Cozystack is an open-source PaaS platform for cloud providers.
With Cozystack, you can transform your bunch of servers into an intelligent system with a simple REST API for spawning Kubernetes clusters, Database-as-a-Service, virtual machines, load balancers, HTTP caching services, and other services with ease.
You can use Cozystack to build your own cloud or to provide a cost-effective development environments.
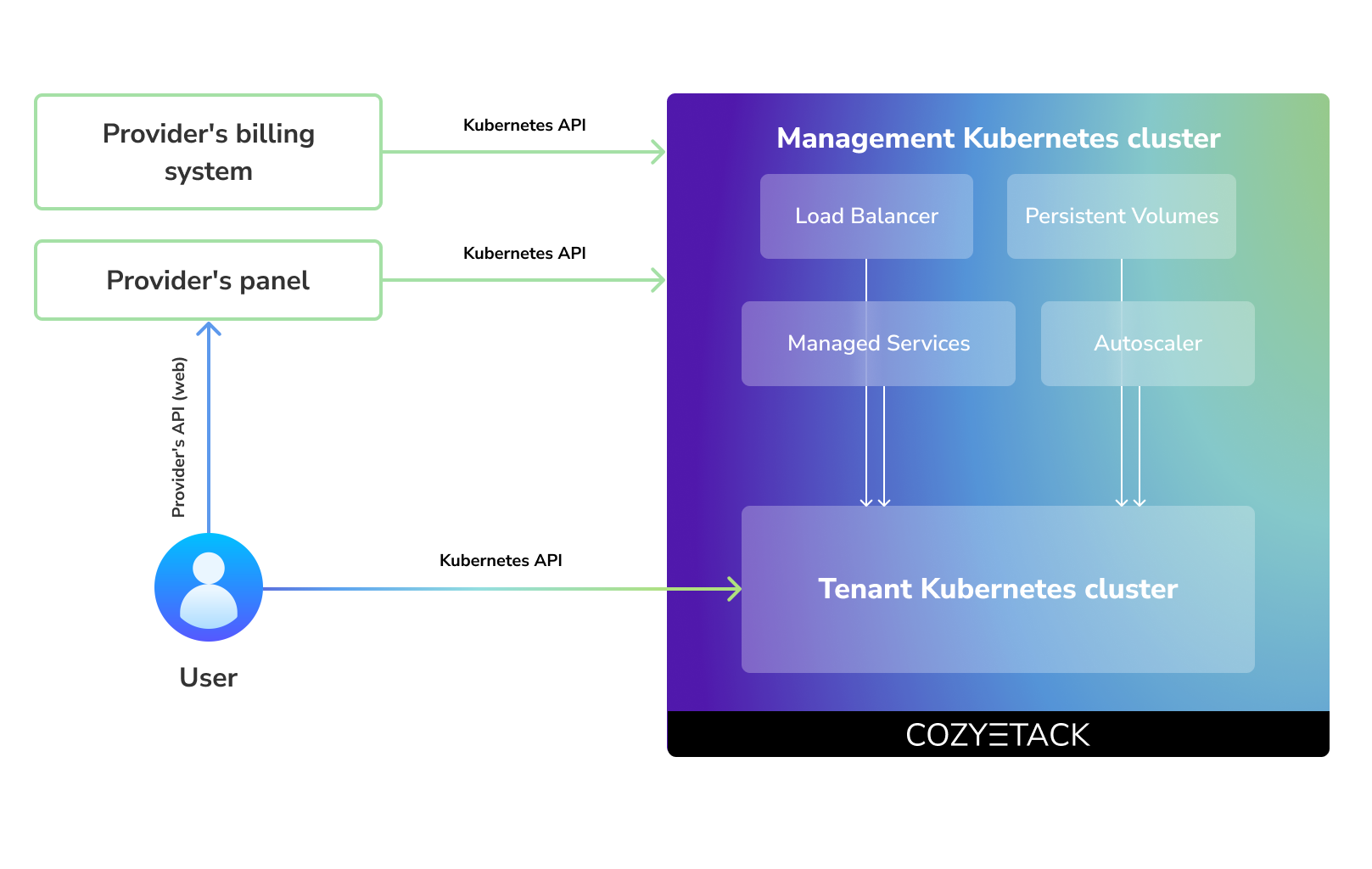
Cozystack positions itself as a kind of framework for building public clouds. The key word here is framework. In this case, it's important to understand that Cozystack is made for cloud providers, not for end users.
