A Visual Studio Code extension for Ruff, an extremely fast Python linter and code formatter, written in Rust. Available on the Visual Studio Marketplace.
Ruff can be used to replace Flake8 (plus dozens of plugins), Black, isort, pyupgrade, and more, all while executing tens or hundreds of times faster than any individual tool.
The extension ships with ruff==0.1.13.
(Interested in using Ruff with another editor? Check out
ruff-lsp.)
Once installed in Visual Studio Code, ruff will automatically execute when you open or edit a
Python or Jupyter Notebook file.
If you want to disable Ruff, you can disable this extension per workspace in Visual Studio Code.
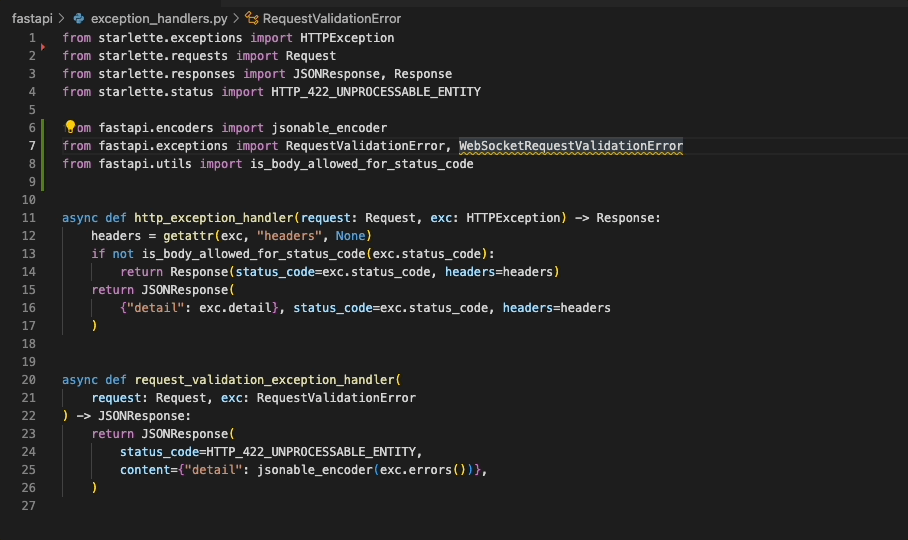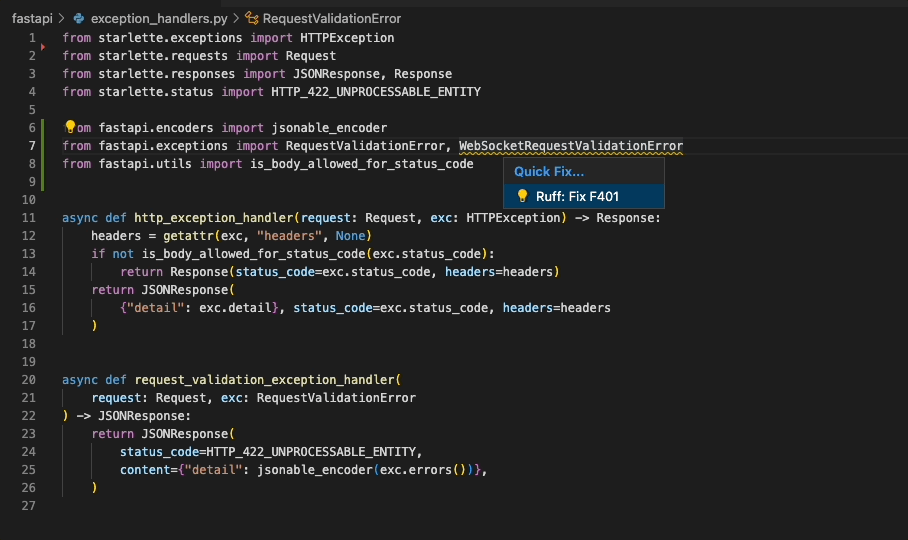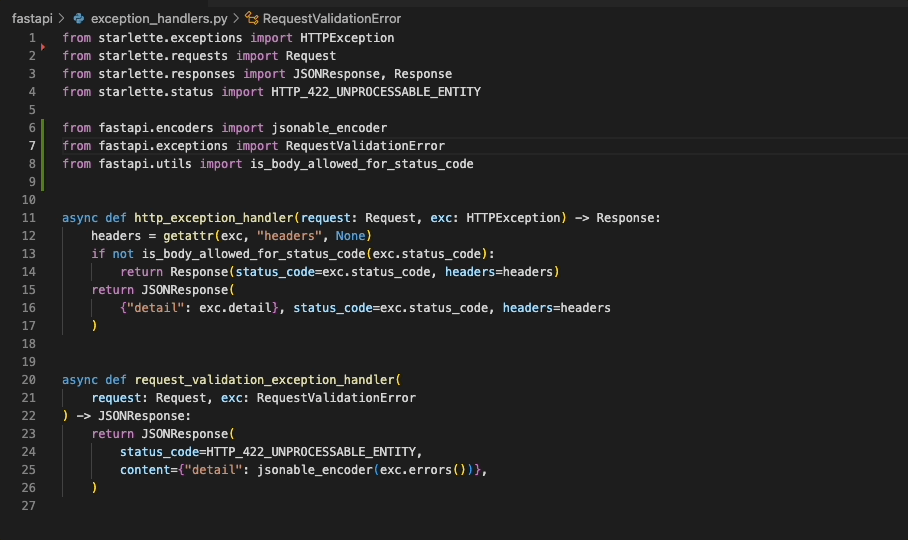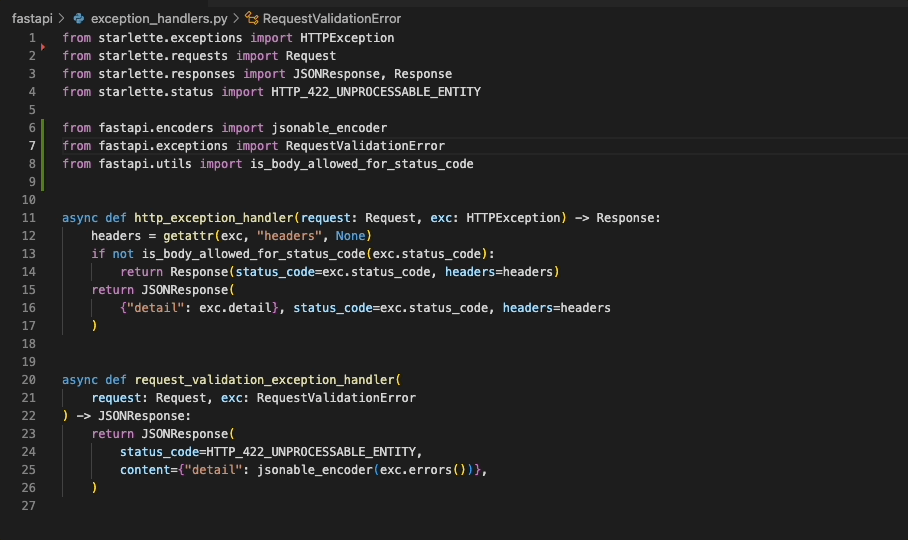
Ruff's automatic fixes are labeled as "safe" and "unsafe". By default, the "Fix all" action will not apply unsafe
fixes. However, unsafe fixes can be applied manually with the "Quick fix" action. Application of unsafe fixes when
using "Fix all" can be enabled by setting unsafe-fixes = true in your Ruff configuration file or adding
--unsafe-fixes flag to the "Lint args" setting.
See the Ruff fix docs for more details on how fix safety works.
The extension has support for Jupyter Notebooks via the Notebook Document Synchronization capabilities of the Language
Server Protocol which were added in 3.17. This has been implemented in ruff-lsp as of version v0.0.43 which provides
full support for all of the existing capabilities available to Python files in Jupyter Notebooks, including diagnostics,
code actions, and formatting.
This requires Ruff version v0.1.3 or later.
| Settings | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| lint.args | [] |
Additional command-line arguments to pass to ruff check, e.g., "args": ["--config=/path/to/pyproject.toml"]. Supports a subset of Ruff's command-line arguments, ignoring those that are required to operate the LSP, like --force-exclude and --verbose. |
| path | [] |
Path to a custom ruff executable, e.g., ["/path/to/ruff"]. |
| interpreter | [] |
Path to a Python interpreter to use to run the linter server. |
| importStrategy | fromEnvironment |
Strategy for loading the ruff executable. fromEnvironment picks up Ruff from the environment, falling back to the bundled version if needed. useBundled uses the version bundled with the extension. |
| lint.run | onType |
