This software works fine for me, but is new and likely contains bugs. Please report any issues.
The turnandrun program monitors dials, and runs commands at set positions.
It was written to provide a manual interface to an internet radio player running on a Raspberry Pi. In the following video it is running on Moode and manages a single dial that is turned to marked positions to select stations to play, or to stop the audio.
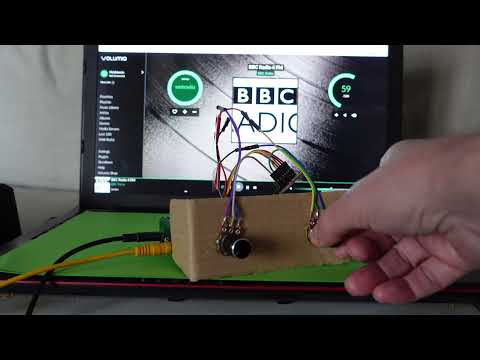
The following video shows turnandrun running on Volumio and managing two dials: One dial controls the volume and the other dial selects radio stations and stops playback
The instructions below describe a 10k potentiometer connected to an ADS1115 or ADS1015 ADC, and installation on Moode, Volumio or Raspberry Pi OS). However, it should be possible to adapt them to another input device, or another ADC, or another operating system.
A simple configuration file specifies commands to be run at certain positions of the dial. These commands can be anything.
The software should work with ADS1115 and ADS1015 modules. I have an ADS1115 module and 10k potentiometer, wired like the following diagram (in fact, I have a cheap fake ADS1115 module, that is really an ADS1015, and counts in steps of 16, but is fine for use with turnandrun)
Note: the wiring diagram connects ADDR to GND, which onfigures the board to use default I2C address 0x48.
Enable the kernel driver for the first channel of the ADS1X15 board.
Edit the boot configuration file (on Volumio use
sudo nano /boot/userconfig.txt)
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
For an ADS1115, add the line
dtoverlay=ads1115,cha_enable,cha_gain=1
For an ADS1015, add the line
dtoverlay=ads1015,cha_enable,cha_gain=1
Ensure the I2C module is loaded at boot. Edit the modules file
sudo nano /etc/modules
Add the following line, if it is not already included
i2c-dev
Reboot to activate these changes
sudo reboot
Choose one of the two instrallation methods.
This is the recommended installation method for debian-based systems, for example Raspberry Pi OS, Moode and Volumio.
The following commands will download and install the most recent turnandrun binary package (may not be completely up to date with the repository)
wget -N http://pitastic.com/turnandrun/packages/turnandrun_moode_install_latest.sh
sudo bash turnandrun_moode_install_latest.sh
wget -N http://pitastic.com/turnandrun/packages/turnandrun_volumio_install_latest.sh
sudo bash turnandrun_volumio_install_latest.sh
This is the installation method for non-debian based systems (for example RuneAudio, rAudio-1, and Arch Linux), or for using the repository version if the package is no up to date, of simply if building from source is preferred.
Install the packages needed, according to your system. On debian-based systems the commands are
sudo apt update
sudo apt install build-essential autoconf libtool libiio-dev i2c-tools
Download, build and install turnandrun
git clone https://github.com/antiprism/turnandrun
cd turnandrun
./bootstrap
CPPFLAGS="-W -Wall -Wno-psabi" ./configure
make
sudo make install-strip
The program is configured using a simple text file. The default
configuration file is /etc/turnandrun.conf (or specify a different
file, e.g. for testing, with turnandrun -c path_to_conf_file).
Edit the default configuration file and add your settings
sudo nano /etc/turnandrun.conf
The configuration file contains a section for each channel that is
being managed. A channel section begins with a line containing
the word CHANNEL followed by a letter from a, b, c, d, e.g. CHANNEL a.
The letter is the channel on the ADS1X115 board that a potentiometer is
conected to. Channel 'a' is the first channel, perhaps marked 'A0'
on the board, and enabled in
/boot/config.txt (on Volumio /boot/userconfig.txt)
with 'cha_enable,cha_gain=1'.
Channel 'b' is the second channel, perhaps marked 'A1'
on the board, and enabled with 'chb_enable,chb_gain=1'.
Likewise for channel values 'c' and 'd'.
Channel settings only need to be included in the configuration file to
change the default value. The settings are added one on each line in
the form setting=value.
turn_before_run = bool (default: 1, valid: 0, 1): Specifies if the command corresponding to the current dial position should be run on startup - '0' run the command, '1' wait for the dial to change position before running any command. Don't change from the default unless you are happy for any of the commands to be run when the machine is started up, for example, when it is plugged it in, or when it starts up after a power cut in the night.
command_delay = seconds (default: 1, range: 0 - 10): Number of seconds for the dial to be at a mark before running the command. The delay stops commands from being executed when the dial is turned through one mark to get to another.
frequency = per_second (default: 10 range: 1 - 100) Number of times per second to read the dial position.
overlap = percent (default: 5, range: 0 - 50) Adjacent dial marks are separated by a distance. The bands corresponding to adjacent dial marks overlap at the half way mark between them by a percentage of this distance. See Band Selection Logic.
print_commands = bool (default: 0, valid: 0, 1) Print the commands when selected by the dial (to help with debugging). This setting overides command line option -r.
enable = bool (default: 1, valid: 0, 1) Enable or disable the channel (use to disable the channel)
run_commands = bool (default: 1, valid: 0, 1) Run the commans when selected by the dial. This setting overides command line option -d.
Use marks around the dial as positions where you would like commands to be executed. These positions correspond to a raw dial dial reading, which can be associated with a command to run in a confguration file.
To see the raw readings, us the dry run option
turnandrun -d
Make a record of the raw values corresponding to marks where you want to run commands.
