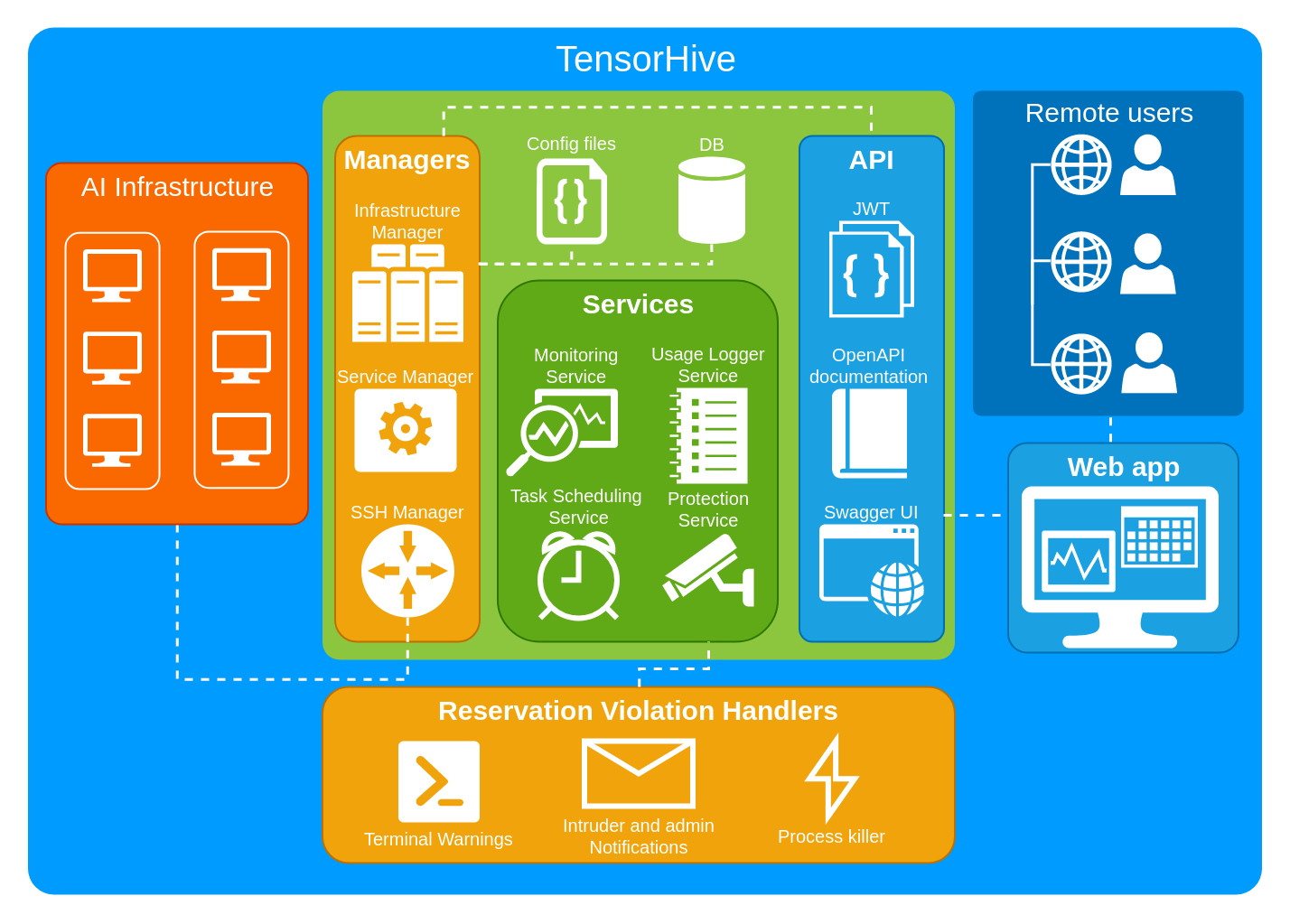
TensorHive architecture (simplified)
-----------------------
@@ -223,13 +225,13 @@ This diagram will help you to grasp the rough concept of the system.
-Contibution and feedback
+Contribution and feedback
------------------------
We'd :heart: to collect your observations, issues and pull requests!
Feel free to **report any configuration problems, we will help you**.
-We are working on user groups for differentiated GPU access control,
+Currently we are working on user groups for differentiated GPU access control,
grouping tasks into jobs and process-killing reservation violation handler,
deadline - July 2020 :shipit:, so stay tuned!
@@ -246,10 +248,10 @@ for parallelization of neural network training using multiple GPUs".
Project created and maintained by:
- Paweł Rościszewski [(@roscisz)](https://github.com/roscisz)
--  [Michał Martyniak (@micmarty)](http://martyniak.me)
+-  [Michał Martyniak (@micmarty)](https://micmarty.github.io)
- Filip Schodowski [(@filschod)](https://github.com/filschod)
- Recent contributions:
+ Top contributors:
- Tomasz Menet [(@tomenet)](https://github.com/tomenet)
- Dariusz Piotrowski [(@PiotrowskiD)](https://github.com/PiotrowskiD)
- Karol Draszawka [(@szarakawka)](https://github.com/szarakawka)
diff --git a/examples/PyTorch/README.md b/examples/PyTorch/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2b216e89
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/PyTorch/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+# Using TensorHive for running distributed trainings in PyTorch
+
+## Detailed example description
+
+In this example we show how the TensorHive `task execution` module can be
+used for convenient configuration and execution of distributed trainings
+implemented in PyTorch. For this purpose, we run
+[this PyTorch DCGAN sample application](https://github.com/roscisz/dnn_training_benchmarks/tree/master/PyTorch_dcgan_lsun/README.md)
+in a distributed setup consisting of a NVIDIA DGX Station server `ai` and NVIDIA DGX-1 server `dl`,
+equipped with 4 and 8 NVIDIA Tesla V100 GPUs respectively.
+
+In the presented scenario, the servers were shared by a group of users using TensorHive
+and at the moment we were granted reservations for GPUs 1 and 2 on `ai` and GPUs 1 and 7 on `dl`.
+The python environment and training code were available on both nodes and
+fake training dataset was used.
+
+
+## Running without TensorHive
+
+In order to enable networking, we had to set the `GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME`
+environment variable to proper network interface names on both nodes.
+We selected the 20011 TCP port for communication.