Run Ruff on every keystroke (onType) or on save (onSave). |
| enable | true |
Whether to enable the Ruff extension. Modifying this setting requires restarting VS Code to take effect. |
| organizeImports | true |
Whether to register Ruff as capable of handling source.organizeImports actions. |
| fixAll | true |
Whether to register Ruff as capable of handling source.fixAll actions. |
| codeAction.fixViolation.enable | true |
Whether to display Quick Fix actions to autofix violations. |
| codeAction.disableRuleComment.enable | true |
Whether to display Quick Fix actions to disable rules via noqa suppression comments. |
| showNotification | off |
Setting to control when a notification is shown: off, onError, onWarning, always. |
You can configure Ruff to format Python code on-save by enabling the editor.formatOnSave action in
settings.json, and setting Ruff as your default formatter:
{
"[python]": {
"editor.formatOnSave": true,
"editor.defaultFormatter": "charliermarsh.ruff"
}
}And, for Jupyter Notebooks:
{
"notebook.formatOnSave.enabled": true,
"[python]": {
"editor.defaultFormatter": "charliermarsh.ruff"
}
}You can configure Ruff to fix lint violations on-save by enabling the source.fixAll action in
settings.json:
{
"[python]": {
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll": true
}
}
}And, for Jupyter Notebooks:
{
"notebook.codeActionsOnSave": {
"notebook.source.fixAll": true
}
}Similarly, you can configure Ruff to organize imports on-save by enabling the
source.organizeImports action in settings.json:
{
"[python]": {
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.organizeImports": true
}
}
}And, for Jupyter Notebooks:
{
"notebook.codeActionsOnSave": {
"notebook.source.organizeImports": true
}
}Taken together, you can configure Ruff to format, fix, and organize imports on-save via the
following settings.json:
{
"[python]": {
"editor.formatOnSave": true,
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll": true,
"source.organizeImports": true
},
"editor.defaultFormatter": "charliermarsh.ruff"
}
}And, for Jupyter Notebooks:
{
"notebook.formatOnSave.enabled": true,
"notebook.codeActionsOnSave": {
"notebook.source.fixAll": true,
"notebook.source.organizeImports": true
},
"[python]": {
"editor.defaultFormatter": "charliermarsh.ruff"
}
}Note: if you're using Ruff to organize imports in VS Code and also expect to run Ruff from the
command line, you'll want to enable Ruff's isort rules by adding "I" to your
extend-select.
