Spring Security’s Servlet support is based on Servlet Filters.
The servlet container creates a filter chain that contains both Filters and Servlets. This filter chain processes
the HttpServletRequest.
In the case of Spring MVC, the Servlet is an instance of DispatcherServlet. One servlet can handle a
single HttpServletRequest
and HttpServletResponse. However, more than one filter can be used to:
- Prevent downstream
FilterandServletfrom being invoked. - Modify the request or response used by downstream
FilterandServlet.
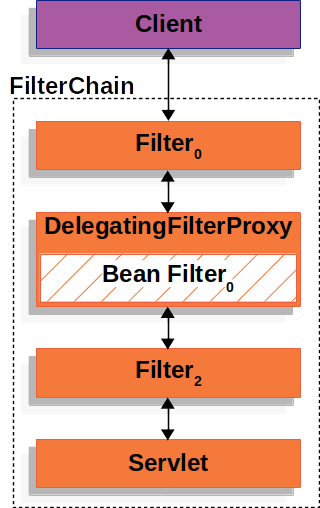
A Filter is part of the Servlet specification, not Spring. Therefore, the servlet container only allows filters to be
registered according to its own standard and does not directly support registering Spring-defined beans.
To address this, Spring Security provides DelegatingFilterProxy, which delegates filtering tasks to a
Spring-managed bean that implements the javax.servlet.Filter interface.
You can register DelegatingFilterProxy as a Filter in the servlet container. It then delegates all filtering
operations to a Spring-managed bean that implements the Filter interface.
Additionally, DelegatingFilterProxy delays looking up the Filter bean until it is needed (lazy initialization).
Spring
typically uses a ContextLoaderListener to load the Spring Beans, which is done only after the Filter instances need
to be registered.
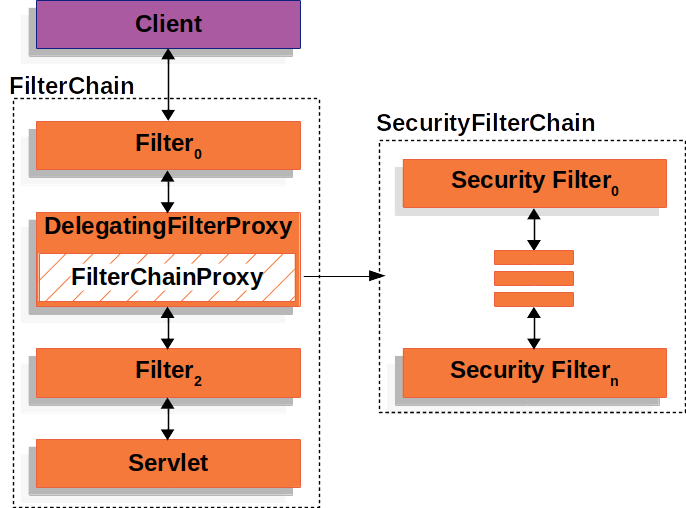
FilterChainProxy is a bean wrapped by DelegatingFilterProxy. It is a special Filter provided by Spring Security
that allows delegating to multiple Filter instances through SecurityFilterChain.
Security filters of SecurityFilterChain are typically beans and are registered with the FilterChainProxy instead
of DelegatingFilterProxy.
An advantage of FilterChainProxy is:
- It is the starting point of the Spring Security Filter Chain.
Therefore, if you want to debug the Spring Security Filter Chain, setting a breakpoint in FilterChainProxy is a good
idea.
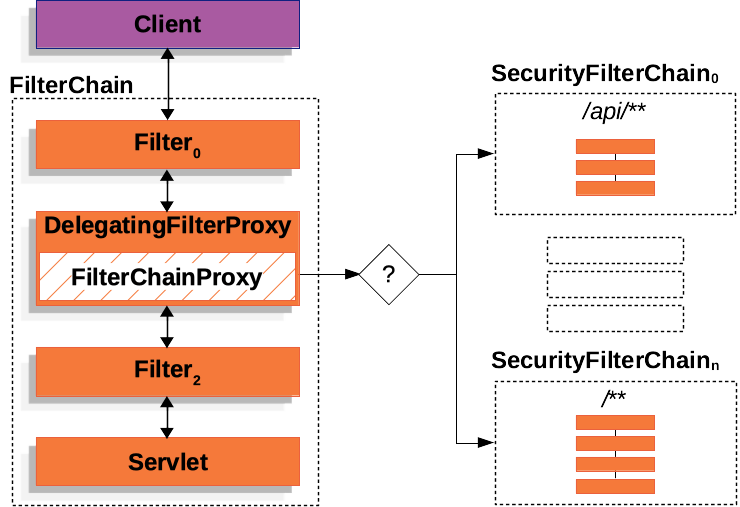
- It provides more flexible invocation of
SecurityFilterChainbased onHttpServletRequest.