+
+For our 4 GPU scenario, the following 4 processes had to be executed,
+taking into account setting consecutive `rank` parameters starting from 0 and the `world-size`
+parameter to 4:
+
+worker 0 on `ai`:
+```
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1
+export GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME=enp2s0f1
+./dnn_training_benchmarks/PyTorch_dcgan_lsun/examples/dcgan/venv/bin/python dnn_training_benchmarks/PyTorch_dcgan_lsun/examples/dcgan/main.py --init-method tcp://ai.eti.pg.gda.pl:20011 --backend=gloo --rank=0 --world-size=4 --dataset fake --cuda
+```
+
+worker 1 on `ai`:
+```
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2
+export GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME=enp2s0f1
+./dnn_training_benchmarks/PyTorch_dcgan_lsun/examples/dcgan/venv/bin/python dnn_training_benchmarks/PyTorch_dcgan_lsun/examples/dcgan/main.py --init-method tcp://ai.eti.pg.gda.pl:20011 --backend=gloo --rank=1 --world-size=4 --dataset fake --cuda
+```
+
+worker 2 on `dl`:
+```
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1
+export GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME=enp1s0f0
+./dnn_training_benchmarks/PyTorch_dcgan_lsun/examples/dcgan/venv/bin/python dnn_training_benchmarks/PyTorch_dcgan_lsun/examples/dcgan/main.py --init-method tcp://ai.eti.pg.gda.pl:20011 --backend=gloo --rank=2 --world-size=4 --dataset fake --cuda
+```
+
+worker 3 on ai:
+```
+export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=7
+export GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME=enp1s0f0
+./dnn_training_benchmarks/PyTorch_dcgan_lsun/examples/dcgan/venv/bin/python dnn_training_benchmarks/PyTorch_dcgan_lsun/examples/dcgan/main.py --init-method tcp://ai.eti.pg.gda.pl:20011 --backend=gloo --rank=3 --world-size=4 --dataset fake --cuda
+```
+
+
+## Running with TensorHive
+
+Because running the distributed training required in our scenario means
+logging into multiple nodes, configuring environments and running processes
+with multiple, similar parameters, differing only slightly, it is a good
+use case for the TensorHive `task execution` module.
+
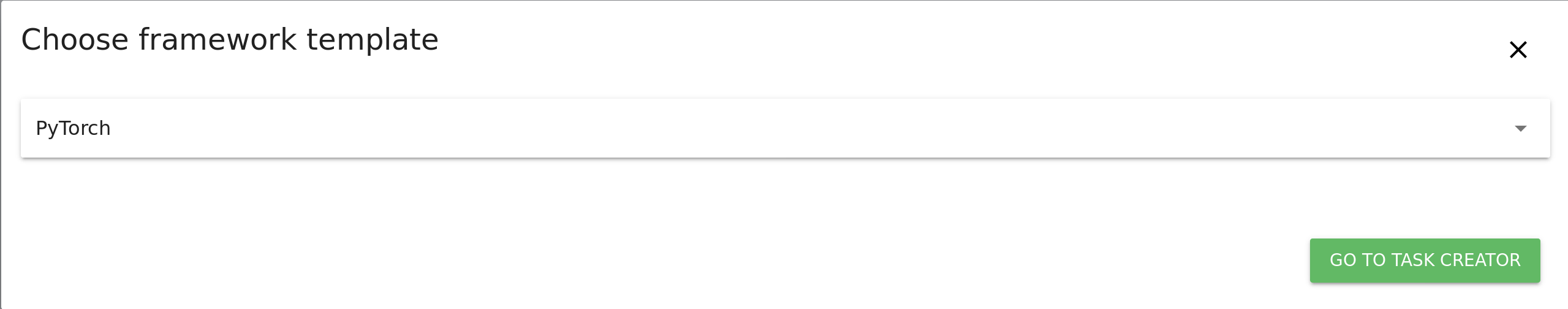
+To use it, first head to `Task Overview` and click on `CREATE TASKS FROM TEMPLATE`. Choose PyTorch from the drop-down list:
+
+
+
+Fill the PyTorch process template with your specific python command, command-line
+parameters and environment variables.
+You don't need to fill in rank or world-size parameters as TensorHive will do that automatically for you:
+
+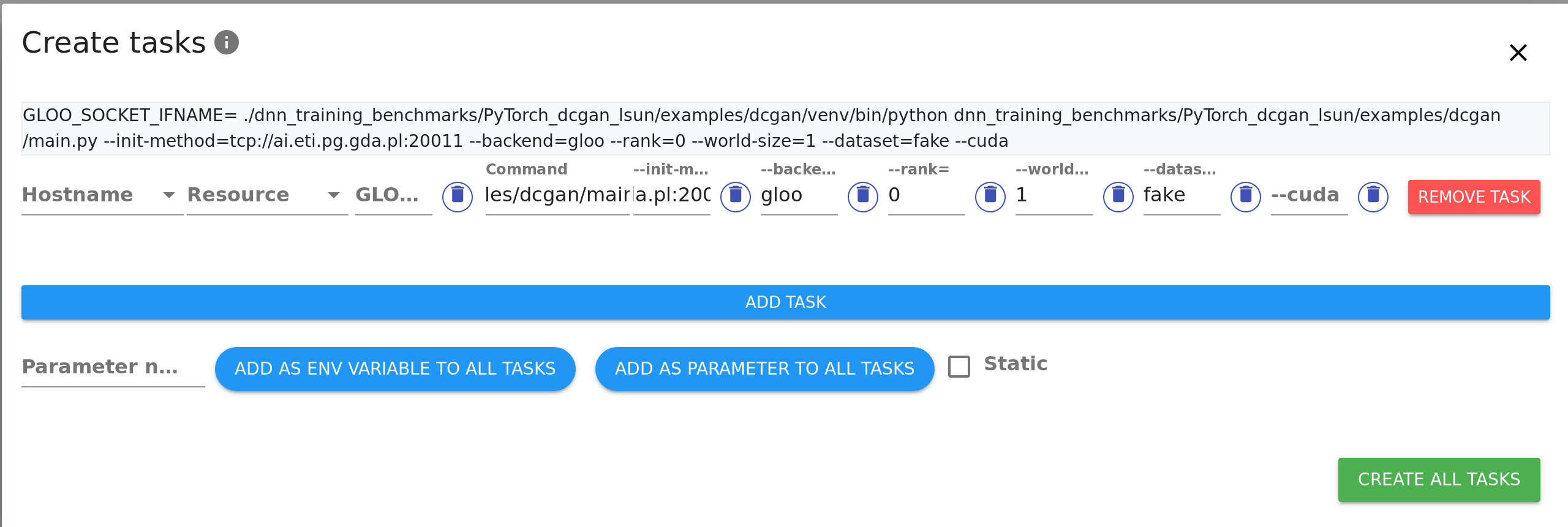
+
+Add as many tasks as resources you wish the code to run on using `ADD TASK` button. You can see that every parameter filled is copied to newly created tasks to save time. Adjust hostnames and resources on the added tasks as needed.
