Team members:
Munir Rudy Herman, Farhan Azmi
Enhancing Tailored Discovery on TikTok Shop
The TikTok Shop offers an exceptional, personalized shopping experience for every customer. However, limiting this experience to just the shop tab is not enough.
The TikTok shop aims to expand more widely across the platform, attracting a wider audience. The unique shopping experience should not be confined to the TikTok Shop tab alone.
Our solution to expand the TikTok shop more widely across the platform is by incorporating hyperpersonalisation by extracting user interaction data such as product clicks and user searches. This interaction data will then be placed into our model, which then makes recommendations in a card that will be displayed when the user scrolls in the For You page.
The user circumstances will be extracted from the search bar of the main For You page. Why? Sometimes, the FYP does not necessarily have content or video that we might be interested in. So what do we do? We query the search bar to see relevant videos. With this - we saw an opportunity to extract user circumstances from the search field. In addition to the frequent use of the FYP, FYP also give users the flexibility of typing whatever they want into the search bar - enabling for greater personalisation.
Shown below is the screenshot and gif demonstrating the functionality:
| Screenshot | Gif Demo |
|---|---|
 |
 |
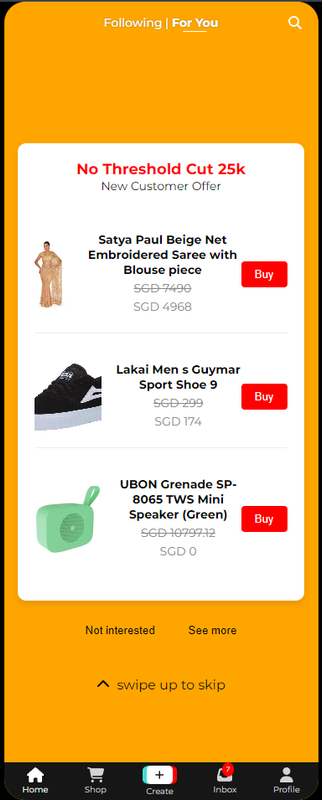
Any searches performed in the search field plus product clicks are logged to feed in the recommendation model.