Despite having a graphical interface, the current security model does not imply public user access to your management cluster.
Instead, end users get access to their own Kubernetes clusters, can order LoadBalancers and additional services from it, but they have no access and know nothing about your management cluster powered by Cozystack.
Thus, to integrate with your billing system, it's enough to teach your system to go to the management Kubernetes and place a YAML file signifying the service you're interested in. Cozystack will do the rest of the work for you.
One of the use cases is a self-portal for users within your company, where they can order the service they're interested in or a managed database.
You can implement best GitOps practices, where users will launch their own Kubernetes clusters and databases for their needs with a simple commit of configuration into your infrastructure Git repository.
Thanks to the standardization of the approach to deploying applications, you can expand the platform's capabilities using the functionality of standard Helm charts.
We created Cozystack primarily for our own needs, having vast experience in building reliable systems on bare metal infrastructure. This experience led to the formation of a separate boxed product, which is aimed at standardizing and providing a ready-to-use tool for managing your infrastructure.
Currently, Cozystack already solves a huge scope of infrastructure tasks: starting from provisioning bare metal servers, having a ready monitoring system, fast and reliable storage, a network fabric with the possibility of interconnect with your infrastructure, the ability to run virtual machines, databases, and much more right out of the box.
All this makes Cozystack a convenient platform for delivering and launching your application on Bare Metal.
All components of the platform are based on open source tools and technologies which are widely known in the industry.
If a feature being developed for the platform could be useful to a upstream project, it should be contributed to upstream project, rather than being implemented within the platform.
Cozystack is based on Kubernetes and involves close interaction with its API. We don't aim to completely hide the all elements behind a pretty UI or any sort of customizations; instead, we provide a standard interface and teach users how to work with basic primitives. The web interface is used solely for deploying applications and quickly diving into basic concepts of platform.
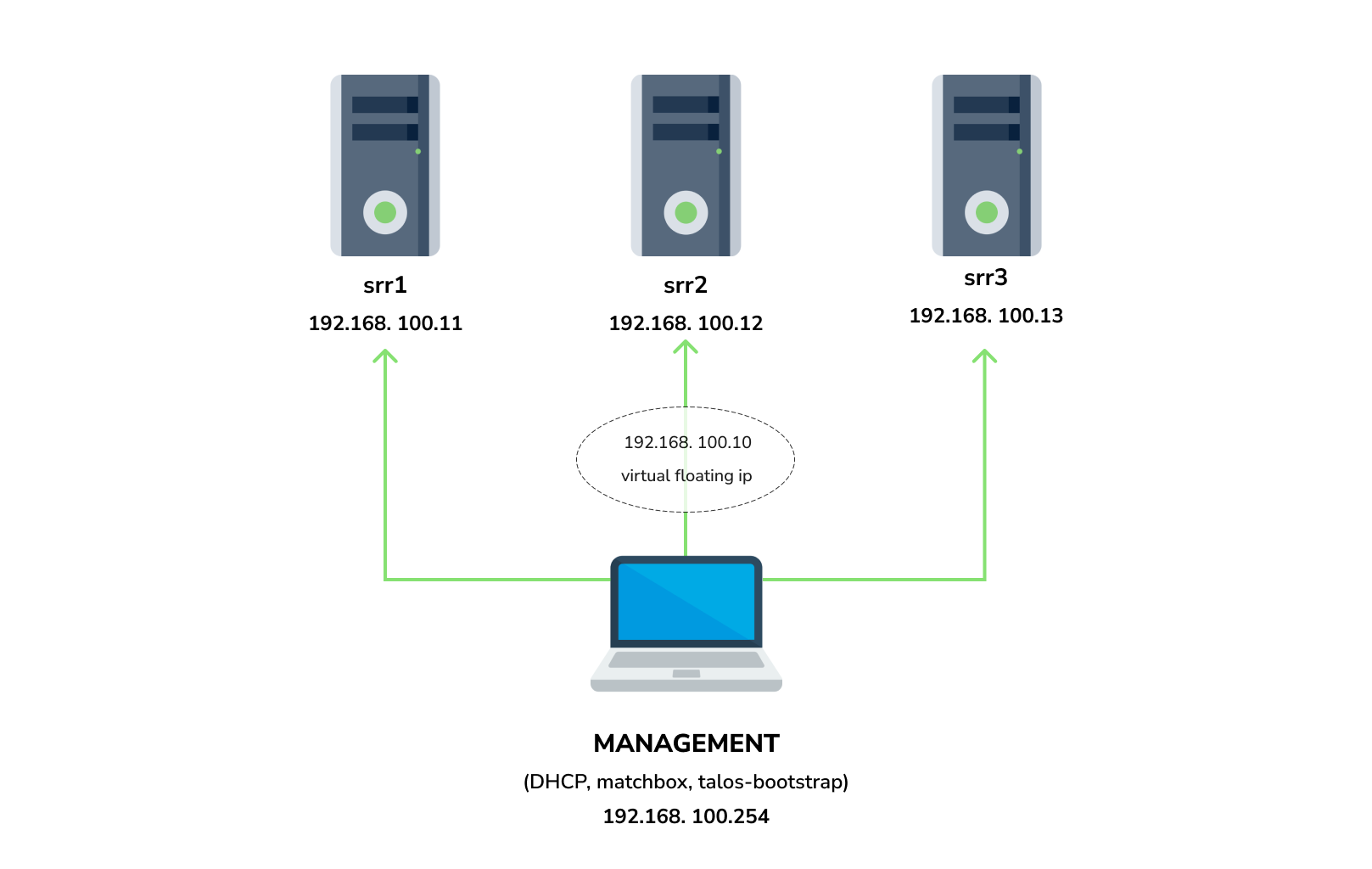
You need 3 physical servers or VMs with nested virtualisation:
CPU: 4 cores
CPU model: host
RAM: 8-16 GB
HDD1: 32 GB
HDD2: 100GB (raw)
And one management VM or physical server connected to the same network. Any Linux system installed on it (eg. Ubuntu should be enough)
Note: The VM should support x86-64-v2 architecture, the most probably you can achieve this by setting cpu model to host
dockertalosctldialognmapmakeyqkubectlhelm
Start matchbox with prebuilt Talos image for Cozystack:
sudo docker run --name=matchbox -d --net=host ghcr.io/aenix-io/cozystack/matchbox:v0.0.1 \
-address=:8080 \
-log-level=debugStart DHCP-Server:
sudo docker run --name=dnsmasq -d --cap-add=NET_ADMIN --net=host quay.io/poseidon/dnsmasq \
-d -q -p0 \
--dhcp-range=192.168.100.3,192.168.100.254 \
