Some new Sonoff devices support the new Itead DIY architecture which allows OTA firmware upload. With Sonoff DIY, a user has more control over the hardware features of the device and also allows for upgrading the firmware without additional hardware. The following procedure upgrades Sonoff eWelink firmware to Tasmota.
IMPORTANT: There are some reports suggesting that the Windows version of Sonoff DIY Tool contains a trojan. It is not clear if it actually contains the malicious code or these are just false positives due to the way Python code was converted to native executables. Nevertheless, proceed with care.
Currently the following devices officially support Sonoff DIY:
- Sonoff Basic R3
- Sonoff RF R3
- Sonoff Mini
As Sonoff DIY is enabled by connecting GPIO16 to GND it may well be possible that other Sonoff devices running eWelink 3.1 or higher will also support it.
- Open the device and remove the jumper labeled OTA if present
- Power on device and connect to eWelink
- eWelink firmware updated to at least 3.1
-
Download the Sonoff DIY
tool_01DIY85from Github:./tool.exe(Microsoft Windows)./code.py(not yet tested)
-
Power off the Sonoff DIY device and install the DIY OTA jumper
-
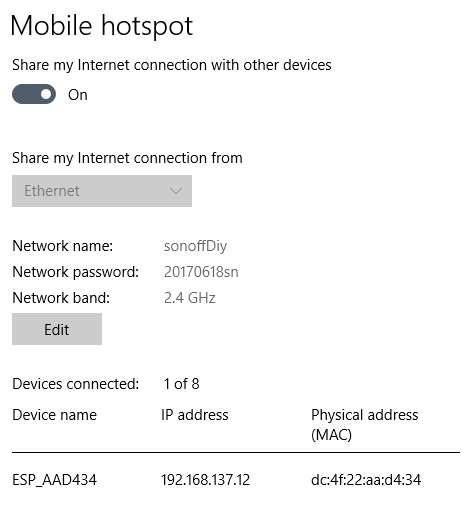
Modify your PC configuration to provide a Mobile hotspot:
- SSID:
sonoffDiy(case sensitive!) - Password:
20170618sn
- SSID:
-
Power on the Sonoff device and verify that it shows up on the Mobile hotspot Settings page
-
Start the
tool_01DIY85utility -
The utility should discover the device
-
Select the device and toggle it
ONandOFFto verify you are connected to the right device -
Select
Firmware flash(Brush machineon newer versions of the tool) -
Select a Tasmota binary (e.g.,
tasmota-wifiman.bin) or your own self-compiled binary. It must fit in the available free program space. You can use the 2.3.0 Core for this initial flash since it has the smallest program memory footprint. Do NOT use the tasmota-minimal pre-compiled binary as it does not allow you to change any settings.You may wish to compile your own firmware with all the features you require and disabling the features you do not. This will usually result in a "full" binary that is under 500k. You can use the resulting firmware file instead of the pre-compiled
tasmota-wifiman.bin. -
Select the device in the flash pop-up and then select OK
-
Tasmota will be uploaded and started
If the firmware update gets stuck at 0%, the Sonoff device could not reach the manufacturer server because your mobile hotspot does not share the Internet connection. If this happens, use the DIY tool to set the SSID and password of your Wi-Fi network on the Sonoff device. The device will connect to your network. Disable the hotspot and use your Wi-Fi for DIY tool laptop as well. Now start
Brush machineagain, flash Tasmota. Then continue with this guide.
- Quit DIY mode tool
- Stop mobile hotspot
- Power off the device and remove DIY jumper as it is no longer needed and might interfere with future Tasmota features that use GPIO16
This procedure is recommended for MacOS, but also works for Linux.
