| layout | title | order | group | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
page |
VTA |
13 |
navigation |
VTA |
{% include JB/setup %}
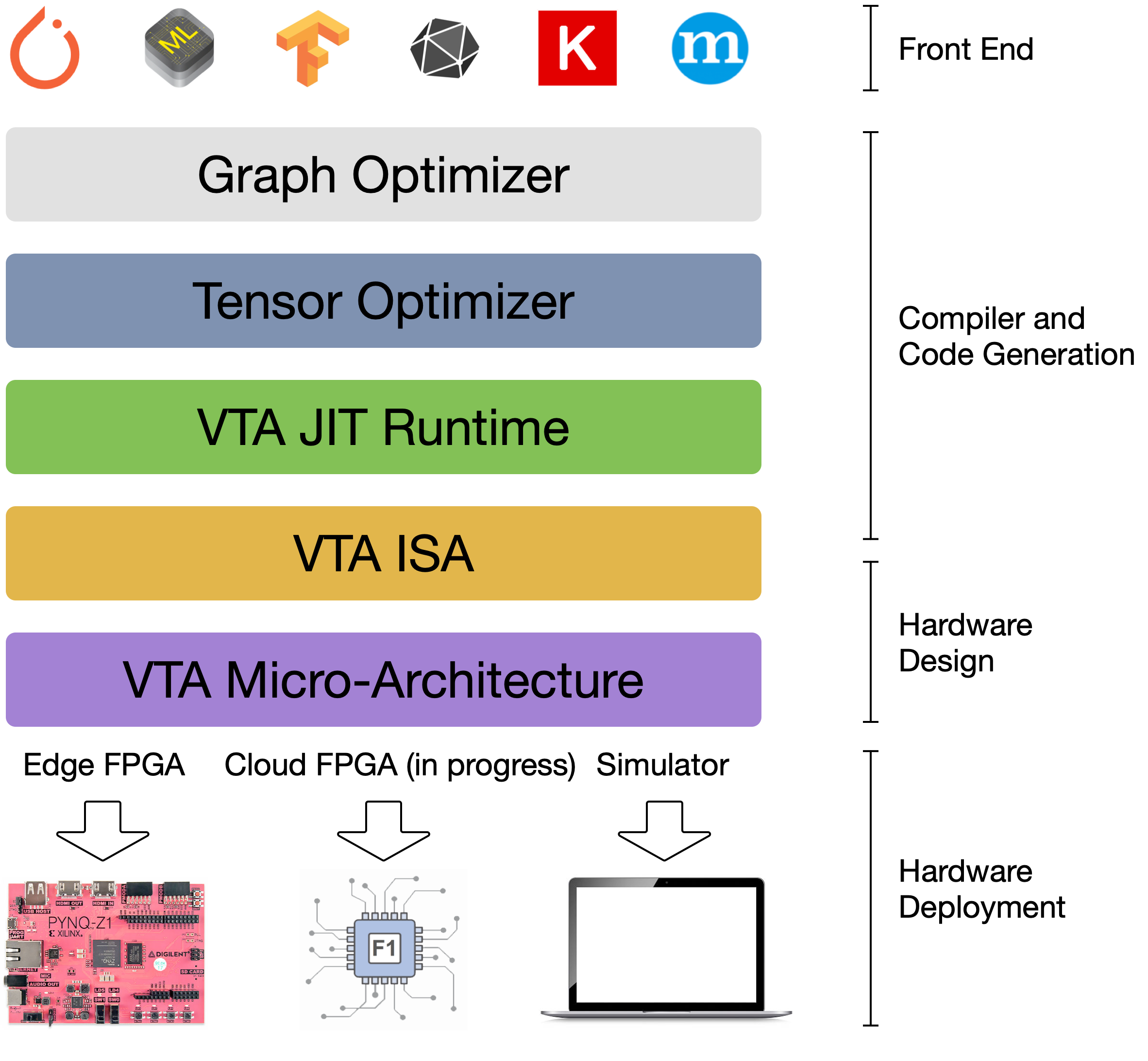
The Versatile Tensor Accelerator (VTA) is an extension of the TVM framework designed to advance deep learning and hardware innovation. VTA is a programmable accelerator that exposes a RISC-like programming abstraction to describe compute and memory operations at the tensor level. We designed VTA to expose the most salient and common characteristics of mainstream deep learning accelerators, such as tensor operations, DMA load/stores, and explicit compute/memory arbitration.
VTA is more than a standalone accelerator design: it’s an end-to-end solution that includes drivers, a JIT runtime, and an optimizing compiler stack based on TVM. The current release includes a behavioral hardware simulator, as well as the infrastructure to deploy VTA on low-cost FPGA hardware for fast prototyping. By extending the TVM stack with a customizable, and open source deep learning hardware accelerator design, we are exposing a transparent end-to-end deep learning stack from the high-level deep learning framework, down to the actual hardware design and implementation. This forms a truly end-to-end, from software-to-hardware open source stack for deep learning systems.
{:center: style="text-align: center"}
 {: width="50%"}
{:center}
{: width="50%"}
{:center}
The VTA and TVM stack together constitute a blueprint for end-to-end, accelerator-centric deep learning system that can:
- Provide an open deep learning system stack for hardware, compilers, and systems researchers alike to incorporate optimizations and co-design techniques.
- Lower the barrier of entry for machine learning practitioners to experiment with novel network architectures, operators and data representations that require specialized hardware support.
VTA is a component of TVM which was a research project at the SAMPL group of Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science & Engineering, University of Washington. The project is now driven by an open source community involving multiple industry and academic institutions. The project adopts Apache-style merit based governace model.
Read more about VTA in our TVM blog post, or in the VTA techreport.