+
+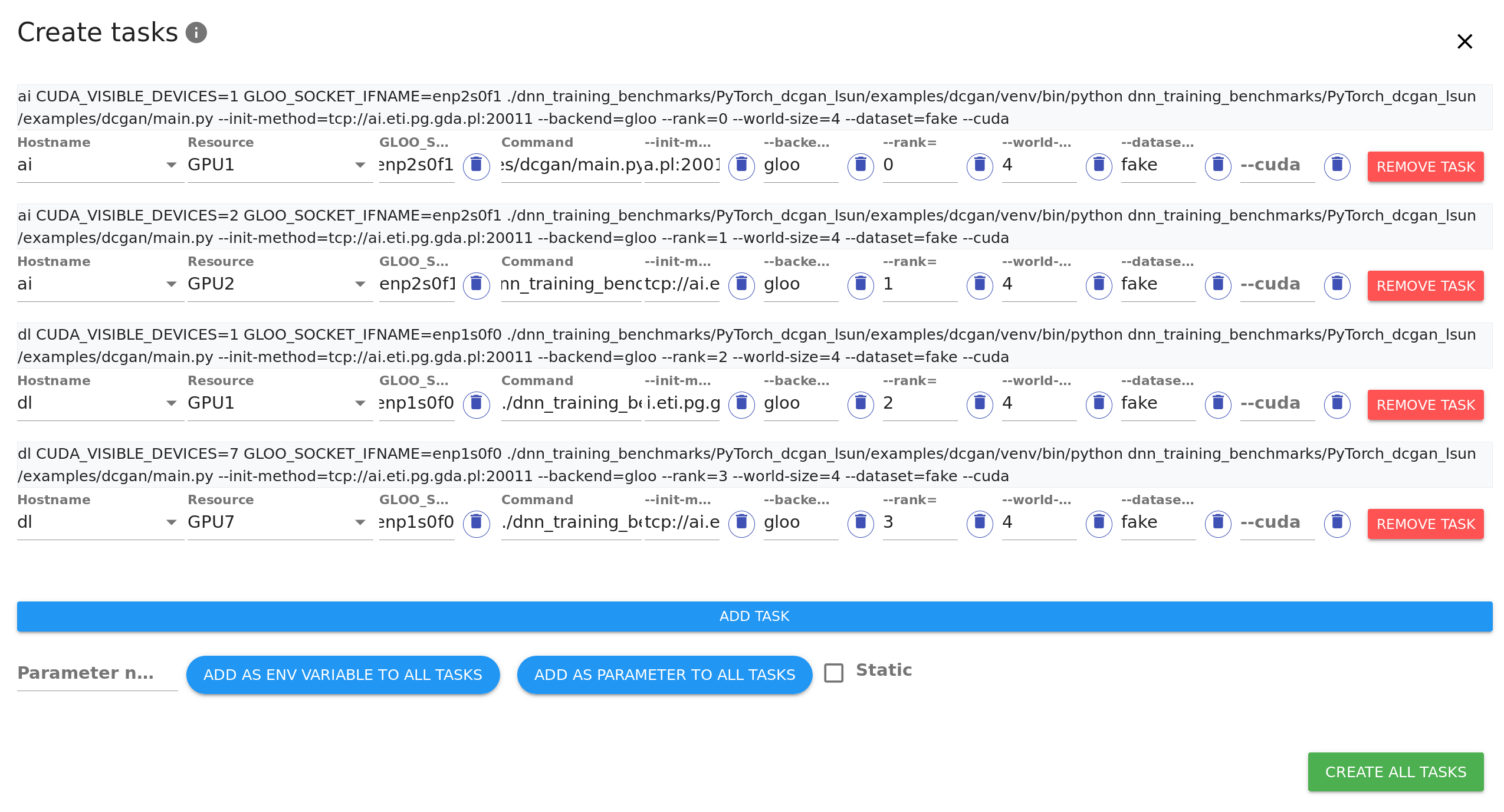
+
+
+Click `CREATE ALL TASKS` button in the right bottom corner to create the tasks.
+Then, select them in the process table and use the `Spawn selected tasks` button,
+to run them on the appropriate nodes:
+
+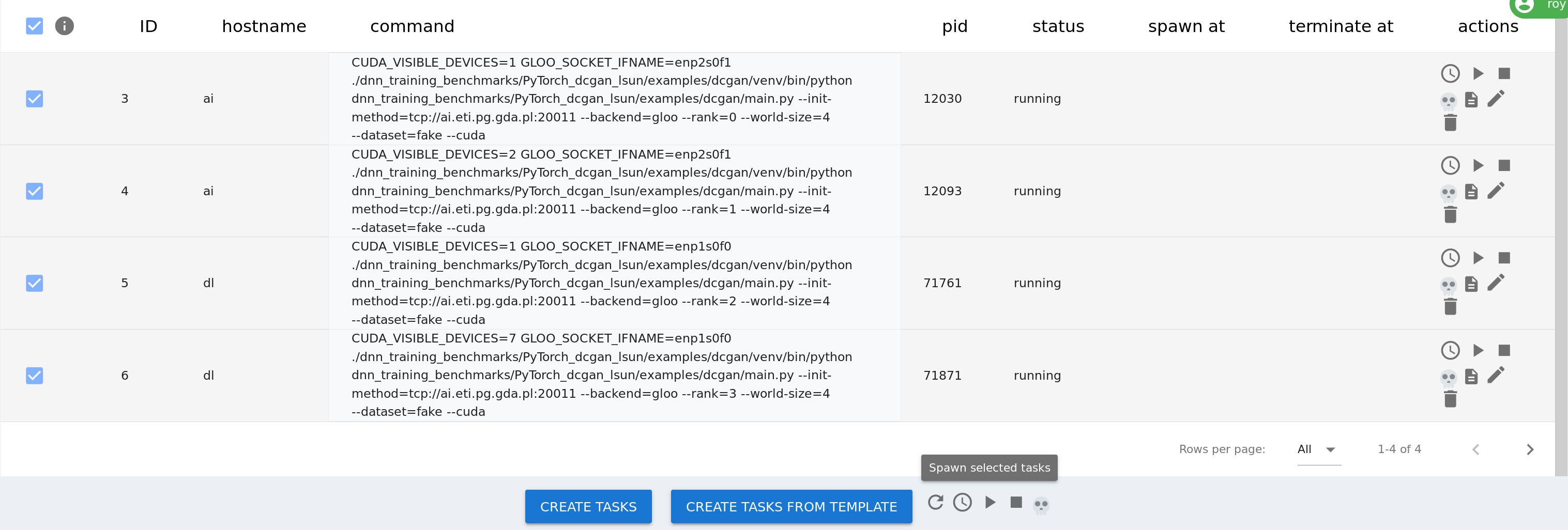
+
+After that, the tasks can be controlled from `Task Overview`.
