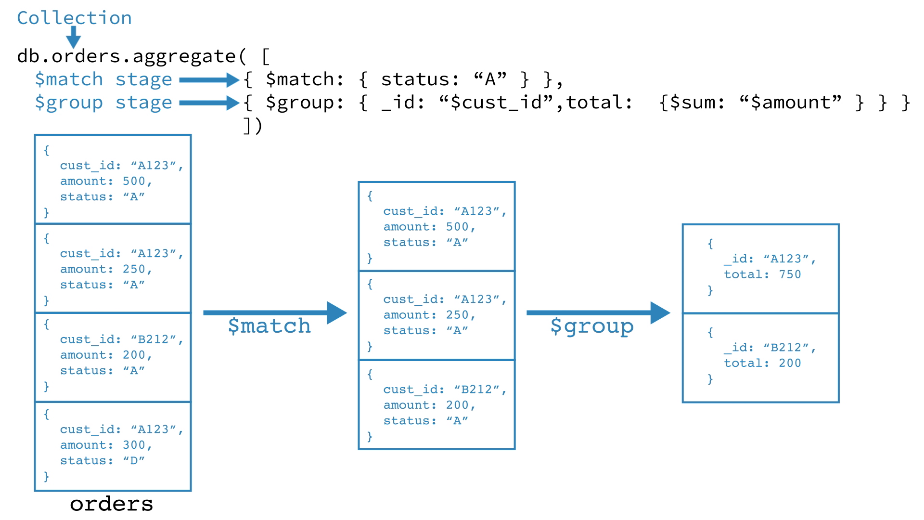
聚合操作处理数据记录并返回计算结果。聚合操作将来自多个 document 的值分组,并可以对分组的数据执行各种操作以返回单个结果。 MongoDB 提供了三种执行聚合的方式:聚合管道,map-reduce 函数和单一目的聚合方法。
MongoDB 的聚合框架以数据处理管道(Pipeline)的概念为模型。
MongoDB 通过 db.collection.aggregate() 方法支持聚合操作。并提供了 aggregate 命令来执行 pipeline。
MongoDB Pipeline 由多个阶段(stages)组成。每个阶段在 document 通过 pipeline 时都会对其进行转换。pipeline 阶段不需要为每个输入 document 都生成一个输出 document。例如,某些阶段可能会生成新 document 或过滤 document。
同一个阶段可以在 pipeline 中出现多次,但 $out、$merge,和 $geoNear 阶段除外。所有可用 pipeline 阶段可以参考:Aggregation Pipeline Stages。
- 第一阶段:
$match阶段按状态字段过滤 document,然后将状态等于“ A”的那些 document 传递到下一阶段。 - 第二阶段:
$group阶段按 cust_id 字段对 document 进行分组,以计算每个唯一 cust_id 的金额总和。
最基本的管道阶段提供过滤器,其操作类似于查询和 document 转换(修改输出 document 形式)。
其他管道操作提供了用于按特定字段对 document 进行分组和排序的工具,以及用于汇总数组(包括 document 数组)内容的工具。另外,管道阶段可以将运算符用于诸如计算平均值或连接字符串之类的任务。
聚合管道也可以在分片 collection 上操作。
Pipeline 可以确定是否仅需要 document 中必填字段即可获得结果。
($project、$unset、$addFields、$set) + $match 串行优化
对于包含投影阶段($project 或 $unset 或 $addFields 或 $set),且后续跟随着 $match 阶段的 Pipeline ,MongoDB 会将所有 $match 阶段中不需要在投影阶段中计算出的值的过滤器,移动一个在投影阶段之前的新 $match 阶段。
如果 Pipeline 包含多个投影阶段 和 / 或 $match 阶段,则 MongoDB 将为每个 $match 阶段执行此优化,将每个 $match 过滤器移动到该过滤器不依赖的所有投影阶段之前。
【示例】Pipeline 串行优化示例
优化前:
{ $addFields: {
maxTime: { $max: "$times" },
minTime: { $min: "$times" }
} },
{ $project: {
_id: 1, name: 1, times: 1, maxTime: 1, minTime: 1,
avgTime: { $avg: ["$maxTime", "$minTime"] }
} },
{ $match: {
name: "Joe Schmoe",
maxTime: { $lt: 20 },
minTime: { $gt: 5 },
avgTime: { $gt: 7 }
} }优化后:
{ $match: { name: "Joe Schmoe" } },
{ $addFields: {
maxTime: { $max: "$times" },
minTime: { $min: "$times" }
} },
{ $match: { maxTime: { $lt: 20 }, minTime: { $gt: 5 } } },
{ $project: {
_id: 1, name: 1, times: 1, maxTime: 1, minTime: 1,
avgTime: { $avg: ["$maxTime", "$minTime"] }
} },
{ $match: { avgTime: { $gt: 7 } } }说明:
{ name: "Joe Schmoe" } 不需要计算任何投影阶段的值,所以可以放在最前面。
{ avgTime: { $gt: 7 } } 依赖 $project 阶段的 avgTime 字段,所以不能移动。
maxTime 和 minTime 字段被 $addFields 阶段所依赖,但自身不依赖其他,所以会新建一个 $match 阶段,并将其置于 $project 阶段之前。
如果可能,优化阶段会将 Pipeline 阶段合并到其前身。通常,合并发生在任意序列重新排序优化之后。