--dhcp-option=option:router,192.168.100.1 \
--enable-tftp \
--tftp-root=/var/lib/tftpboot \
--dhcp-match=set:bios,option:client-arch,0 \
--dhcp-boot=tag:bios,undionly.kpxe \
--dhcp-match=set:efi32,option:client-arch,6 \
--dhcp-boot=tag:efi32,ipxe.efi \
--dhcp-match=set:efibc,option:client-arch,7 \
--dhcp-boot=tag:efibc,ipxe.efi \
--dhcp-match=set:efi64,option:client-arch,9 \
--dhcp-boot=tag:efi64,ipxe.efi \
--dhcp-userclass=set:ipxe,iPXE \
--dhcp-boot=tag:ipxe,http://192.168.100.254:8080/boot.ipxe \
--log-queries \
--log-dhcpWhere:
192.168.100.3,192.168.100.254range to allocate IPs from192.168.100.1your gateway192.168.100.254is address of your management server
Check status of containers:
docker ps
example output:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
22044f26f74d quay.io/poseidon/dnsmasq "/usr/sbin/dnsmasq -…" 6 seconds ago Up 5 seconds dnsmasq
231ad81ff9e0 ghcr.io/aenix-io/cozystack/matchbox:v0.0.1 "/matchbox -address=…" 58 seconds ago Up 57 seconds matchboxWrite configuration for Cozystack:
cat > patch.yaml <<\EOT
machine:
kubelet:
nodeIP:
validSubnets:
- 192.168.100.0/24
kernel:
modules:
- name: openvswitch
- name: drbd
parameters:
- usermode_helper=disabled
- name: zfs
install:
image: ghcr.io/aenix-io/cozystack/talos:v1.6.4
files:
- content: |
[plugins]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri"]
device_ownership_from_security_context = true
path: /etc/cri/conf.d/20-customization.part
op: create
cluster:
network:
cni:
name: none
podSubnets:
- 10.244.0.0/16
serviceSubnets:
- 10.96.0.0/16
EOT
cat > patch-controlplane.yaml <<\EOT
cluster:
allowSchedulingOnControlPlanes: true
controllerManager:
extraArgs:
bind-address: 0.0.0.0
scheduler:
extraArgs:
bind-address: 0.0.0.0
apiServer:
certSANs:
- 127.0.0.1
proxy:
disabled: true
discovery:
enabled: false
etcd:
advertisedSubnets:
- 192.168.100.0/24
EOTRun talos-bootstrap to deploy cluster:
talos-bootstrap installSave admin kubeconfig to access your Kubernetes cluster:
cp -i kubeconfig ~/.kube/configCheck connection:
kubectl get nsexample output:
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 7m56s
kube-node-lease Active 7m56s
kube-public Active 7m56s
kube-system Active 7m56sNote:: All nodes should currently show as "Not Ready", don't worry about that, this is because you disabled the default CNI plugin in the previous step. Cozystack will install it's own CNI-plugin on the next step.
write config for cozystack:
Note: please make sure that you written the same setting specified in patch.yaml and patch-controlplane.yaml files.
cat > cozystack-config.yaml <<\EOT
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: cozystack
namespace: cozy-system
data:
cluster-name: "cozystack"
ipv4-pod-cidr: "10.244.0.0/16"
ipv4-pod-gateway: "10.244.0.1"
ipv4-svc-cidr: "10.96.0.0/16"
ipv4-join-cidr: "100.64.0.0/16"
EOTCreate namesapce and install Cozystack system components:
kubectl create ns cozy-system
kubectl apply -f cozystack-config.yaml
kubectl apply -f manifests/cozystack-installer.yaml(optional) You can track the logs of installer:
kubectl logs -n cozy-system deploy/cozystack -fWait for a while, then check the status of installation:
kubectl get hr -AWait until all releases become to Ready state:
NAMESPACE NAME AGE READY STATUS
cozy-cert-manager cert-manager 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-cert-manager cert-manager-issuers 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-cilium cilium 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-cluster-api capi-operator 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-cluster-api capi-providers 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-dashboard dashboard 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-fluxcd cozy-fluxcd 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-grafana-operator grafana-operator 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-kamaji kamaji 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-kubeovn kubeovn 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-kubevirt-cdi kubevirt-cdi 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-kubevirt-cdi kubevirt-cdi-operator 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-kubevirt kubevirt 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-kubevirt kubevirt-operator 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-linstor linstor 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-linstor piraeus-operator 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-mariadb-operator mariadb-operator 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-metallb metallb 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-monitoring monitoring 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-postgres-operator postgres-operator 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-rabbitmq-operator rabbitmq-operator 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-redis-operator redis-operator 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-telepresence telepresence 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
cozy-victoria-metrics-operator victoria-metrics-operator 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeeded
tenant-root tenant-root 4m1s True Release reconciliation succeededSetup alias to access LINSTOR:
alias linstor='kubectl exec -n cozy-linstor deploy/linstor-controller -- linstor'list your nodes
linstor node listexample output:
+-------------------------------------------------------+
| Node | NodeType | Addresses | State |
|=======================================================|
| srv1 | SATELLITE | 192.168.100.11:3367 (SSL) | Online |
| srv2 | SATELLITE | 192.168.100.12:3367 (SSL) | Online |
| srv3 | SATELLITE | 192.168.100.13:3367 (SSL) | Online |
+-------------------------------------------------------+list empty devices:
linstor physical-storage listexample output:
+--------------------------------------------+
| Size | Rotational | Nodes |
|============================================|
| 107374182400 | True | srv3[/dev/sdb] |
| | | srv1[/dev/sdb] |
| | | srv2[/dev/sdb] |
+--------------------------------------------+create storage pools:
linstor ps cdp lvm srv1 /dev/sdb --pool-name data --storage-pool data
linstor ps cdp lvm srv2 /dev/sdb --pool-name data --storage-pool data
linstor ps cdp lvm srv3 /dev/sdb --pool-name data --storage-pool datalist storage pools:
linstor sp lexample output:
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| StoragePool | Node | Driver | PoolName | FreeCapacity | TotalCapacity | CanSnapshots | State | SharedName |
|=====================================================================================================================================|