+The following actions are currently available:
+- Schedule (Choose when to run the task)
+- Spawn (Run the task now)
+- Terminate (Send terminate command to the task)
+- Kill (Send kill command)
+- Show log (Read output of the task)
+- Edit
+- Remove
+
+Having that high level control over all of the tasks from a single place can be extremely time-saving!
diff --git a/examples/PyTorch/img/choose_template.png b/examples/PyTorch/img/choose_template.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a863218b
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/PyTorch/img/choose_template.png differ
diff --git a/examples/PyTorch/img/full_conf.png b/examples/PyTorch/img/full_conf.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9f417c0e
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/PyTorch/img/full_conf.png differ
diff --git a/examples/PyTorch/img/parameters.png b/examples/PyTorch/img/parameters.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..788d0dbb
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/PyTorch/img/parameters.png differ
diff --git a/examples/PyTorch/img/running.png b/examples/PyTorch/img/running.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c463fa37
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/PyTorch/img/running.png differ
diff --git a/examples/README.md b/examples/README.md
index e45e8d6f..96ea3ea6 100644
--- a/examples/README.md
+++ b/examples/README.md
@@ -1,16 +1,11 @@
# Examples
-This directory contains examples of deep neural network training applications that serve as
-requirement providers towards TensorHive. We are testing their performance and ease of use depending
-on computing resource management software used. This allows us to learn about various features of
-existing resource management systems and base our design decisions on the experiences with approaches
-such as native application execution, application-specific scripts, Docker and
-[Kubernetes](https://gist.github.com/PiotrowskiD/1e3f659a8ac7db1c2ca02ba0ae5fcfaf).
-
-The applications can be also useful for others as benchmarks. Our benchmark results, useful resources
-and more info about configuration and running examples can be found in corresponding folders.
-We plan to add TensorHive usage examples to the individual directories when distributed training deployment
-is supported by TensorHive
-
-
-
-
+This directory contains usage examples of the TensorHive task execution
+module for chosen DNN training scenarios:
+
+Directory | Description
+--- | ---
+TF_CONFIG | Using the default cluster configuration method in TensorFlowV2 - the TF_CONFIG environment variable.
+TensorFlow_ClusterSpec | Using the standard ClusterSpec parameters, often used in TensorFlowV1 implementations.
+PyTorch | Using standard parameters used in PyTorch implementations.
+deepspeech | Redirection to the DeepSpeech test application, kept for link maintenance.
+t2t_transformer | Redirection to the DeepSpeech test application, kept for link maintenance.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/examples/TF_CONFIG/README.md b/examples/TF_CONFIG/README.md
index f640d6cc..092f8e64 100644
--- a/examples/TF_CONFIG/README.md
+++ b/examples/TF_CONFIG/README.md
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
-# Using TensorHive for running distributed trainings using TF_CONFIG
+# Running distributed trainings through TensorHive using TF_CONFIG
-This example shows how to use the TensorHive `task nursery` module to
-conveniently orchestrate distributed trainings configured using
-the TF_CONFIG environment variable. This
-[MSG-GAN training application](https://github.com/roscisz/dnn_training_benchmarks/tree/master/TensorFlowV2_MSG-GAN_Fashion-MNIST)
+This example shows how to use the TensorHive `task execution` module to
+conveniently configure and execute distributed trainings using
+the TF_CONFIG environment variable.
+[This MSG-GAN training application](https://github.com/roscisz/dnn_training_benchmarks/tree/master/TensorFlowV2_MSG-GAN_Fashion-MNIST)
was used for the example.
## Running the training without TensorHive
@@ -31,7 +31,9 @@ TF_CONFIG='{"cluster":{"worker":["gl01:2222", "gl02:2222"]}, "task":{"type": "wo
**Other environment variables**
Depending on the environment, some other environment variables may have to be configured.
-For example, because our TensorFlow compilation uses a custom MPI library, the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment
+For example, in multi-GPU nodes, setting proper value of the CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES is useful
+to prevent the process from needlessly utilizing GPU memory. In this example,
+because the utilized TensorFlow compilation uses a custom MPI library, the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment
variable has to be set for each process to /usr/mpi/gcc/openmpi-4.0.0rc5/lib/.
**Choosing the appropriate Python version**
@@ -46,7 +48,7 @@ is used, so the python binary has to be defined as follows:
**Summary**
-Finally, full commands required to start in the exemplary setup our environment, will be as follows:
+Finally, full commands required to launch the training in our exemplary environment will be as follows:
gl01:
@@ -67,12 +69,12 @@ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH='/usr/mpi/gcc/openmpi-4.0.0rc5/lib/'
## Running the training with TensorHive
-The TensorHive `task nursery` module allows convenient orchestration of distributed trainings.
+The TensorHive `task execution` module allows convenient orchestration of distributed trainings.