-
eWelink firmware updated to at least 3.1
-
OS with
curland a network services discovery tool (e.g.,mDNSfor MacOS oravahi-browsefor Linux) -
sonoffDiySSID on your local network. Use a router/access point or configure your laptop/smartphone as a hotspot with the proper SSID and password. -
A
<webServer>available on the same local network. Very simple web servers likeSimpleHTTPServerwill not work. For Mac, the OSX built-in web server is recommended. -
A Tasmota binary (e.g.,
tasmota-wifiman.bin) or your own self-compiled binary. It must fit in the available free program space. You can use the 2.3.0 Core for this initial flash since it has the smallest program memory footprint. Do NOT use the tasmota-minimal pre-compiled binary as it does not allow you to change any settings.You may wish to compile your own firmware with all the features you require and disabling the features you do not. This will usually result in a "full" binary that is under 500k. You can use the resulting firmware file instead of the pre-compiled
tasmota-wifiman.bin. This way you will not have to perform the secondary OTA firmware update. Nevertheless, it is still recommended that you perform aReset 5immediately after the Sonoff DIY flash completes.Upload the firmware file to the
<webServer>available on the same local network. -
SHA256
<SHAsum>of firmware binary file$ shasum -a 256 tasmota-wifiman.bin1da0e89be4c01df033fa6da9d0c1db58c3deea354d7ad194f607d1f518db48f9
- Open the device and remove the jumper labeled OTA if present
- Power on device and connect to eWelink
- Update eWelink firmware to at least 3.1
-
Power off the Sonoff DIY device and install the DIY OTA jumper
-
Create a new SSID on your router:
- SSID:
sonoffDiy(case sensitive!) - Password:
20170618sn
- SSID:
-
Wait for the Sonoff device to connect
-
Obtain the
<deviceIP>address (search on the router or perform an IP scan) -
Discover the Zeroconf details.
In this example, the<deviceID>is 1000988699MacOS
$ dns-sd -B _ewelink._tcpBrowsing for _ewelink._tcp DATE: ---Mon 12 Aug 2019--- 20:19:31.956 ...STARTING... Timestamp A/R Flags if Domain Service Type Instance Name 20:19:31.957 Add 2 5 local. _ewelink._tcp. eWeLink_1000988699Linux
$ avahi-browse -t _ewelink._tcp --resolve+ wlp3s0 IPv4 eWeLink_1000988699 _ewelink._tcp local = wlp3s0 IPv4 eWeLink_1000988699 _ewelink._tcp local hostname = [eWeLink_1000988699.local] address = [192.168.1.109] port = [8081] txt = ["data1={"switch":"off","startup":"off","pulse":"off","pulseWidth":500,"rssi":-47}" "seq=1" "apivers=1" "type=diy_plug" "id=1000988699" "txtvers=1"]
-
Test with
/zeroconf/infoPOST$ curl http://<deviceIP>:8081/zeroconf/info -XPOST --data '{"deviceid":"<deviceID>","data":{} }'{"seq":2,"error":0,"data":"{"switch":"off","startup":"off","pulse":"off","pulseWidth":500,"ssid":"sonoffDiy","otaUnlock":false}"} -
Unlock OTA updates at
/zeroconf/ota_unlock$ curl http://<deviceIP>:8081/zeroconf/ota_unlock -XPOST --data '{"deviceid":"<deviceID>","data":{} }'{"seq":2,"error":0}If OTA unlocking gets stuck, the Sonoff device could not reach the manufacturer server because your mobile hotspot does not share the Internet connection. If this happens, POST a request on
/zeroconf/wifiwith'{"deviceid":"<deviceID>","data":{ "ssid": "yourssid", "password": "yourpasswd" } }'to set the SSID and password of your Wi-Fi network on the Sonoff device. The device will connect to your network. Disable the hotspot and use your Wi-Fi as well, and restart/zeroconf/infoand/zeroconf/ota_unlock. -
Flash firmware at
/zeroconf/ota_flash$ curl http://<deviceIP>:8081/zeroconf/ota_flash -XPOST --data '{"deviceid":"<deviceID>","data":{"downloadUrl": "http://<webServer>/tasmota-wifiman.bin", "sha256sum": "<SHAsum>"} }'{"seq":2,"error":0} -
Ping the device for about 30 seconds until it has rebooted
Once the firmware upload completes and the device restarts, the usual tasmota-xxxx SSID should now be available.
-
Set up Wi-Fi to connect your device to your network
-
Perform a
Reset 5to wipe any flash remnants BEFORE attempting a Tasmota OTA flash for the first time -
If you flashed
tasmota-wifiman.bin, it is recommended that you upgrade to the firmware and Core variant that is needed for your device and use case (e.g.,tasmota.bin). You must perform this update using the localFile uploadOTA. Do not use a web OTA for this step. Download the firmware file from the repository to your computer.Some users have reported that upgrading via web OTA from
tasmota-wifiman.binto another binary has resulted in an unresponsive device which has required a wired flash to recover. -
Once the desired firmware is on the device, continue the regular Tasmota setup process. Use the the appropriate Template from the repository to assign the device components to the GPIO pins. For example, the Sonoff Mini template assigns these GPIO:
GPIOTasmota
ComponentDevice
Function0 Button1 (17) Button 4 Switch1 (9) S1/S2 12 Relay1 (21) L Out 13 LED1 (56) Link/Power Indicator