当 $sort 在 $limit 之前时,如果没有中间阶段修改文档数量(例如 $unwind、$group),则优化程序可以将 $limit 合并到 $sort 中。如果有管道阶段更改了 $sort 和 $limit 阶段之间的文档数,则 MongoDB 不会将 $limit 合并到 $sort 中。
【示例】$sort + $limit
优化前:
{ $sort : { age : -1 } },
{ $project : { age : 1, status : 1, name : 1 } },
{ $limit: 5 }优化后:
{
"$sort" : {
"sortKey" : {
"age" : -1
},
"limit" : NumberLong(5)
}
},
{ "$project" : {
"age" : 1,
"status" : 1,
"name" : 1
}
}如果一个 $limit 紧随另一个 $limit,那么它们可以合并为一。
优化前:
{ $limit: 100 },
{ $limit: 10 }优化后:
{
$limit: 10
}如果一个 $skip 紧随另一个 $skip ,那么它们可以合并为一。
优化前:
{ $skip: 5 },
{ $skip: 2 }优化后:
{
$skip: 7
}如果一个 $skip 紧随另一个 $skip ,那么它们可以通过 $and 合并为一。
优化前:
{ $match: { year: 2014 } },
{ $match: { status: "A" } }优化后:
{
$match: {
$and: [{ year: 2014 }, { status: 'A' }]
}
}如果一个 $unwind 紧随另一个 $lookup,并且 $unwind 在 $lookup 的 as 字段上运行时,优化程序可以将 $unwind 合并到 $lookup 阶段。这样可以避免创建较大的中间文档。
优化前:
{
$lookup: {
from: "otherCollection",
as: "resultingArray",
localField: "x",
foreignField: "y"
}
},
{ $unwind: "$resultingArray"}优化后:
{
$lookup: {
from: "otherCollection",
as: "resultingArray",
localField: "x",
foreignField: "y",
unwinding: { preserveNullAndEmptyArrays: false }
}
}结果集中的每个文档均受 BSON 文档大小限制(当前为 16 MB)
Pipeline 的内存限制为 100 MB。
聚合 pipeline 比 map-reduce 提供更好的性能和更一致的接口。
Map-reduce 是一种数据处理范式,用于将大量数据汇总为有用的聚合结果。为了执行 map-reduce 操作,MongoDB 提供了 mapReduce 数据库命令。
在上面的操作中,MongoDB 将 map 阶段应用于每个输入 document(即 collection 中与查询条件匹配的 document)。 map 函数分发出多个键-值对。对于具有多个值的那些键,MongoDB 应用 reduce 阶段,该阶段收集并汇总聚合的数据。然后,MongoDB 将结果存储在 collection 中。可选地,reduce 函数的输出可以通过 finalize 函数来进一步汇总聚合结果。
MongoDB 中的所有 map-reduce 函数都是 JavaScript,并在 mongod 进程中运行。 Map-reduce 操作将单个 collection 的 document 作为输入,并且可以在开始 map 阶段之前执行任意排序和限制。 mapReduce 可以将 map-reduce 操作的结果作为 document 返回,也可以将结果写入 collection。
MongoDB 支持一下单一目的的聚合操作:
所有这些操作都汇总了单个 collection 中的 document。尽管这些操作提供了对常见聚合过程的简单访问,但是它们相比聚合 pipeline 和 map-reduce,缺少灵活性和丰富的功能性。
MongoDB pipeline 提供了许多等价于 SQL 中常见聚合语句的操作。
下表概述了常见的 SQL 聚合语句或函数和 MongoDB 聚合操作的映射表:
| SQL Terms, Functions, and Concepts | MongoDB Aggregation Operators |
|---|---|
WHERE |
$match |
GROUP BY |
$group |
HAVING |
