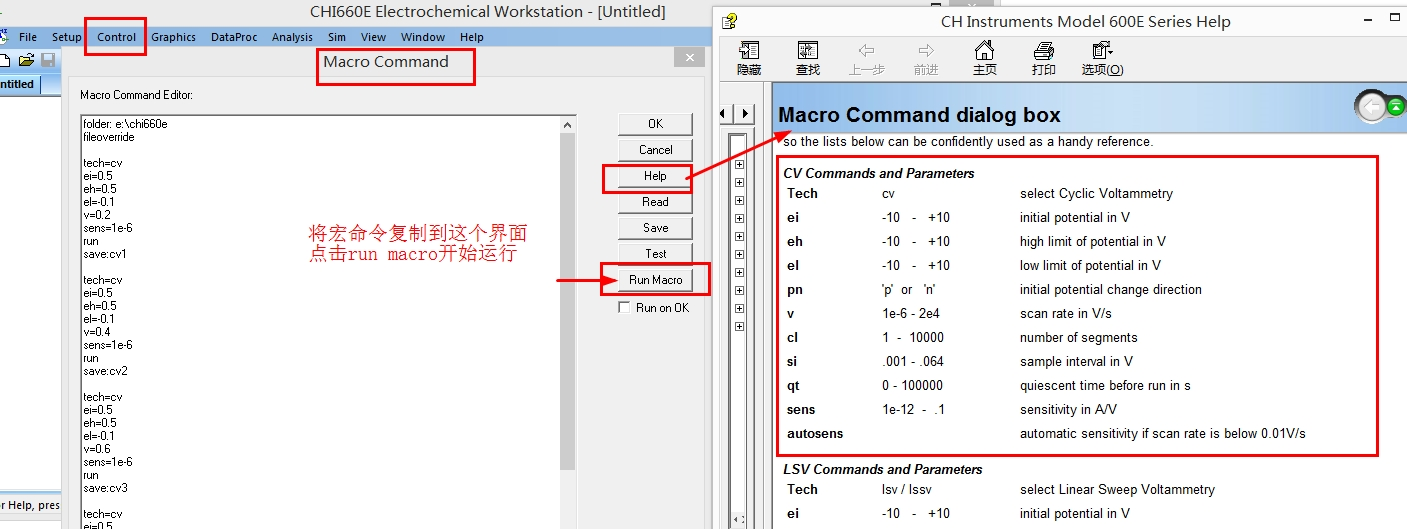
You can find the Macro Command from 'Control->Macro Command'. Use this command to execute a series of other commands. This is analogous to batch files in Windows or shell scripts in Unix/Linux and is much more flexible than the Repetitive Runs command.
Save macro to file for later use. The program displays the Save As dialog box so you can name your file.
Click this button to execute the macro. The system will verify the commands and parameter ranges of your macro before proceeding.
Type in the desired series of commands in the editor box. Each command occupies one line. The command is case insensitive. Space will be ignored. If a parameter is required following the command, a colon ":" or a equal sign "=" is used to separate the command and parameter.
With this generator you can use a few simple functions to generate flexible control scripts that automatically control the instrument for repeated tests and parameter adjustments over long periods of time. The code can generate TXT file and MCR file format at the same time, TXT is easy to edit and modify, MCR format file can be directly read in the editing interface.
Take an electrochemical double layer test as an example:
file=open('output.txt','w+') #creating a read-write text document
chi = CHI660e() #inital the class variables
chi.init_output_txt(file) #inital the output file
CycleNum = (0.001, 0.002, 0.005, 0.01, 0.02, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5) #inital scan rate list
for loop in CycleNum:
chi.init_cv_tech(ei=-0.15, eh=-0.25, el=-0.15, v=loop) #inital cv variables
chi.run_cv(file, 'CV-'+str(loop), add_note=True) #generate the code
chi.gene_mcr_file(file) #Build your macro file. Note: it will make seek point to the end