While Filter instances are invoked based on URL, SecurityFilterChain instances are invoked based on anything in
the HttpServletRequest.
FilterChainProxy determines which SecurityFilterChain should be used based on the HttpServletRequest.
SecurityFilterChain has its own security Filter instances, which can be zero or more.
-
Order of Security filters
As with standard Servlet Filters, Spring Security Filters are ordered. To view the order of Spring Security Filters, check the INFO log level.
However, this is bound to the
DefaultSecurityFilterChain, so if you want to see the order of a custom filter chain, you need to configure your application to log security events. -
If you want to invoke a specific filter only once per request, extend the
OncePerRequestFilterclass rather than implementing theFilterinterface.Multiple invocations of a
Filtercan occur in cases of forward or include requests, etc. -
If multiple filters have the same order, it means that they have no deterministic order. It does not mean that they override each other.
-
When you declare a
Filteras a bean using the@Beanannotation or@Componentannotation, it will be invoked twice, once by the container and once by Spring Security, even in different orders. -
If you want to change the log level, see here.
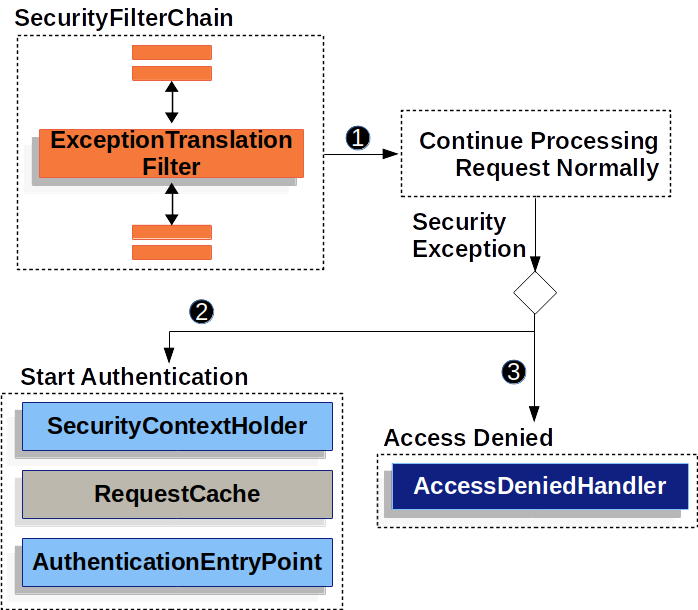
To translate security exceptions into HTTP responses, Spring Security provides the ExceptionTranslationFilter.
ExceptionTranslationFilter is a security filter inserted into FilterChainProxy.
-
ExceptionTranslationFilterinvokesFilterChain.doFilter(request, response)to continue processing the application. -
If a user is not authenticated or an
AuthenticationExceptionis thrown, the authentication process starts.SecurityContextHolderis cleared.HttpServletRequestis stored inRequestCachefor use after successful authentication.AuthenticationEntryPointis used to request user credentials, such as redirecting to the login page.
-
If an
AccessDeniedExceptionis thrown, access is denied. TheAccessDeniedHandleris invoked to handle the access denial.
If a user tries to access a resource that requires authentication but is not authenticated,
AuthenticationFilterwill throw an exception. Then,ExceptionTranslationFilterhandles it and starts the authentication process.
- Spring Security operates beneath the Servlet Filters.
DelegateFilterProxywraps Spring-managedFilterbeans as standard Servlet Filters.FilterChainProxyis the starting point of the Spring Security filter chain.FilterChainProxydetermines whichSecurityFilterChainshould be used.SecurityFilterChainhas its own securityFilterinstances.RequestCacheis used to storeHttpServletRequestfor use after successful authentication.