$match |
SELECT |
$project |
ORDER BY |
$sort |
LIMIT |
$limit |
SUM() |
$sum |
COUNT() |
$sum$sortByCount |
JOIN |
$lookup |
SELECT INTO NEW_TABLE |
$out |
MERGE INTO TABLE |
$merge (Available starting in MongoDB 4.2) |
UNION ALL |
$unionWith (Available starting in MongoDB 4.4) |
【示例】
db.orders.insertMany([
{
_id: 1,
cust_id: 'Ant O. Knee',
ord_date: new Date('2020-03-01'),
price: 25,
items: [
{ sku: 'oranges', qty: 5, price: 2.5 },
{ sku: 'apples', qty: 5, price: 2.5 },
],
status: 'A',
},
{
_id: 2,
cust_id: 'Ant O. Knee',
ord_date: new Date('2020-03-08'),
price: 70,
items: [
{ sku: 'oranges', qty: 8, price: 2.5 },
{ sku: 'chocolates', qty: 5, price: 10 },
],
status: 'A',
},
{
_id: 3,
cust_id: 'Busby Bee',
ord_date: new Date('2020-03-08'),
price: 50,
items: [
{ sku: 'oranges', qty: 10, price: 2.5 },
{ sku: 'pears', qty: 10, price: 2.5 },
],
status: 'A',
},
{
_id: 4,
cust_id: 'Busby Bee',
ord_date: new Date('2020-03-18'),
price: 25,
items: [{ sku: 'oranges', qty: 10, price: 2.5 }],
status: 'A',
},
{
_id: 5,
cust_id: 'Busby Bee',
ord_date: new Date('2020-03-19'),
price: 50,
items: [{ sku: 'chocolates', qty: 5, price: 10 }],
status: 'A',
},
{
_id: 6,
cust_id: 'Cam Elot',
ord_date: new Date('2020-03-19'),
price: 35,
items: [
{ sku: 'carrots', qty: 10, price: 1.0 },
{ sku: 'apples', qty: 10, price: 2.5 },
],
status: 'A',
},
{
_id: 7,
cust_id: 'Cam Elot',
ord_date: new Date('2020-03-20'),
price: 25,
items: [{ sku: 'oranges', qty: 10, price: 2.5 }],
status: 'A',
},
{
_id: 8,
cust_id: 'Don Quis',
ord_date: new Date('2020-03-20'),
price: 75,
items: [
{ sku: 'chocolates', qty: 5, price: 10 },
{ sku: 'apples', qty: 10, price: 2.5 },
],
status: 'A',
},
{
_id: 9,
cust_id: 'Don Quis',
ord_date: new Date('2020-03-20'),
price: 55,
items: [
{ sku: 'carrots', qty: 5, price: 1.0 },
{ sku: 'apples', qty: 10, price: 2.5 },
{ sku: 'oranges', qty: 10, price: 2.5 },
],
status: 'A',
},
{
_id: 10,
cust_id: 'Don Quis',
ord_date: new Date('2020-03-23'),
price: 25,
items: [{ sku: 'oranges', qty: 10, price: 2.5 }],
status: 'A',
},
])SQL 和 MongoDB 聚合方式对比: