This project provides an approach so that you can easily create various Microservices for 'Your' Eco-System using a Common core. This project allows you to wrap those specific individual Microservices with a Standards Framework to bootstrap 'Your' Eco-System.
These standard facilities can be shared throughout your Eco-System Product Suite for Developing, Building and Deploying Microservices Architecture Services and Various Components.
An important feature to note, is that Security with a IdP using JWTs is included in this core.
Security within Your Enterprise is critical and using Microservices is no exception.
Otherwise, you run the risk of having a Microservice about as secure as an in home appliance with a default password.
Simply ensure you have the necessary Pre-requisites and you should be good to go...
- Java JDK 8
- Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy Files for Java 8 should be applied. Download Here.
- Maven
Your Microservice is comprised of the following primary components:
- Your Microservice Annotation Definition.
- Your Microservice Configuration to back our Annotation Definition
- IdP -- Identity Provider, Full JWT Token Based Authentication.
- Persistent Store -- Using H2 In Memory Database for Testing and Example Usage. Any JDBC Compliant Database is acceptable.
- Common Services
- Bulletin -- Provides ability to inject System Bulletin Updates via File System.
The Bulletin Service provides a means to respond to current state of runtime Application. - Pulse -- Provides simple status of current Runtime Application.
- Bulletin -- Provides ability to inject System Bulletin Updates via File System.
- REST Client to Interact with Other Your Microservice Instances.
All built upon the Spring Framework standards.
To Build this project, simple ensure your have the above Pre-requisites and issue the following Maven command to build:
mvn clean verify package
Once the project has been built, simple change to the your-microservice-example directory contained in the project and proceed depending upon your applicable Operating System.
Using the default settings, you will bootstrap the example Microservice on Port 9090.
You can change this setting in the applicable application.properties. The JPDA debugging port
is established in these scripts using port 9044.
If you need to modify this, please simply modify the supplied example bootstrap scripts.
To simulate some form of real Data, the H2 Database is seeded with a number of entries to support an initial login to the back-end facilities as well as Integration Tests.
Upon bootstrap of the Data Layer, the SQL Script located with the Core Resources to executed to Load the initial Data into the H2 database.
db\h2\insert-data.sql
Remember, the H2 Database is an In-memory database, so upon subsequent restarts, all data is cleared and initialized per above SQL script.
To persist data in between restarts, simply change the H2 JDBC URL to use the File system for persistence. However, you will need to remove the above initialization with the scripts on your second pass, otherwise exceptions will be thrown and the instance will not boot.
For a Production implementation, you would remove this initialization capability to use an established Database and switch out the H2 JDBC Driver with your applicable driver.
Also included is the Embedded H2 Server Administration application. Which allows you to view and query against the H2 In-Memory database.
To access the H2 application, simply use the following URL:
http://localhost:8082
$ cd your-microservice-example
$ ./bin/run_your_microservice_example.sh
$ cd your-microservice-example
$ bin\run_your_microservice_example.bat
Interfacing with the Your Microservices requires a Http tool to send requests and provide responses.
For JWTs, I am using the JWT Library nimbus-jose-jwt for providing a Java interface to JWT capabilities.
In my examples, I used Postman to perform these operations. However, any tool, such as cUrl can be used to interface with Your-Microservice.
By providing a username and password to authenticate against the Your Microservice IdP, you will receive a JWT, which you will use on all subsequent operations until the Token Expires.
Specify the necessary Headers to specify to Accept application/json.
Specify the necessary Body, which includes the Authentication Data to obtain an Access Token.
Upon successful Authentication of the Entity credentials, you will receive a valid construct which
includes the Bearer JWT, which is then used on all subsequent requests.

An entry in the Token History Table will be created to track this Token and allow this
Token Store to be shared among Microservices to provide a centralized Token Store. Other approaches, of course, can be considered.

Access the Bulletin resource follows:
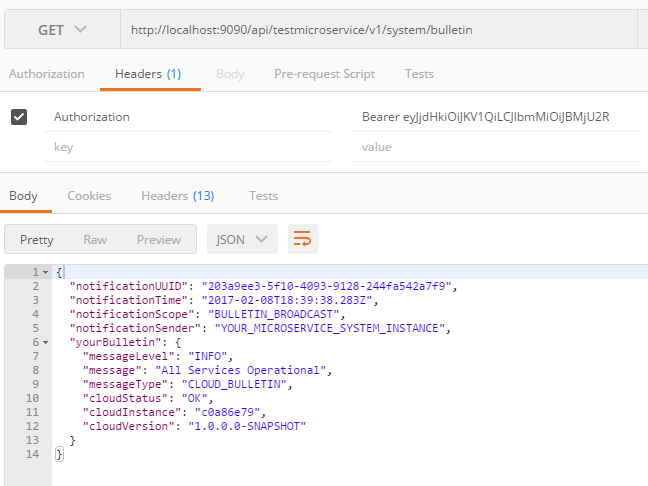
Access the Pulse resource follows:
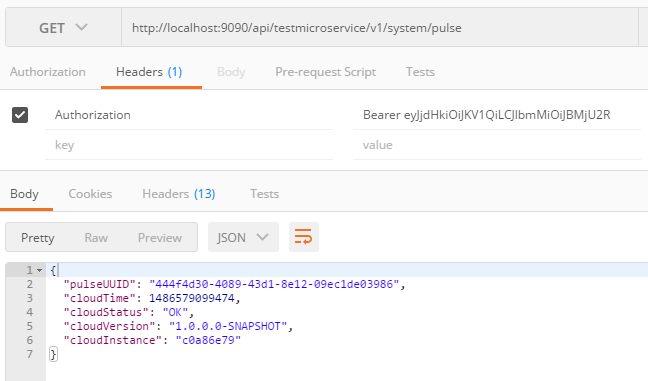
Logging out of the Microservice, simple destroys the associated Token on the backing store.

Once successfully logged out of the Microservice, you will need to obtain a new Access Token to perform any subsequent access.
- 8082: Embedded H2 Server
- 9044: JPDA Debugging
- 9090: Your Microservice Example Http
The Your Microservice Domain Model provides a simple but extensible Data Model to represent Entities, Entity Roles, Entity Organizations, event History and the IdP Token History.
The YourEntityTokenHistory provides a common store for the IdP Tokens. The actual Token is not stored anywhere, however, the JWT's JTI and Subject are contained within each Token History Row to provide lookup to validate that a Token is still active and not flagged as revoked by other means such as an Administrative process. The internal Core scheduler will automatically purge all expired Tokens from this Table.
Once the IdP Filter has validated the incoming JWT, the usage count will be updated, if this JOQL does not properly update the Token's usage count, then the Token is assumed invalid and the access is denied and revoked.
Unlike other IdP, no refresh Token is supplied ever, you only will receive an access token.
- Orchestration Layer -- Build out the Orchestration layer to provide Microservices to work in concert with other Microservices.
-
Applied workaround for issue with Spring Boot repackaging and Failsafe: spring-projects/spring-boot#6254
-
SSL has not been configured, using any type of Token Based Authentication Requires SSL!
If you are intending on running this or any variant, you MUST CONFIGURE and RUN SSL!
- Initial IdP code forked from: https://github.com/brahalla/Cerberus

