This addon provides a statechart abstraction based on XState
for adding statecharts to your Ember.js application. Statecharts can be used to describe
complex behaviour of your objects and separate ui-concern from behavioral concerns
in your applications. This is especially useful in Ember.Component-architecture
but can be used across all layers of your application (e.g. when implementing
global application state).
- Ember.js v3.28 or above
- Embroider or ember-auto-import v2
For classic Ember.js-versions pre Ember Octane please use the 0.8.x-version
of this addon.
For Ember.js versions < 3.24 please use the 0.13.x-version of this addon.
ember install ember-statecharts
ember-statecharts implemens the useMachine-resource. You need to install
ember-resources to work with it.
ember install ember-resources
Because ember-statecharts works with XState internally you have to install it as a dependency as well.
pnpm install -D xstate
or
yarn add --dev xstate
or
npm install --save-dev xstate
Statecharts have been around for a long time and have been used to model stateful, reactive system successfully. You can read about statecharts in the original paper Statecharts - A Visual Formalism for Complex Systems by David Harel.
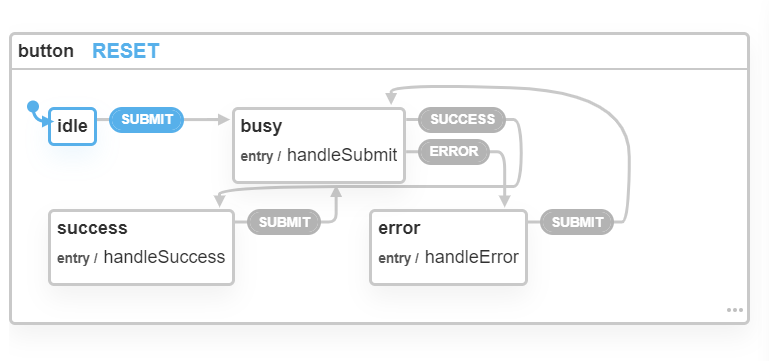
With statecharts we finally have a good abstraction to model and discuss behaviour with other stakeholders of our applications in addition to a design language that visualizes this behaviour. Here's an example of a button component:
In addition to their modeling capabilities Statecharts are executable and can be used to drive user experience behavior in your Ember.js applications:
import Component from '@glimmer/component';
import { useMachine } from 'ember-statecharts';
import { createMachine } from 'xstate';
function noop() {}
const buttonMachine = createMachine(
{
initial: 'idle',
states: {
idle: {
on: {
SUBMIT: 'busy',
},
},
busy: {
invoke: {
src: 'onSubmit',
onDone: 'success',
onError: 'error'
}
},
success: {
entry: ['onSuccess'],
on: {
SUBMIT: 'busy',
},
},
error: {
entry: ['onError'],
on: {
SUBMIT: 'busy',
},
},
},
},
{
actions: {
onSuccess() {},
onError() {},
},
services: {
onSubmit: async () => {}
}
}
);
export default class QuickstartButton extends Component {
statechart = useMachine(this, () => {
const { onSubmit, onSuccess, onError } = this;
return {
machine: quickstartButtonMachine.withConfig({
actions: {
onSuccess,
onError,
},
services: {
onSubmit
}
}),
};
});
get isBusy() {
return this.statechart.state.matches('busy');
}
get isDisabled() {
return this.isBusy || this.args.disabled;
}
handleClick = () => {
this.statechart.send('SUBMIT');
}
async onSubmit() {
await (this.args.onSubmit || noop)();
}
onSuccess = (_context, { data }) => {
return this.args.onSuccess?(data);
}
onError = (_context, { data }) => {
return this.args.onError?(data);
}
}Please refer to the documentation page for a detailed guide of how you can use statecharts to improve your Ember.js application architecture.
See the Contributing guide for details.
This project has been developed by https://www.effective-ember.com/ and contributors. It is licensed under the MIT License.