-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 498
Alibaba Dragonwell8 User Guide
Over the years, more than a billion lines of Java code have been written in Alibaba. While adopting OpenJDK to run these applications, we have found a need to customize it specifically for large-scale Java application deployments. Our customization has been well tested in our environment. We are now contributing some of our work into the Java community.
Alibaba Dragonwell, as a downstream version of OpenJDK, is the in-house OpenJDK implementation at Alibaba. It is optimized for online e-commerce, financial and logistics applications running on 100,000+ servers. Alibaba Dragonwell is the engine that runs these distributed Java applications in extreme scaling.
Alibaba Dragonwell is certified as compatible with the Java SE standard. The current release supports Linux/x86_64 platform only.
Alibaba Dragonwell is a "friendly fork" under the same licensing terms as the upstream OpenJDK project. Alibaba is committed to collaborate closely with the OpenJDK community. We intend to bring as many customized features as possible from Alibaba Dragonwell to the upstream.
Alibaba Dragonwell JDK currently supports Linux/x86_64 platform only.
Two options to install Alibaba Dragonwell are described below.
- Option 1: Download and install pre-built Alibaba Dragonwell
- You may download a pre-built Alibaba Dragonwell JDK from its GitHub page: https://github.com/alibaba/dragonwell8/releases
- Uncompress the package to the installation directory.
- Option 2: Install via YUM
(Please stay tuned, will be available soon)
Supports RedHat, CentOS, and AliOS only.
- Add Aliyun's RPM repository to your /etc/repos.d/.
- Install Alibaba Dragonwell using YUM:
yum install dragonwell-8
To enable Alibaba Dragonwell JDK for your application, simply set JAVA_HOME to point to the installation directory of Alibaba Dragonwell.
The rationale in JWarmup is to record profiling data in a "previous run" including hot compiled methods, ordering of class initialization, etc. In a later "normal run", the JVM would eagerly load and resolve these classes based on the recorded profiling data, and proactively use C2 to compile the related methods.
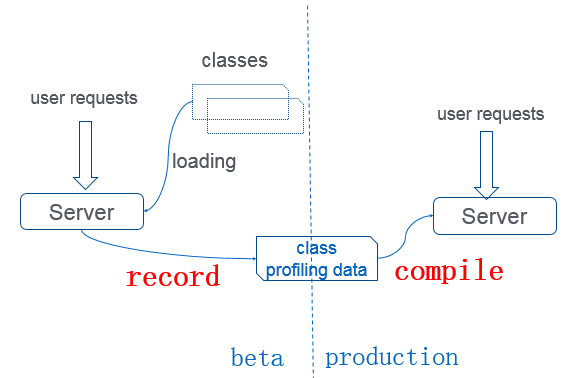
The typical usage is showed as above:
- In beta stage, the profiling data is recorded and stored into a file on disk with the generated loads.
- In production stage, JVM proactively loads, resolves related classes and compiles the hot methods
- In beta stage, use the JVM options as below (assuming CMS is used):
-XX:-ClassUnloading -XX:-CMSClassUnloadingEnabled -XX:-ClassUnloadingWithConcurrentMark -XX:CompilationWarmUpLogfile=jwarmup.log -XX:+CompilationWarmUpRecording -XX:CompilationWarmUpRecordTime=300
Caveats: The recording model does not support class unloading for now.
- In production stage, use the JVM options as below:
-XX:+CompilationWarmUp -XX:-TieredCompilation -XX:CompilationWarmUpLogfile=jwarmup.log -XX:CompilationWarmUpDeoptTime=0
Caveats: The warmup model does not support tiered compilation for now.
Caveats: JWarmUp will deoptimize all warmup compilation methods after given time. Disable it by setting CompilationWarmUpDeoptTime to 0.
- Trigger compilation at appropriate time
after all necessary initialization work of your application is done, call the following API to notify JVM:
com.alibaba.jwarmup.JWarmUp.notifyApplicationStartUpIsDone()After that, the methods will be compiled by JVM proactively.
Java Flight Recorder (JFR) is a tool to collect diagnostic and profiling data for Java applications. It is closely integrated into JVM and its performance overhead is minimal. The overhead is negligible if the default JFR config (-XX:+EnableJFR) is enabled.
In Alibaba Dragonwell, an option called "EnableJFR" is used to enable/disable the JFR feature. It's disabled by default. To enable JFR, you may start java with "-XX:+EnableJFR". For example:
java -XX:+EnableJFR -XX:StartFlightRecording=duration=1m,filename=rec.jfr MyApp
When running the JTreg test, please add the extra option -vmoption:-XX:+EnableJFR. Otherwise the test case will not run correctly. Here is an example of running JFR JTreg test:
make test JTREG_TEST_EXTRA_OPTIONS=-vmoption:-XX:+EnableJFR TEST=jdk_jfr
Java Mission Control (JMC) is the GUI to analyze JFR results. Please use JMC version 7.0 or later version to open the JFR record file. Currently, you can not use JMC to control JFR. But it will be supported in the future. More details on JFR and JMC are available on the Oracle website.