It is available in the Tasks Overview view. The `CREATE TASKS FROM TEMPLATE` button allows to
conveniently configure tasks supporting a specific framework or distribution method. In this
example we choose the Tensorflow - TF_CONFIG template, and click `GO TO TASK CREATOR`:
-
+
In the task creator, we set the Command to
```
@@ -82,7 +84,7 @@ In the task creator, we set the Command to
In order to add the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable, we enter the parameter name,
select Static (the same value for all processes) and click `ADD AS ENV VARIABLE TO ALL TASKS`:
-
+
Then, set the appropriate value of the environment variable (/usr/mpi/gcc/openmpi-4.0.0rc5/lib/).
@@ -93,20 +95,20 @@ to specify batch size, we enter parameter name --batch_size, again select Static
Select the required hostname and resource (CPU/GPU_N) for the specified training process. The resultant
command that will be executed by TensorHive on the selected node will be displayed above the process specification:
-
+
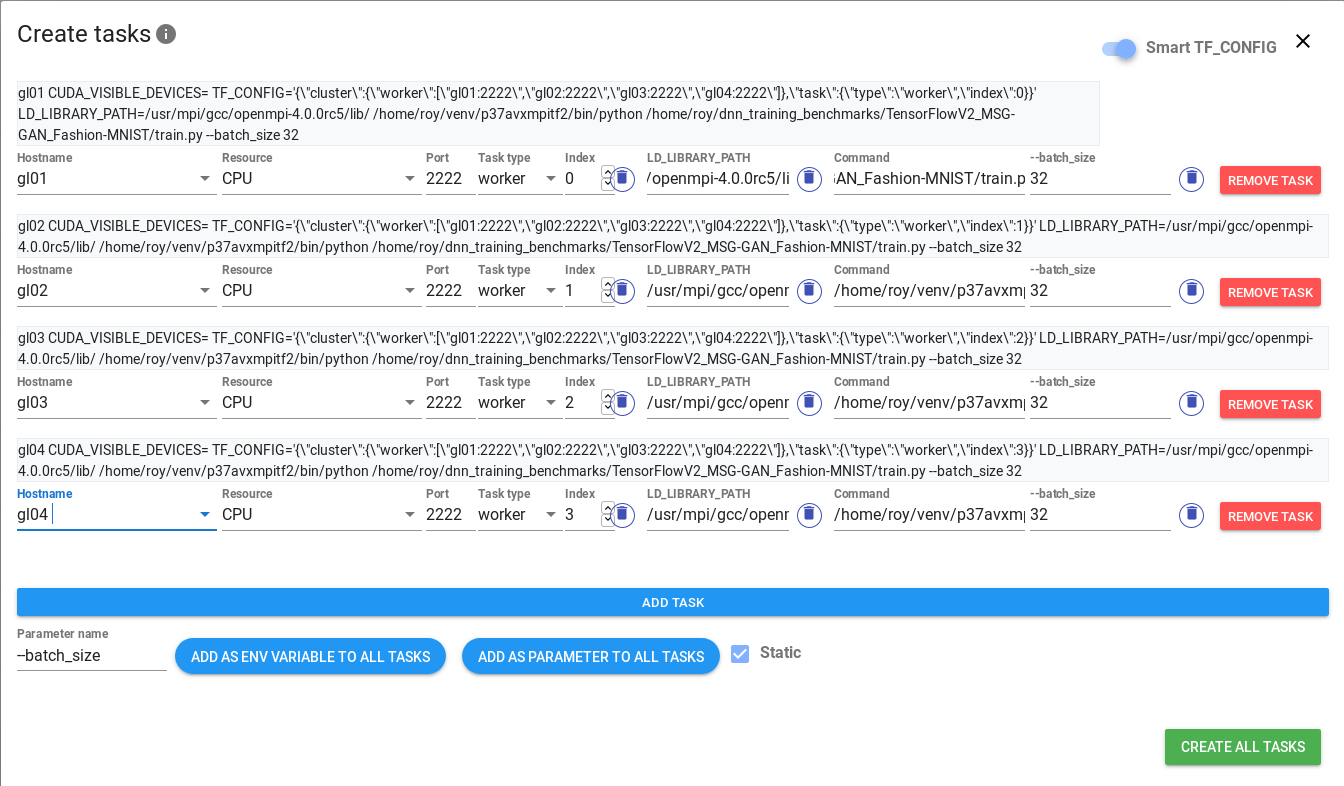
Note that the TF_CONFIG and CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES variables are configured automatically. Now, use
the `ADD TASK` button to duplicate the processes and modify the required target hosts to create
your training processes. For example, this screenshot shows the configuration for training on 4
hosts: gl01, gl02, gl03, gl04:
-
+
-After clicking the `CREATE ALL TASKS` button, the processes will be available in the process list for future actions.
+After clicking the `CREATE ALL TASKS` button, the processes will be available on the process list for future actions.
To run the processes, select them and use the `Spawn selected tasks` button. If TensorHive is configured properly,
the task status should change to `running`:
-
+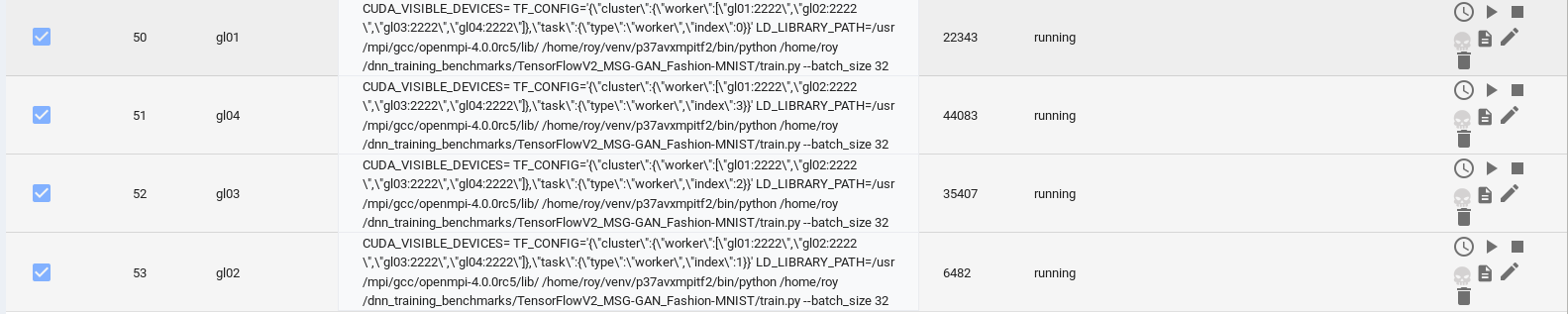
Note, that the appropriate process PID will be displayed in the `pid` column. Task overview can
be used to schedule, spawn, stop, kill, edit the tasks, and see logs from their execution.
diff --git a/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/README.md b/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..863cda66
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
+# Running distributed trainings through TensorHive using ClusterSpec
+
+This example shows how to use the TensorHive `task execution` module to
+conveniently configure and execute distributed trainings configured using
+standard TensorFlowV1 parameters for the [ClusterSpec](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/train/ClusterSpec)
+cluster configuration class.