Note: All of the above mentioned Notebook configurations will run the action for each cell individually.
This is the way VS Code handles Notebook actions and is unrelated to ruff-lsp. If you'd prefer to run
them on the entire notebook at once, prefer to use the Ruff prefixed commands such as
Ruff: Organize Imports and Ruff: Fix all auto-fixable problems.
If you're using the VS Code Python extension,
you can configure VS Code to fix violations on-save using Ruff, then re-format with the Black extension,
via the following settings.json:
{
"[python]": {
"editor.formatOnSave": true,
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll": true
},
"editor.defaultFormatter": "ms-python.black-formatter"
}
}If you'd like to use Ruff as a linter, but continue to sort imports with the isort extension,
you can disable Ruff's import-sorting capabilities via the following settings.json:
{
"[python]": {
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll": true,
"source.organizeImports": true
}
},
"ruff.organizeImports": false
}If you'd like to run Ruff on-save, but avoid allowing other extensions to run on-save, you can
use Ruff's scoped source.fixAll and source.organizeImports actions via the following settings.json:
{
"[python]": {
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll.ruff": true,
"source.organizeImports.ruff": true
}
}
}If you'd like to run Ruff, but disable code formatting (by Ruff, or by another formatter), be sure
to unset the editor.defaultFormatter in settings.json:
{
"[python]": {
"editor.defaultFormatter": null,
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll": true
}
}
}The Ruff VS Code extension will respect any Ruff configuration as defined in your project's
pyproject.toml, ruff.toml, or .ruff.toml file (see: Configuring Ruff in the Ruff documentation).
In general, we recommend configuring Ruff via pyproject.toml or ruff.toml so that your
configuration is shared between the VS Code extension and the command-line tool, and between all
contributors to the project.
However, to provide custom arguments to the Ruff CLI, you can use the ruff.lint.args and
ruff.format.args settings in settings.json. For example, to enable the pyupgrade rule set in
VS Code, add the following to settings.json:
{
"ruff.lint.args": ["--extend-select=UP"]
}To override the VS Code extension's Ruff configuration entirely, and override any local
pyproject.toml file or similar, you can pass a custom --config argument to the Ruff CLI, again
using the ruff.lint.args and ruff.format.args options in settings.json:
{
"ruff.lint.args": ["--config=/path/to/ruff.toml"],
"ruff.format.args": ["--config=/path/to/ruff.toml"]
}Finally, to use a common Ruff configuration across all projects, consider creating a user-specific
pyproject.toml or ruff.toml file as described in the FAQ.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Ruff: Fix all auto-fixable problems | Fix all auto-fixable problems. |
| Ruff: Format Imports | Organize imports. |
| Ruff: Format Document | Format the entire document. |
| Ruff: Restart Server | Force restart the linter server. |
This extension requires a version of the VSCode Python extension that supports Python 3.7+. Ruff itself is compatible with Python 3.7 to 3.12.
This extension is based on the Template for VS Code Python tools extensions.
- Install
just, or see thejustfilefor corresponding commands. - Create and activate a virtual environment (e.g.,
python -m venv .venv && source .venv/bin/activate). - Install development dependencies (
just install). - To automatically format the codebase, run:
just fmt. - To run lint and type checks, run:
just check. - To run tests, run:
just test.
To run the extension, navigate to src/extension.ts and run (F5). You should see the LSP output
and Python log messages in the debug console under "Python Server".
- Clone ruff-lsp to, e.g.,
../ruff-lsp. - In
../ruff-lsp, run:pip install -t ../ruff-vscode/bundled/libs/ -e ..
- Clone ruff to, e.g.,
/home/ferris/ruff. - Run
cargo buildin the Ruff repository. - Set "Ruff: Path" to
/home/ferris/ruff/target/debug/ruffin the VS Code settings.
MIT