| DfltDisklessStorPool | srv1 | DISKLESS | | | | False | Ok | srv1;DfltDisklessStorPool |
| DfltDisklessStorPool | srv2 | DISKLESS | | | | False | Ok | srv2;DfltDisklessStorPool |
| DfltDisklessStorPool | srv3 | DISKLESS | | | | False | Ok | srv3;DfltDisklessStorPool |
| data | srv1 | LVM | data | 100.00 GiB | 100.00 GiB | False | Ok | srv1;data |
| data | srv2 | LVM | data | 100.00 GiB | 100.00 GiB | False | Ok | srv2;data |
| data | srv3 | LVM | data | 100.00 GiB | 100.00 GiB | False | Ok | srv3;data |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+Create default storage classes:
kubectl create -f- <<EOT
---
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: local
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
provisioner: linstor.csi.linbit.com
parameters:
linstor.csi.linbit.com/storagePool: "data"
linstor.csi.linbit.com/layerList: "storage"
linstor.csi.linbit.com/allowRemoteVolumeAccess: "false"
volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer
allowVolumeExpansion: true
---
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: replicated
provisioner: linstor.csi.linbit.com
parameters:
linstor.csi.linbit.com/storagePool: "data"
linstor.csi.linbit.com/autoPlace: "3"
linstor.csi.linbit.com/layerList: "drbd storage"
linstor.csi.linbit.com/allowRemoteVolumeAccess: "true"
property.linstor.csi.linbit.com/DrbdOptions/auto-quorum: suspend-io
property.linstor.csi.linbit.com/DrbdOptions/Resource/on-no-data-accessible: suspend-io
property.linstor.csi.linbit.com/DrbdOptions/Resource/on-suspended-primary-outdated: force-secondary
property.linstor.csi.linbit.com/DrbdOptions/Net/rr-conflict: retry-connect
volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer
allowVolumeExpansion: true
EOTlist storageclasses:
kubectl get storageclassesexample output:
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
local (default) linstor.csi.linbit.com Delete WaitForFirstConsumer true 11m
replicated linstor.csi.linbit.com Delete WaitForFirstConsumer true 11mTo access your services select the range of unused IPs, eg. 192.168.100.200-192.168.100.250
Note: These IPs should be from the same network as nodes or they should have all necessary routes for them.
Configure MetalLB to use and announce this range:
kubectl create -f- <<EOT
---
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: L2Advertisement
metadata:
name: cozystack
namespace: cozy-metallb
spec:
ipAddressPools:
- cozystack
---
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: IPAddressPool
metadata:
name: cozystack
namespace: cozy-metallb
spec:
addresses:
- 192.168.100.200-192.168.100.250
autoAssign: true
avoidBuggyIPs: false
EOTGet token from tenant-root:
kubectl get secret -n tenant-root tenant-root -o go-template='{{ printf "%s\n" (index .data "token" | base64decode) }}'Enable port forward to cozy-dashboard:
kubectl port-forward -n cozy-dashboard svc/dashboard 8080:80Open: http://localhost:8080/
- Select
tenant-root - Click
Upgradebutton - Write a domain into
hostwhich you wish to use as parent domain for all deployed applications Note:- if you have no domain yet, you can use
192.168.100.200.nip.iowhere192.168.100.200is a first IP address in your network addresses range. - alternatively you can leave the default value, however you'll be need to modify your
/etc/hostsevery time you want to access specific application.