Each command is added to the configuration file as a single line in
the form raw_reading=comand_label,command, where raw_reading is the
raw number, command_label is short label to identify the command
(cannot include a comma), and command is the text of
the command to run. En example command line might be
24000 = stop, mpc -q stop
For more examples see commands.
This is a radio player configuration. It includes some channel settings as an example, but works well with defaults, and specifies commands for four dial positions. The first dial position stops the audio, and the other three positions play BBC Radio 1, 2 and 4.
CHANNEL a
turn_before_run = 1
overlap = 5
command_delay = 1
frequency = 10
0 = stop, volumio stop
8000 = BBC Radio 1, curl localhost:3000/api/v1/replaceAndPlay -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"item":{"service":"webradio","uri":"http://stream.live.vc.bbcmedia.co.uk/bbc_radio_one"}}'
16000 = BBC Radio 2, curl localhost:3000/api/v1/replaceAndPlay -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"item":{"service":"webradio","uri":"http://stream.live.vc.bbcmedia.co.uk/bbc_radio_two"}}'
24000 = BBC Radio 4, curl localhost:3000/api/v1/replaceAndPlay -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"item":{"service":"webradio","uri":"http://stream.live.vc.bbcmedia.co.uk/bbc_radio_fourfm"}}'
CHANNEL a
turn_before_run = 1
overlap = 5
command_delay = 1
frequency = 10
0 = stop, mpc -q stop
8000 = BBC Radio 1, mpc -q clear && mpc -q add http://stream.live.vc.bbcmedia.co.uk/bbc_radio_one && mpc -q play
16000 = BBC Radio 2, mpc -q clear && mpc -q add http://stream.live.vc.bbcmedia.co.uk/bbc_radio_two && mpc -q play
24000 = BBC Radio 4, mpc -q clear && mpc -q add http://stream.live.vc.bbcmedia.co.uk/bbc_radio_fourfm && mpc -q play
This method is compatible with also setting the volume by another means
(e.g. from a music player's web interface). However, if the volume is set
by another means the dial position will not indicate the actual volume
until the dial is moved again, and when it is moved there may be a jump in
volume to near the current dial position (but this can be mitigated by turning
the dial quickly and/or using not using a very small value of command_delay).
Volume control commands depend on the OS and equipment. To help configure a
volume control I have provided a short script, that must be edited by hand
to set some values before running. The script is
vols_conf.py
(and installed in, e.g., /usr/share/turnandrun/doc/resources/vols_conf.py).
Make a copy of the script, edit it, then run it, with e.g.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/antiprism/turnandrun/main/doc/resources/vols_conf.py
nano vols_conf.py
python vols_conf.py > vol_cmds.txt
The file vol_cmds.txt contains the commands to add to the configuration file.
Example MPD volume control file with a small number of volume settings. A smaller command delay is used to make the dial more responsive, which is more natural for something that changes contually like a volume control
CHANNEL a
command_delay = 0.1
00100 = volume_000,mpc -q volume 0
02720 = volume_010,mpc -q volume 10
05340 = volume_020,mpc -q volume 20
07960 = volume_030,mpc -q volume 30
10580 = volume_040,mpc -q volume 40
13200 = volume_050,mpc -q volume 50
15820 = volume_060,mpc -q volume 60
18440 = volume_070,mpc -q volume 70
21060 = volume_080,mpc -q volume 80
23680 = volume_090,mpc -q volume 90
26300 = volume_100,mpc -q volume 100
This diagram shows the three types of selection zone that surround dial mark 3. The dial mark selection changes after the dial reading corresponds to the same dial mark for command_delay seconds. If the reading stays in the select zone then the dial mark is selected. If the reading does not leave the do not deselect zone then no new dial mark is selected. If the dial reading moves past an adjacent mark then the jump select zone determines the new dial mark.
Run the program with option -d for a dry run.
turnandrun -d
This will produce a report on the screen of: the configuration options, the current dial value and mark it corresponds to, and each time a command would be run. If no configuration file is found then the default configuration for all channels is used, allowing the raw reading values from the dial to be monitored.
After installing the service the turnandrun program will run when the machine starts. Install the service with
sudo turnandrun_service_install
(and if you later want to uninstall the service run
sudo turnandrun_service_uninstall)
The following text is printed by running turnandrun -h
Usage: turnandrun [options]
A 10k potentiometer is connected to an ADS1115 or ADS1015 ADC and a
simple configuration file determines commands to run at certain
positions.
Options
-h,--help this help message
--version version information
-c <file> configuration file name (default: /etc/turnandrun.conf)
Format
One to four sections, each section starting CHANNEL followed
by a letter a, b, c, d (corresponding to the ADS1X15 channel
used for the readings)
e.g. CHANNEL a
The section heading is followed by settings lines
turn_before_run = bool (default: 1, valid: 0, 1)
e.g. turn_before_run = false
command_delay = seconds (default: 1, range: 0 - 10)
e.g. command_delay = 0.5
frequency = per_second (default: 10 range: 1 - 100)
e.g. frequency = 20
overlap = percent_band (default: 5, range: 0 - 50)
e.g. overlap = 1
enable = bool (default: 1, valid: 0, 1)
e.g. enable = 0
print_commands (default: 0, valid: 0, 1)
e.g. print_commands = 1
run_commands (default: 1, valid: 0, 1)
e.g. run_commands = 0
and should contain two or more command lines
dial_reading_number = command_label, command_to_run
e.g. 1245 = Play, mpc -q play
-r report, print configuration report on startup
-m <freq> monitor , print current dial readings to screen with frequency
freq
-d dry run, no commands are run, -r and -m 10 are set, configuration
file errors do not cause the program to exit