+[This DeepSpeech training application](https://github.com/roscisz/dnn_training_benchmarks/tree/master/TensorFlowV1_DeepSpeech_ldc93s1)
+was used for the example.
+
+## Running the training without TensorHive
+
+In order to run the training manually, a separate worker process `python DeepSpeech.py`
+on each node and a separate parameter server process have to be run
+with the appropriate parameter values set as follows:
+
+**Application-specific parameters**
+
+The training application used in this example requires specifying train, dev and
+test data sets through the `train_files`, `dev_files` and `test_files` parameters.
+
+**ClusterSpec parameters**
+
+The `ps_hosts`, `worker_hosts`, `job_name` and `task_index` parameters
+have to be appropriately configured depending
+on the set of nodes taking part in the computations.
+For example, a training on two nodes 172.17.0.3 and 172.17.0.4 would require the following
+parameter values:
+
+worker on 172.17.0.3:
+```bash
+--ps_hosts=172.17.0.3:2224
+--worker_hosts=172.17.0.3:2222,172.17.0.4:2223
+--job_name=worker
+--task_index=0
+```
+
+worker on 172.17.0.4:
+```bash
+--ps_hosts=172.17.0.3:2224
+--worker_hosts=172.17.0.3:2222,172.17.0.4:2223
+--job_name=worker
+--task_index=1
+```
+parameter server on 172.17.0.3:
+```bash
+--ps_hosts=172.17.0.3:2224
+--worker_hosts=172.17.0.3:2222,172.17.0.4:2223
+--job_name=ps
+--task_index=0
+```
+
+**Other environment variables**
+
+Depending on the environment, some other environment variables may have to be configured.
+For example, in multi-GPU nodes, setting proper value of the CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES is useful
+to prevent the process from needlessly utilizing GPU memory.
+In this example, because the Mozilla DeepSpeech native client libraries are used, the
+LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable has to be set for each process to `native_client/`.
+
+**Choosing the appropriate Python version**
+
+In some cases, a specific Python binary has to be used for the training.
+For example, in our environment, a python binary from a virtual environment
+is used, so the python binary has to be defined as follows:
+
+```
+./venv/bin/python
+```
+
+**Summary**
+
+Finally, full commands required to launch the training in our exemplary environment will be as follows:
+
+worker on 172.17.0.3:
+```bash
+export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=native_client/
+./venv/bin/python ./DeepSpeech.py --train_files=ldc93s1/ldc93s1.csv --dev_files=ldc93s1/ldc93s1.csv --test_files=ldc93s1/ldc93s1.csv --ps_hosts=172.17.0.3:2224 --worker_hosts=172.17.0.3:2222,172.17.0.4:2223 --job_name=worker --task_index=0
+```
+
+worker on 172.17.0.4:
+```bash
+export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=native_client/
+./venv/bin/python ./DeepSpeech.py --train_files=ldc93s1/ldc93s1.csv --dev_files=ldc93s1/ldc93s1.csv --test_files=ldc93s1/ldc93s1.csv --ps_hosts=172.17.0.3:2224 --worker_hosts=172.17.0.3:2222,172.17.0.4:2223 --job_name=worker --task_index=1
+```
+
+parameter server on 172.17.0.3:
+```bash
+export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=native_client/
+./venv/bin/python ./DeepSpeech.py --train_files=ldc93s1/ldc93s1.csv --dev_files=ldc93s1/ldc93s1.csv --test_files=ldc93s1/ldc93s1.csv --ps_hosts=172.17.0.3:2224 --worker_hosts=172.17.0.3:2222,172.17.0.4:2223 --job_name=ps --task_index=0
+```
+
+## Running the training with TensorHive
+
+The TensorHive `task execution` module allows convenient orchestration of distributed trainings.
+It is available in the Tasks Overview view. The `CREATE TASKS FROM TEMPLATE` button allows to
+conveniently configure tasks supporting a specific framework or distribution method. In this
+example we choose the Tensorflow - cluster parameters template, and click `GO TO TASK CREATOR`:
+
+
+
+In the task creator, we set the Command to
+```
+./venv/bin/python ./DeepSpeech.py --train_files=ldc93s1/ldc93s1.csv --dev_files=ldc93s1/ldc93s1.csv --test_files=ldc93s1/ldc93s1.csv
+```
+
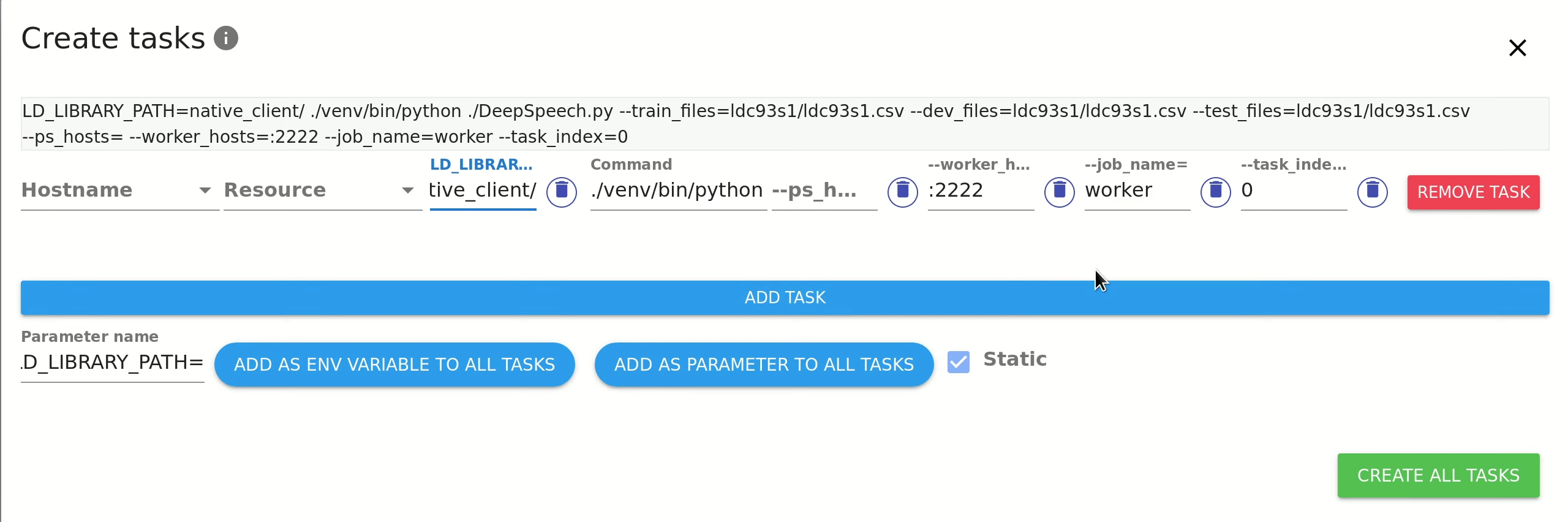
+In order to add the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable, we enter the parameter name,
+select Static (the same value for all processes) and click `ADD AS ENV VARIABLE TO ALL TASKS`.