G1ElasticHeap is a GC feature to return memory of Java heap to OS to reduce the memory footprint of Java process. To enable this feature, you need to use G1 GC by options: -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:+G1ElasticHeap.
There are 3 modes which can be enabled in G1ElasticHeap.
Memory will be uncommitted by periodic GC. To enable periodic uncommit, use option -XX:+ElasticHeapPeriodicUncommit or dynamically enable the option via jinfo:
jinfo -flag +ElasticHeapPeriodicUncommit PID
Related options:
ElasticHeapPeriodicYGCIntervalMillis, 15000
(target young GC interval 15 seconds in default)
(eg, if Java runs with MaxNewSize=4g, young GC every 30 seconds, G1ElasticHeap will keep 15s GC interval and make a max 2g young generation to uncommit 2g memory)
ElasticHeapPeriodicInitialMarkIntervalMillis, 3600000
(Target initial mark interval, 1 hour in default. Unused memory of old generation will be uncommitted after last mixed GC.)
ElasticHeapPeriodicUncommitStartupDelay, 300
(Delay after startup to do memory uncommit, 300 seconds in default)
ElasticHeapPeriodicMinYoungCommitPercent, 50
(Percentage of young generation to keep, default 50% of the young generation will not be uncommitted)
To limit the young/old generation separately. Use jcmd or MXBean to enable. Example:
jcmd PID ElasticHeap young_commit_percent=40 uncommit_ihop=40
young_commit_percent: percentage of young generation to keep, rest of young generation will be uncommitted
uncommit_ihop: Percentage to trigger G1 concurrent cycle and mixed GC (like InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent). Unused memory of old generation will be uncommitted after last mixed GC.
Use MXBean:
MBeanServer server = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer();
ElasticHeapMXBean elasticHeapMXBean = ManagementFactory.newPlatformMXBeanProxy(server,
"com.alibaba.management:type=ElasticHeap",
ElasticHeapMXBean.class);
elasticHeapMXBean.setYoungGenCommitPercent(40);
elasticHeapMXBean.setUncommitIHOP(40);
Dynamically to limit the heap as a percentage of origin Xmx.
Use jcmd:
jcmd PID ElasticHeap softmx_percent=60
Use MXBean:
elasticHeapMXBean.setSoftmxPercent(70);
ElasticHeapMinYoungCommitPercent, 10
(Mininum percentage of young generation)
ElasticHeapYGCIntervalMinMillis, 5000
(Mininum young GC interval)
ElasticHeapInitialMarkIntervalMinMillis, 60000
(Mininum initial mark interval)
ElasticHeapEagerMixedGCIntervalMillis, 15000
(Guaranteed mixed GC interval, to make sure the mixed will happen in time to uncommit memory after last mixed GC)
ElasticHeapOldGenReservePercent, 5
(To keep a mininum percentage of Xmx for old generation in the uncommitment after last mixed GC)
ElasticHeapPeriodicYGCIntervalCeilingPercent, 25
ElasticHeapPeriodicYGCIntervalFloorPercent, 25
(The actual young GC interval will fluctuate between
ElasticHeapPeriodicYGCIntervalMillis * (100 - ElasticHeapPeriodicYGCIntervalFloorPercent) / 100 and
ElasticHeapPeriodicYGCIntervalMillis * (100 + ElasticHeapPeriodicYGCIntervalCeilingPercent) / 100 )
-
Mini-Heapdump support With Alibaba Dragonwell you may dump partial Java heap by omitting the content of all primitive type arrays. A new option
miniis added to the sub-command-dumpofjmaptool. An example:jmap -dump:live,mini,format=b,file=heap121.bin <PID> -
PrintYoungGenHistoAfterParNewGC The flag will print the histogram of the young generation after a ParNew GC. It is supported in jinfo :
jinfo -flag +PrintYoungGenHistoAfterParNewGC <PID> -
-XX:+PrintGCRootsTraceTimeThe flag will print the details of the ParNew GC phase. It helps user to find the problem of long GC pause time. This flag could be enabled byjinfo:
jinfo -flag +PrintGCRootsTraceTime <pid> // turn on the flag
jinfo -flag -PrintGCRootsTraceTime <pid> // turn off the flag
-
Fixed incorrect metaspace usage after full GC Metaspace usage in the GC log are not correctly updated after a full GC. This issue has been fixed in Alibaba Dragonwell.
-
-XX:ArrayAllocationWarningSize= The flag will print the calling stack of an array allocation if the allocation size is greater than the ArrayAllocationWarningSize. The default value is 512M, this flag could be enabled by jinfo:
// print the allocation stack if more than 1M array allocated.
jinfo -flag ArrayAllocationWarningSize=1048576 <pid>
// back to default value(512M)
jinfo -flag ArrayAllocationWarningSize=536870912 <pid>
Please take a look at Alibaba Dragonwell FAQ for support. Or send mail to [email protected] for more help. Or you may scan QR code below with DingTalk to join the group chat.

Alibaba Dragonwell