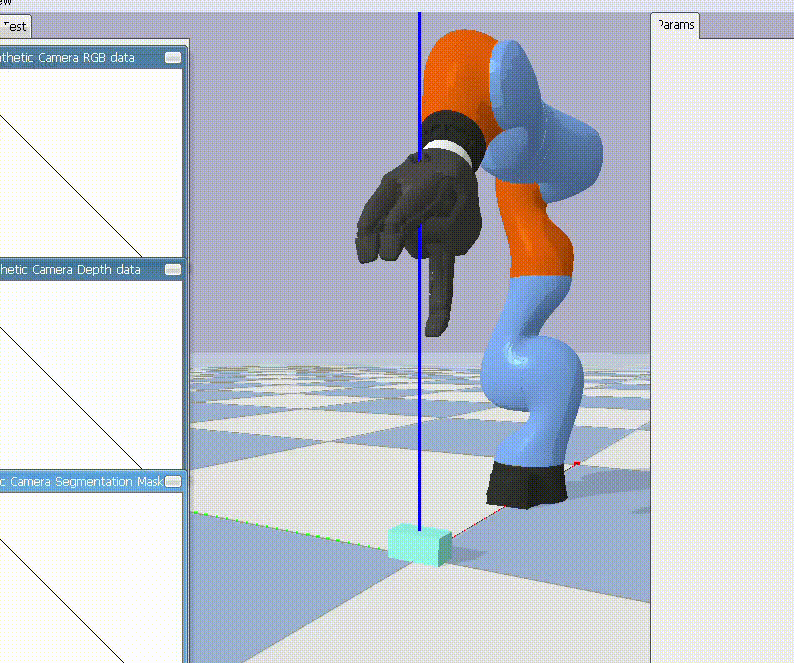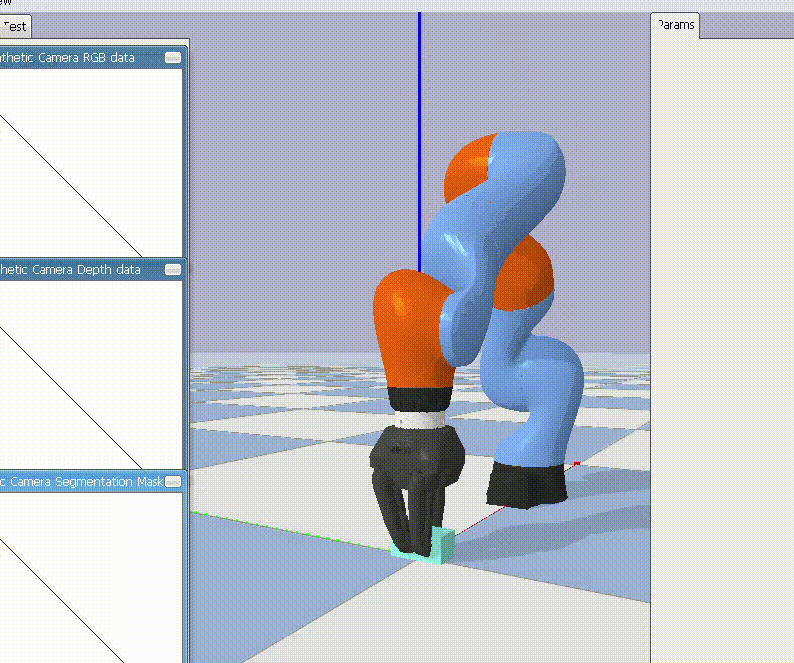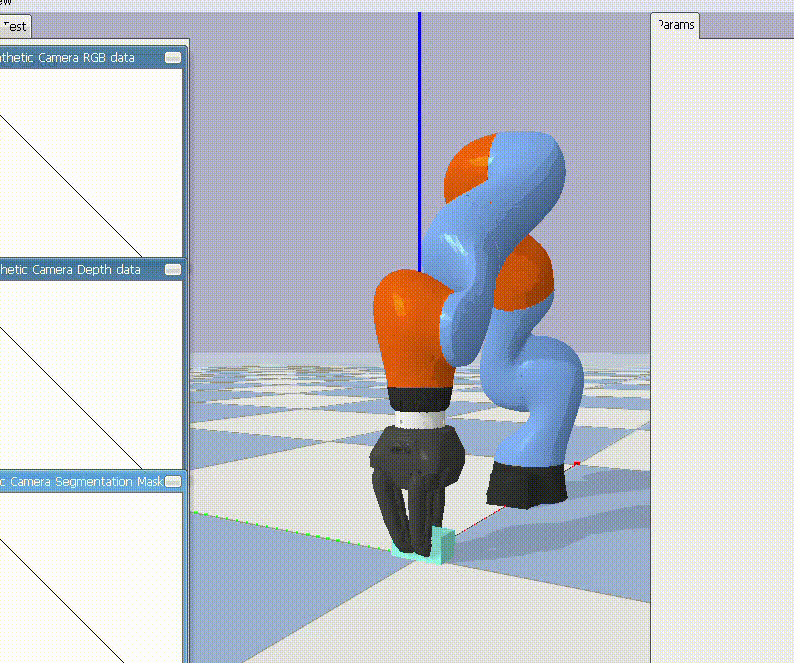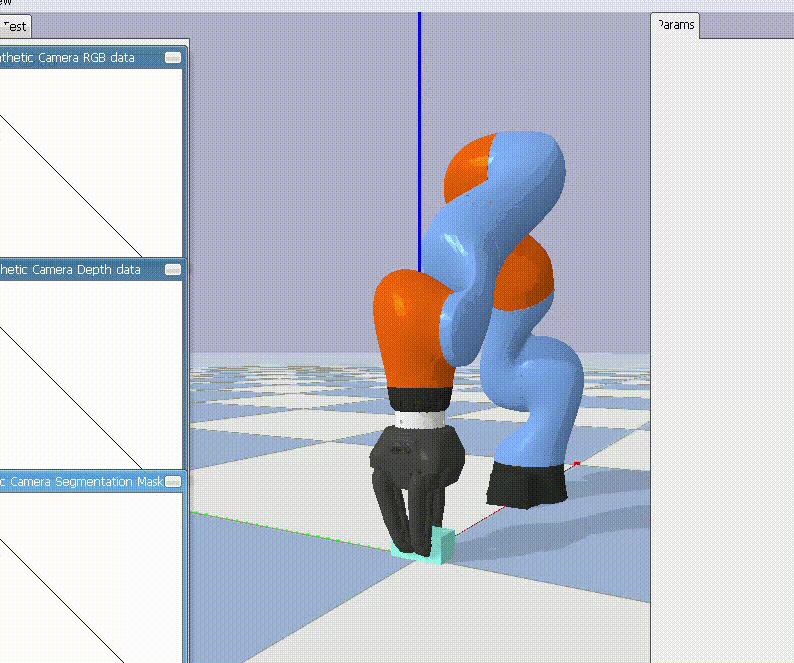
This project delves into the analysis of robotic grasp stability through simulation, particularly focusing on the volume of friction cones generated during different grasping scenarios. Using a Kuka robot in a PyBullet-based environment, it examines the efficacy of robotic grasps by calculating the true volume and the volumes generated by different discretizations of friction cones. The results from these analyses provide vital insights into the grasp's stability, offering a pathway to improve robotic grasping mechanisms in complex, real-world applications like warehouse operations.
- Clone the repository.
git clone [email protected]:Sukruthi-C/Grasping_simulated_Kuka.git
- Install the pre-requisities.
cd Grasping_simulated_Kuka
- Run closure_template.py
python3 closure_template.py --g1
Force closure in robotic grasping is critical as it ensures the robot can securely hold an object without slipping. It's a condition where the robot's gripper applies forces and torques to an object such that it cannot move, regardless of external disturbances. The 4-edge and 8-edge volumes are measures derived from the friction cone at the contact points. They represent the discretized versions of the friction cone's volume. These volumes provide insight into the grasp's stability: larger volumes suggest a more stable grasp.
This project aims to find if the grasp is stable by checking if it is force closure or not. This is done by calculating the true volume, 4 edge volume and 8 edge volume.
- '--g1' : Execute the first predefined grasp
- '--g2' : Execute the second predefined grasp
- '--custom [x y z theta]' : Custom defined grasp
The world.py script initializes the simulation environment and adds a Kuka robot and objects. robot.py controls the robot's movements and grasping mechanics. utils.py processes contact points and calculates the friction cones for grasping stability. The main script, closure_template.py, integrates these components, executes grasping actions, and calculates the stability of the grasps using convex hulls and wrenches.
- world.py: Sets up the simulation world, including the robot and objects.
- robot.py: Defines the Kuka robot's properties and actions.
- utils.py: Contains utility functions for processing contact points and calculating friction cones.
- closure_template.py: The main script that runs the simulation and calculates grasp stability.