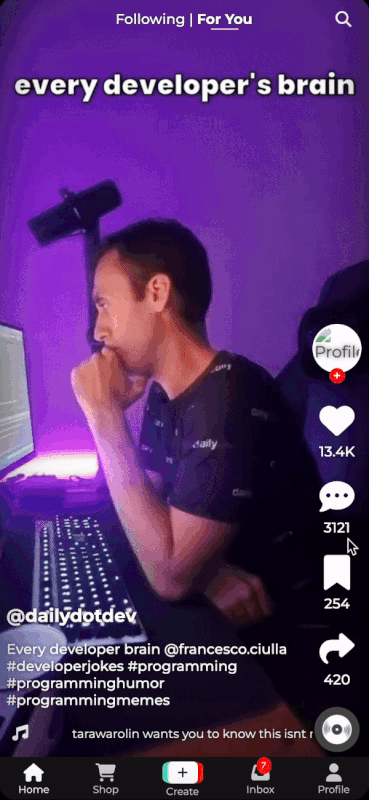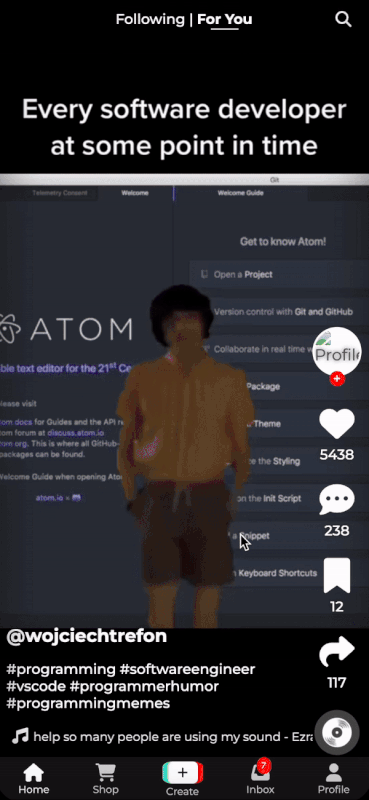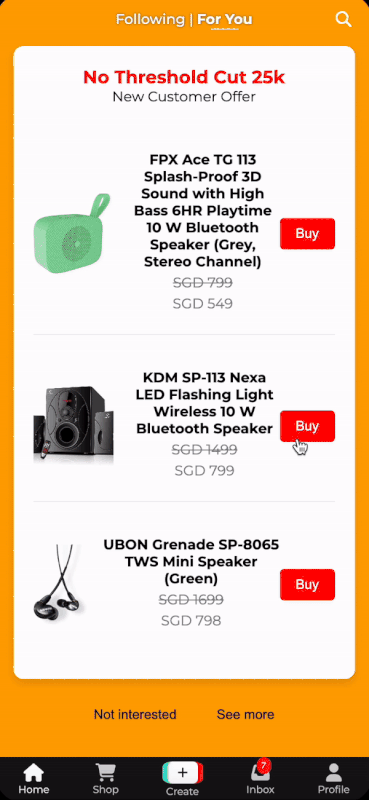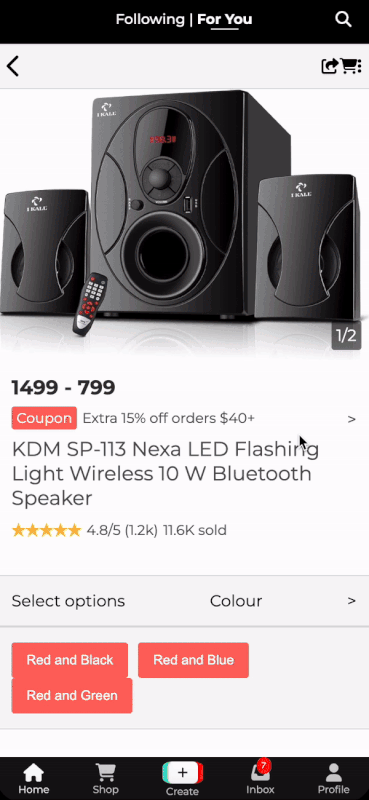
Based on the extracted user circumstances and user-product interactions, the ShopFYPCard will be displayed to the user when he/she scrolls through the For You page. The products shown in the card are personalised to the user. The user is also given the option to click on the product and be redirected to the product in the TikTok shop.
As shown, as the user searched for "Bluetooth Speaker" earlier the shop card in the For You page will update itself to recommend relevant products to that search.
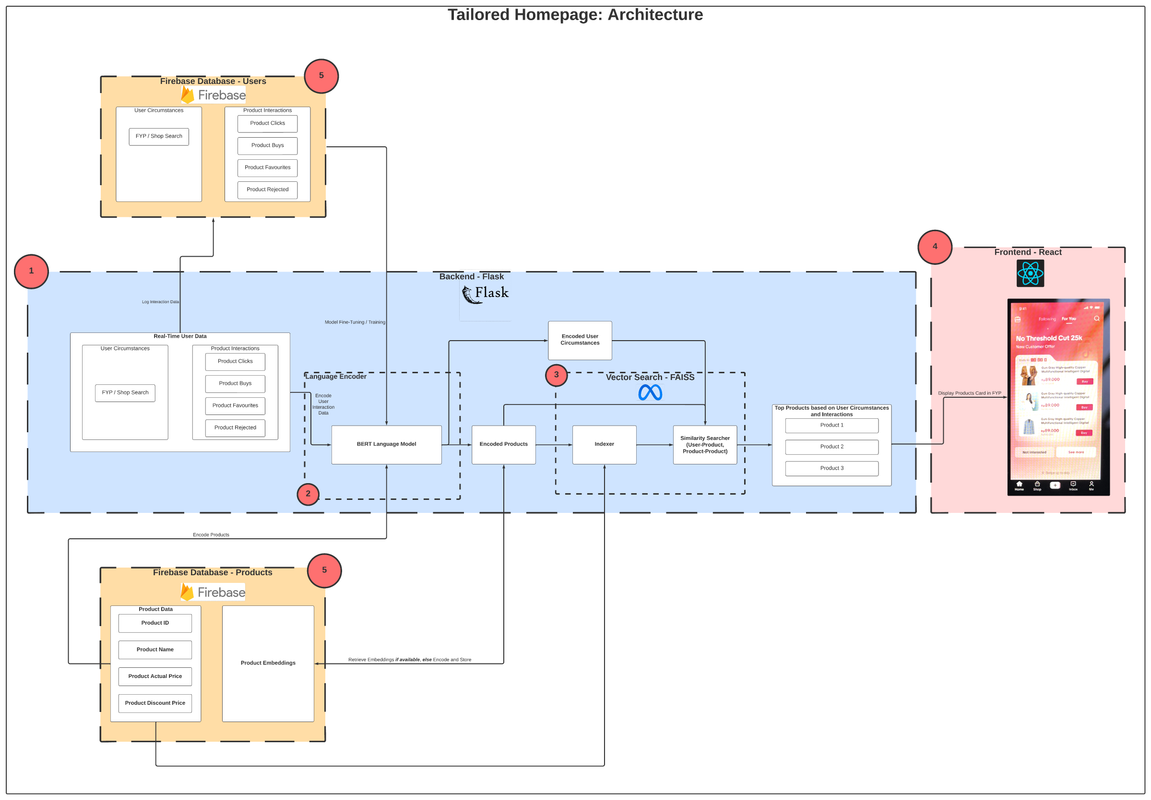
The team's architecture design is shown in the figure below:
For a high-definition view of the architecture diagram, view the diagram on Lucidchart here.
The system is comprised of five main components, (1) The backend, implemented with a lightweight Python-based web library called Flask, (2) the product and user circumstance encoder, implemented using BERT language model, (3) Vector Search with FAISS for similarity search, (4) the frontend/user interface written in React, and (5) Firebase, which is where product and user information are stored.
React was used as the frontend for similating the TikTok For You Page, Search Page, and Product Page.
The backend was implemented using Flask, a lightweight Python-based framework for developing web-based applications or APIs. For our system, the backend handles the following services which can be accessed through endpoints:
| No. | Service | Endpoint |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Batch retrieval of product metadata and embeddings. | - |
| 2 | Logging of user interactions (product clicks) | /click |
| 3 | Building of the vector table (FAISS index) | - |
| 4 | Handling of fast and efficient search via FAISS indexing + Logging of user searches | /search |
| 5 | Retrieval of a product | /product/<product_id> |
| 6 | Generation of product recommendations based on user circumstances and product interactions | /recommend/<user_id> |
Summary of recommendation algorithm
- The embeddings of the products data have been computed ahead of time.
- When the app has started, i.e.,
python3 app.pythis starts the Flask server. - The server will fetch the product metadata and embeddings in batches of 1000.
- After fetching the product data, the embeddings will be used to create a vector table (FAISS index) for fast lookup.
- Every time a user performs a search or a click on a product, that data will be encoded using a BERT language model, and then is logged in the Firebase database collection which stores user interaction data.
- When endpoint no. 6 (
/recommend/<user_id>) is called, it calls therecommend()method in the backend. - The
recommend()method fetches the latest 3 user interaction documents/data for that user in the database, and calls therank_products_with_faiss_search()orrank_products_with_faiss_click()methods depending on whether the interaction logged is a search or click. - Those methods will then return the top 3 products each. Given 3 interaction documents called, it would return a total of 9 products.
