Zymp is a Python library to produce small sequences of DNA packed with enzyme restriction sites. You specify the enzymes you want, the ones you don't want, whether you want the sites to be unique, or any other condition, and Zymp will attempt to find a compact sequence verifying all of this (it really focuses on sequence shortness).
Warning: Zymp is implemented with a "whatever works well enough" philosophy. It has a lot of "whatever" but it generally works "well enough". The algorithm is greedy with many simplifications so don't expect perfect solutions.
Here is how you design a sequence
from zymp import (stacked_sites_array, plot_sequence_sites,
annotate_enzymes_sites, write_record)
enzymes_names = [
'AccI', 'AclI', 'AflII', 'AflIII', 'AgeI', 'ApaLI', 'AseI',
'AvaI', 'BamHI', 'BanII', 'BlnI', 'BmtI', 'BsmI', 'BssHII',
'DdeI', 'DraI', 'Eco47III', 'EcoRI', 'EcoRV', 'HindII',
'HindIII', 'HinfI', 'HpaI', 'KpnI', 'MfeI', 'MluI',
'MspA1I', 'MunI', 'NaeI', 'NcoI', 'NdeI', 'NheI', 'NotI',
'NsiI', 'NspI', 'PstI', 'PvuI', 'PvuII', 'SacI', 'SacII',
'SalI', 'ScaI', 'SfaNI', 'SnaBI', 'SpeI', 'SphI', 'SspI',
'StyI', 'VspI', 'XhoI', 'XmaI', 'ZraI'
]
forbidden_enzymes=['BsmBI', 'BsaI']
# DESIGN AN OPTIMIZED SEQUENCE WITH ZYMP
seq, sites_in_seq, leftover = stacked_sites_array(
enzymes_names, forbidden_enzymes=forbidden_enzymes,
unique_sites=True, tries=100)
print ("Sequence length:", len(seq),
"\nRestriction sites:", len(sites_in_seq),
"\nSites not included: ", leftover)
# PLOT A SUMMARY
ax = plot_sequence_sites(seq, enzymes_names)
ax.figure.savefig("stacked_array.pdf", bbox_inches='tight')
# WRITE THE SEQUENCE AND SITE ANNOTATIONS AS A RECORD
record = annotate_enzymes_sites(
seq, enzymes_names, forbidden_enzymes=forbidden_enzymes)
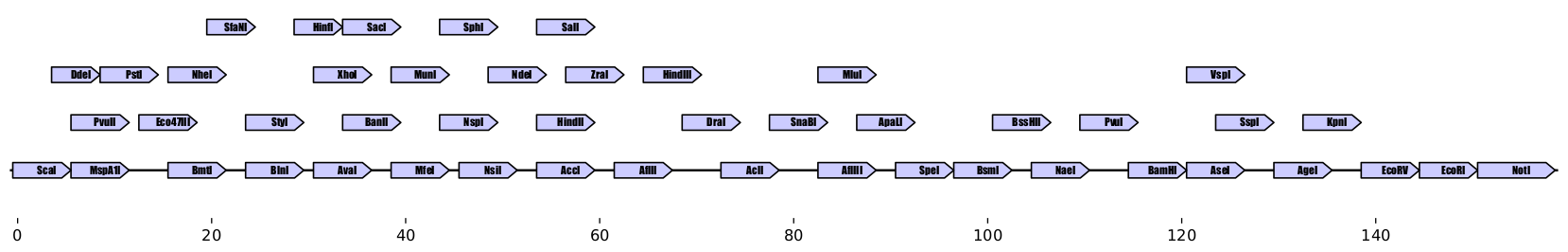
write_record(record, 'stacked_site_array.gb')Plot output:
Console output:
Sequence length: 159
Restriction sites: 49
Sites not included: {'NcoI', 'HpaI', 'SacII'}Zymp has created a 159-nucleotide sequence with 49 of the 52 restriction sites we specified, that's only ~3 nucleotides per site ! and the sequence is free of BsaI or HpaI sites, so it is compatible with Golden Gate assembly.
If NcoI and HpaI are your favorite enzymes, you may be disappointed that they are not in the final sequence. Zymp allows you to add validity conditions for the result:
from zymp import stacked_sites_array
def success_condition(seq, sites_in_seq, leftover):
return {'NcoI', 'HpaI'}.issubset(sites_in_seq)
seq, sites_in_seq, leftover = stacked_sites_array(
enzymes_names, forbidden_enzymes=forbidden_enzymes,
tries=100, success_condition=success_condition)
print ("Sequence length:", len(seq),
"\nRestriction sites:", len(sites_in_seq),
"\nSites not included: ", leftover)New console output:
Sequence length: 158
Restriction sites: 47
Sites not included: {'SacII', 'SacI', 'XhoI', 'BlnI', 'XmaI'}You can install zymp through PIP:
pip install zymp
Alternatively, you can unzip the sources in a folder and type:
python setup.py install
Zymp is an open-source software originally written at the Edinburgh Genome Foundry by Zulko and released on Github under the MIT licence (Copyright 2018 Edinburgh Genome Foundry).
Everyone is welcome to contribute!

Zymp is part of the EGF Codons synthetic biology software suite for DNA design, manufacturing and validation.