- if you have no domain yet, you can use
- Set
etcd,monitoringandingressto enabled position - Click Deploy
Check persistent volumes provisioned:
kubectl get pvc -n tenant-rootexample output:
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS AGE
data-etcd-0 Bound pvc-4cbd29cc-a29f-453d-b412-451647cd04bf 10Gi RWO local <unset> 2m10s
data-etcd-1 Bound pvc-1579f95a-a69d-4a26-bcc2-b15ccdbede0d 10Gi RWO local <unset> 115s
data-etcd-2 Bound pvc-907009e5-88bf-4d18-91e7-b56b0dbfb97e 10Gi RWO local <unset> 91s
grafana-db-1 Bound pvc-7b3f4e23-228a-46fd-b820-d033ef4679af 10Gi RWO local <unset> 2m41s
grafana-db-2 Bound pvc-ac9b72a4-f40e-47e8-ad24-f50d843b55e4 10Gi RWO local <unset> 113s
vmselect-cachedir-vmselect-longterm-0 Bound pvc-622fa398-2104-459f-8744-565eee0a13f1 2Gi RWO local <unset> 2m21s
vmselect-cachedir-vmselect-longterm-1 Bound pvc-fc9349f5-02b2-4e25-8bef-6cbc5cc6d690 2Gi RWO local <unset> 2m21s
vmselect-cachedir-vmselect-shortterm-0 Bound pvc-7acc7ff6-6b9b-4676-bd1f-6867ea7165e2 2Gi RWO local <unset> 2m41s
vmselect-cachedir-vmselect-shortterm-1 Bound pvc-e514f12b-f1f6-40ff-9838-a6bda3580eb7 2Gi RWO local <unset> 2m40s
vmstorage-db-vmstorage-longterm-0 Bound pvc-e8ac7fc3-df0d-4692-aebf-9f66f72f9fef 10Gi RWO local <unset> 2m21s
vmstorage-db-vmstorage-longterm-1 Bound pvc-68b5ceaf-3ed1-4e5a-9568-6b95911c7c3a 10Gi RWO local <unset> 2m21s
vmstorage-db-vmstorage-shortterm-0 Bound pvc-cee3a2a4-5680-4880-bc2a-85c14dba9380 10Gi RWO local <unset> 2m41s
vmstorage-db-vmstorage-shortterm-1 Bound pvc-d55c235d-cada-4c4a-8299-e5fc3f161789 10Gi RWO local <unset> 2m41sCheck all pods are running:
kubectl get pod -n tenant-rootexample output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
etcd-0 1/1 Running 0 2m1s
etcd-1 1/1 Running 0 106s
etcd-2 1/1 Running 0 82s
grafana-db-1 1/1 Running 0 119s
grafana-db-2 1/1 Running 0 13s
grafana-deployment-74b5656d6-5dcvn 1/1 Running 0 90s
grafana-deployment-74b5656d6-q5589 1/1 Running 1 (105s ago) 111s
root-ingress-controller-6ccf55bc6d-pg79l 2/2 Running 0 2m27s
root-ingress-controller-6ccf55bc6d-xbs6x 2/2 Running 0 2m29s
root-ingress-defaultbackend-686bcbbd6c-5zbvp 1/1 Running 0 2m29s
vmalert-vmalert-644986d5c-7hvwk 2/2 Running 0 2m30s
vmalertmanager-alertmanager-0 2/2 Running 0 2m32s
vmalertmanager-alertmanager-1 2/2 Running 0 2m31s
vminsert-longterm-75789465f-hc6cz 1/1 Running 0 2m10s
vminsert-longterm-75789465f-m2v4t 1/1 Running 0 2m12s
vminsert-shortterm-78456f8fd9-wlwww 1/1 Running 0 2m29s
vminsert-shortterm-78456f8fd9-xg7cw 1/1 Running 0 2m28s
vmselect-longterm-0 1/1 Running 0 2m12s
vmselect-longterm-1 1/1 Running 0 2m12s
vmselect-shortterm-0 1/1 Running 0 2m31s
vmselect-shortterm-1 1/1 Running 0 2m30s
vmstorage-longterm-0 1/1 Running 0 2m12s
vmstorage-longterm-1 1/1 Running 0 2m12s
vmstorage-shortterm-0 1/1 Running 0 2m32s
vmstorage-shortterm-1 1/1 Running 0 2m31sNow you can get public IP of ingress controller:
kubectl get svc -n tenant-root root-ingress-controller
example output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
root-ingress-controller LoadBalancer 10.96.16.141 192.168.100.200 80:31632/TCP,443:30113/TCP 3m33sUse grafana.example.org (under 192.168.100.200) to access system monitoring, where example.org is your domain specified for tenant-root
- login:
admin - password:
kubectl get secret -n tenant-root grafana-admin-password -o go-template='{{ printf "%s\n" (index .data "password" | base64decode) }}'