+Then, set the appropriate value of the environment variable (native_client/):
+
+
+
+
+
+The task creator allows also to conveniently specify other command-line arguments. For example,
+should the `train_files`, `dev_files` and `test_files` parameters change throughout the training
+processes, they could be handled by `ADD AS PARAMETER TO ALL TASKS`.
+
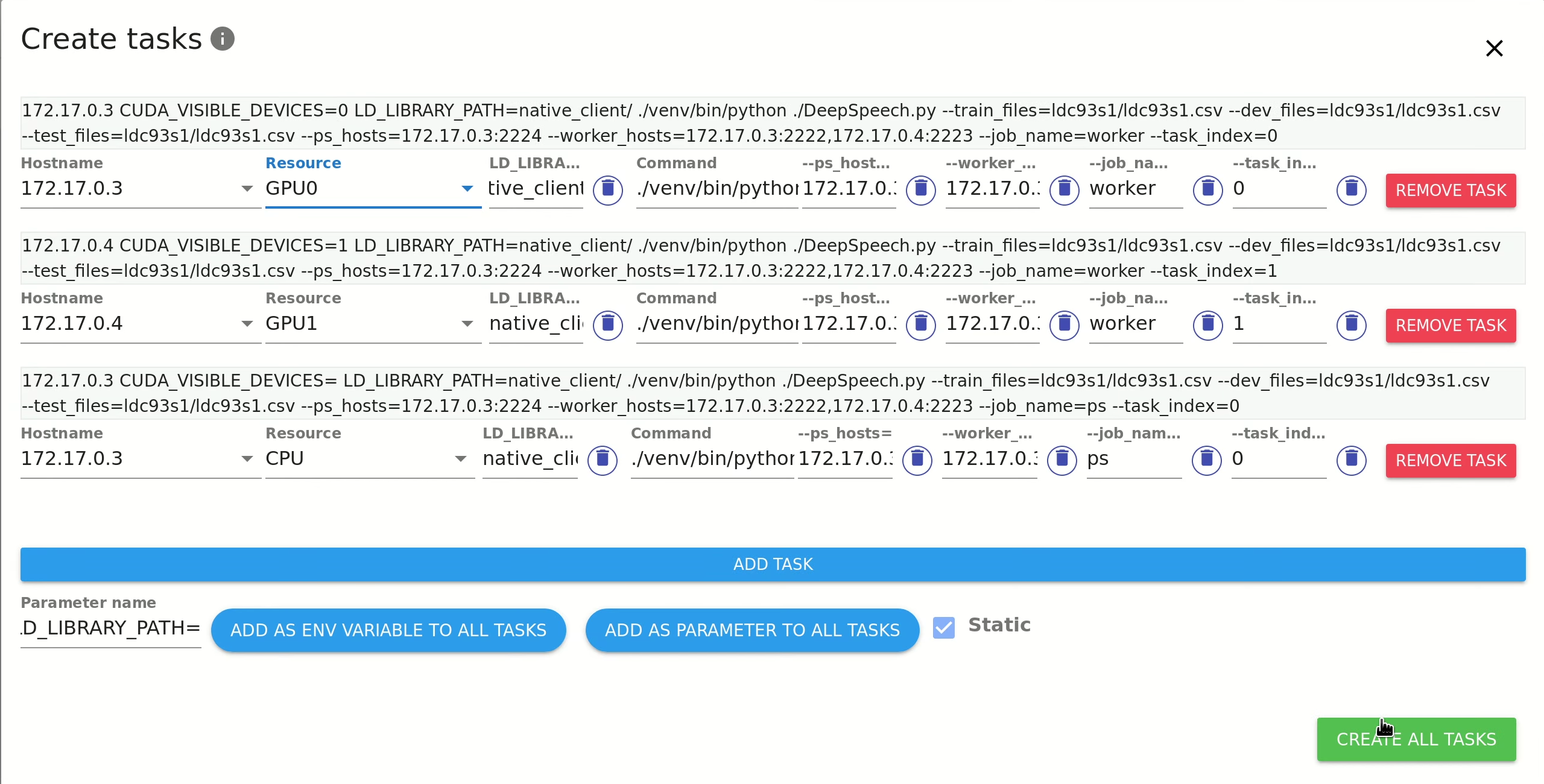
+Use `ADD TASK` to create as many copies of the defined process as required and
+select the appropriate hostname and resource (CPU/GPU_N) for the specified training process. Change
+`job_name` to `ps` for the parameter server process. The resultant
+command that will be executed by TensorHive on the selected node will be displayed above the process specification.