- Any duplicate products will be removed with the
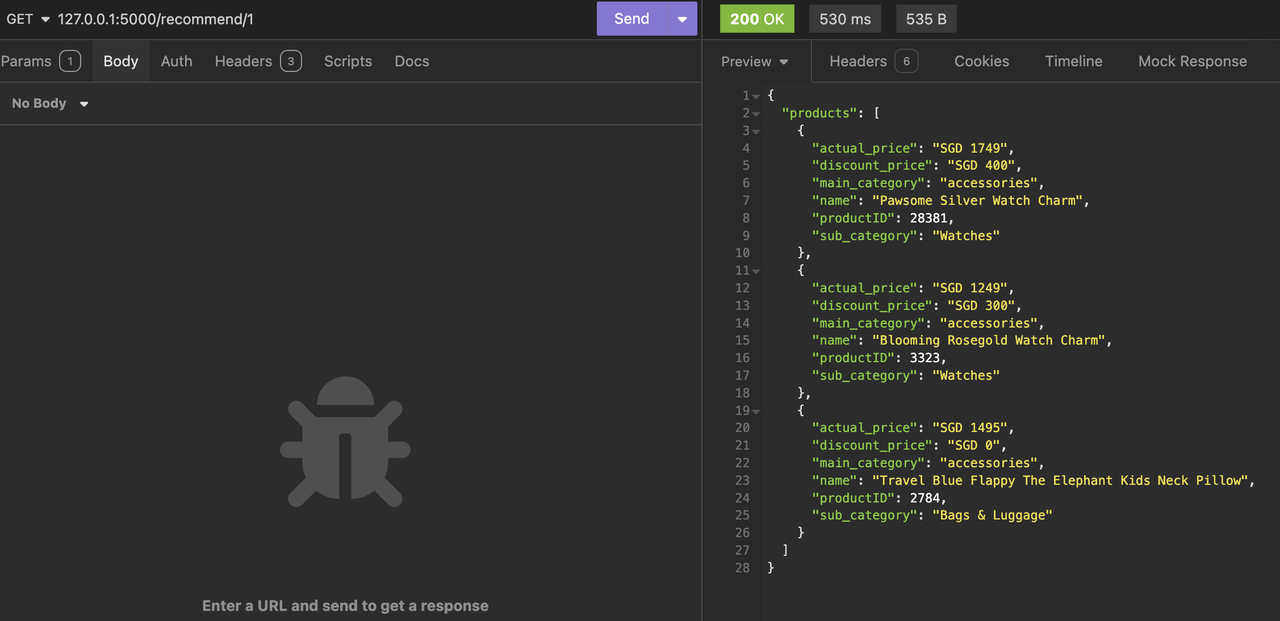
set()function, and the top products in the list is then randomised by calling.shuffle()method on the list. - Slice the list to only contain the first 3 products and then return them as JSON. Below is an example of the recommendation output for a user with an
userIDof 1:
The team has utilised the BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) language model to encode user searches (circumstances) and product-based information.
The rationale on utilising this model is due to the nature of the problem - which is to understand context of user searches and product information. As such, an encoder model is required. The bonus of the BERT model is it's bidirectional attention capability, which means that it is able to understand not only the context given prior tokens, but also subsequent tokens.
The team employed Meta's FAISS to enable more efficient vector lookup for searching and recommending products to the user. Given a search or product vector, the algorithm efficiently computes the L2 (euclidean) distance between the input vector and the vectors stored in the vector table.
The products with greatest similarity to the input vectors are the products recommended to the user.
Firebase serves as the database, storing user data (e.g., product interactions, user circumstance searches) and product data (e.g., product embeddings).
User data was generated using LLM models to create a realistic dataset for testing and development purposes while Products data were retrieved from the Amazon Products Dataset.
-
User Interactions:
- Users interact with the frontend (React) by viewing and engaging with product recommendations.
-
Real-Time Data Logging:
- User interactions (clicks and search) are logged into the Firebase database.
-
Data Processing:
- The backend (Flask) retrieves real-time user data from Firebase.
- User interactions and product details are encoded using the BERT Language Model into embeddings.
-
Product Matching:
- Encoded user interactions are compared with encoded products using FAISS for vector search.
- The most similar products are identified and retrieved.
-
Recommendations Display:
- The top recommended products are sent to the frontend.
- The React frontend displays these products in the FYP card format for the user.
Before running the project, ensure you have the necessary dependencies installed.
First, install the required Python packages for the backend by navigating to the project's root directory and running:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Next, install the necessary packages for the frontend. Navigate to the frontend directory and run:
npm install
To run the backend, cd to the backend directory and execute:
python3 app.py
To run the frontend, cd to the frontend directory and execute:
npm start
We plan to fine-tune the BERT model with more human-like user search data to improve the user-product recommendation accuracy.
Our goal is to enhance the similarity search so it can accurately interpret user inputs like "I want to buy shoes for my 10-year-old son who likes Ben 10" and accurately return the most relevant products. This involves:
- Training the model with possible user queries
- Refining product embeddings to capture user preferences and context better.
These improvements will help provide more accurate and relevant product recommendations.