+Note that the cluster parameters and CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES variable are configured automatically:
+
+
+
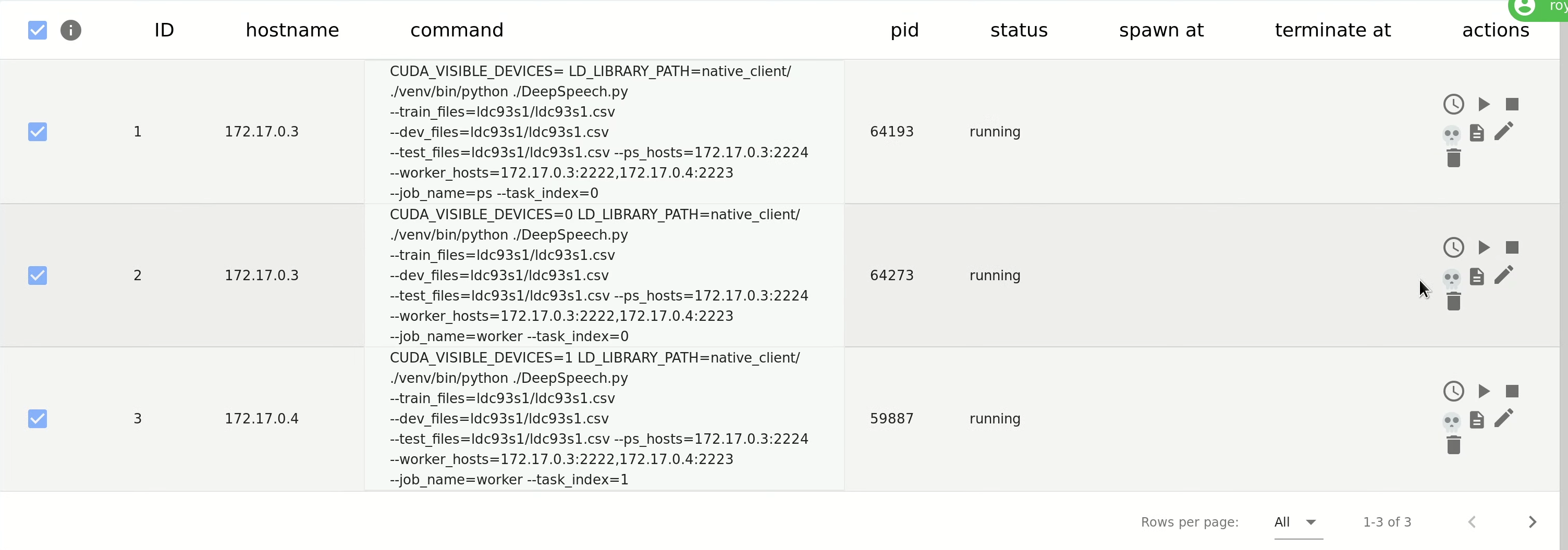
+After clicking the `CREATE ALL TASKS` button, the processes will be available on the process list for future actions.
+To run the processes, select them and use the `Spawn selected tasks` button. If TensorHive is configured properly,
+the task status should change to `running`:
+
+
+
+Note, that the appropriate process PID will be displayed in the `pid` column. Task overview can
+be used to schedule, spawn, stop, kill, edit the tasks, and see logs from their execution.
diff --git a/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/img/choose_template.png b/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/img/choose_template.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..76aae07f
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/img/choose_template.png differ
diff --git a/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/img/env_var.png b/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/img/env_var.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6a44ebd0
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/img/env_var.png differ
diff --git a/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/img/ready.png b/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/img/ready.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d2f16a64
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/img/ready.png differ
diff --git a/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/img/running.png b/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/img/running.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cf3b19e3
Binary files /dev/null and b/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec/img/running.png differ
diff --git a/examples/deepspeech/README.md b/examples/deepspeech/README.md
index e331182f..bc3779e9 100644
--- a/examples/deepspeech/README.md
+++ b/examples/deepspeech/README.md
@@ -4,5 +4,7 @@ The distributed DeepSpeech training application that had been used as a test
application and requirement provider towards TensorHive is now in a
[separate repository](https://github.com/roscisz/dnn_training_benchmarks/tree/master/TensorFlowV1_DeepSpeech_ldc93s1).
-See the [TensorHive examples directory](https://github.com/roscisz/TensorHive/tree/master/examples) for
-examples how TensorHive task execution module can be used for various training applications.
\ No newline at end of file
+The application has been also used in the TensorHive task execution
+module example for the [TensorFlow ClusterSpec](https://github.com/roscisz/TensorHive/tree/master/examples/TensorFlow_ClusterSpec)
+scenario. See also the [TensorHive examples directory](https://github.com/roscisz/TensorHive/tree/master/examples) for other
+examples how TensorHive task execution module can be used for various training scenarios.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/examples/t2t_transformer/README.md b/examples/t2t_transformer/README.md
index 516d1a85..23fa5e9e 100644
--- a/examples/t2t_transformer/README.md
+++ b/examples/t2t_transformer/README.md
@@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ application and requirement provider towards TensorHive is now in a
[separate repository](https://github.com/roscisz/dnn_training_benchmarks/tree/master/TensorFlowV1_T2T-Transformer_English-German).
See the [TensorHive examples directory](https://github.com/roscisz/TensorHive/tree/master/examples) for
-examples how TensorHive task execution module can be used for various training applications.
+examples how TensorHive task execution module can be used for various training scenarios.
diff --git a/images/task_nursery_screenshot1.png b/images/task_nursery_screenshot1.png
deleted file mode 100644
index dbad8558..00000000
Binary files a/images/task_nursery_screenshot1.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/tensorhive/__init__.py b/tensorhive/__init__.py
index 73e3bb4f..80eb7f98 100644
--- a/tensorhive/__init__.py
+++ b/tensorhive/__init__.py
@@ -1 +1 @@
-__version__ = '0.3.2'
+__version__ = '0.3.3'
diff --git a/tensorhive/app/web/dist/static/config.json b/tensorhive/app/web/dist/static/config.json
index 0dcf5b12..4e82c4d5 100644
--- a/tensorhive/app/web/dist/static/config.json
+++ b/tensorhive/app/web/dist/static/config.json
@@ -1 +1 @@
-{"apiPath": "http://localhost:1111/api/0.3.1", "version": "0.3.2", "apiVersion": "0.3.1"}
+{"apiPath": "http://localhost:1111/api/0.3.1", "version": "0.3.3", "apiVersion": "0.3.1"}