The LDBC SNB Data Generator (Datagen) produces the datasets for the LDBC Social Network Benchmark's workloads. The generator is designed to produce directed labelled graphs that mimic the characteristics of those graphs of real data. A detailed description of the schema produced by Datagen, as well as the format of the output files, can be found in the latest version of official LDBC SNB specification document.
📜 If you wish to cite the LDBC SNB, please refer to the documentation repository.
- The Hadoop-based Datagen generates the Interactive workload's SF1-1000 data sets.
- For the BI workload, use the Spark-based Datagen (in this repository).
- For the Interactive workloads's larger data sets, see the conversion script in the driver repository.
For each commit on the main branch, the CI deploys freshly generated small data sets.
To assemble the JAR file with SBT, run:
sbt assemblySome of the build utilities are written in Python. To use them, you have to create a Python virtual environment and install the dependencies.
E.g. with pyenv and pyenv-virtualenv:
pyenv install 3.7.13
pyenv virtualenv 3.7.13 ldbc_datagen_tools
pyenv local ldbc_datagen_tools
pip install -U pip
pip install ./toolsIf the environment already exists, activate it with:
pyenv activateThe ./tools/run.py script is intended for local runs. To use it, download and extract Spark as follows.
Spark 3.2.x is the recommended runtime to use. The rest of the instructions are provided assuming Spark 3.2.x.
To place Spark under /opt/:
scripts/get-spark-to-opt.sh
export SPARK_HOME="/opt/spark-3.2.2-bin-hadoop3.2"
export PATH="${SPARK_HOME}/bin":"${PATH}"To place it under ${HOME}/:
scripts/get-spark-to-home.sh
export SPARK_HOME="${HOME}/spark-3.2.2-bin-hadoop3.2"
export PATH="${SPARK_HOME}/bin":"${PATH}"Both Java 8 and Java 11 are supported, but Java 17 is not (Spark 3.2.2 will fail, since it uses internal Java APIs and does not set the permissions appropriately).
Run:
scripts/build.shOnce you have Spark in place and built the JAR file, run the generator as follows:
export PLATFORM_VERSION=$(sbt -batch -error 'print platformVersion')
export DATAGEN_VERSION=$(sbt -batch -error 'print version')
export LDBC_SNB_DATAGEN_JAR=$(sbt -batch -error 'print assembly / assemblyOutputPath')
./tools/run.py <runtime configuration arguments> -- <generator configuration arguments>The runtime configuration arguments determine the amount of memory, number of threads, degree of parallelism. For a list of arguments, see:
./tools/run.py --helpTo generate a single part-* file, reduce the parallelism (number of Spark partitions) to 1.
./tools/run.py --parallelism 1 -- --format csv --scale-factor 0.003 --mode biThe generator configuration arguments allow the configuration of the output directory, output format, layout, etc.
To get a complete list of the arguments, pass --help to the JAR file:
./tools/run.py -- --help-
Generating
csv-composite-merged-fkfiles in BI mode resulting in compressed.csv.gzfiles:./tools/run.py -- --format csv --scale-factor 0.003 --mode bi --format-options compression=gzip
-
Generating
csv-composite-merged-fkfiles in BI mode and generating factors:./tools/run.py -- --format csv --scale-factor 0.003 --mode bi --generate-factors
-
Generating CSVs in raw mode:
./tools/run.py -- --format csv --scale-factor 0.003 --mode raw --output-dir sf0.003-raw
-
Generating Parquet files in BI mode:
./tools/run.py -- --format parquet --scale-factor 0.003 --mode bi
-
Use epoch milliseconds encoded as longs for serializing date and datetime values in BI mode (this is equivalent to using the
LongDateFormatterin the Hadoop Datagen):./tools/run.py -- --format csv --scale-factor 0.003 --mode bi --epoch-millis
-
For the BI mode, the
--format-optionsargument allows passing formatting options such as timestamp/date formats, the presence/abscence of headers (see the Spark formatting options for details), and whether quoting the fields in the CSV required:./tools/run.py -- --format csv --scale-factor 0.003 --mode bi --format-options timestampFormat=MM/dd/y\ HH:mm:ss,dateFormat=MM/dd/y,header=false,quoteAll=true -
The
--explode-attrsargument implies one of thecsv-singular-{projected-fk,merged-fk}formats, which has separate files to store multi-valued attributes (email,speaks)../tools/run.py -- --format csv --scale-factor 0.003 --mode bi --explode-attrs
-
The
--explode-edgesargument implies one of thecsv-{composite,singular}-projected-fkformats, which has separate files to store many-to-one edges (e.g.Person_isLocatedIn_City,Tag_hasType_TagClass, etc.)../tools/run.py -- --format csv --scale-factor 0.003 --mode bi --explode-edges
-
The
--explode-attrsand--explode-edgesarguments together imply thecsv-singular-projected-fkformat:./tools/run.py -- --format csv --scale-factor 0.003 --mode bi --explode-attrs --explode-edges
To change the Spark configuration directory, adjust the SPARK_CONF_DIR environment variable.
A complex example:
export SPARK_CONF_DIR=./conf
./tools/run.py --parallelism 4 --memory 8G -- --format csv --format-options timestampFormat=MM/dd/y\ HH:mm:ss,dateFormat=MM/dd/y --explode-edges --explode-attrs --mode bi --scale-factor 0.003It is also possible to pass a parameter file:
./tools/run.py -- --format csv --param-file params.iniSNB Datagen images are available via Docker Hub.
The image tags follow the pattern ${DATAGEN_VERSION/+/-}-${PLATFORM_VERSION}, e.g ldbc/datagen-standalone:0.5.0-2.12_spark3.2.
When building images ensure that you use BuildKit.
The standalone image bundles Spark with the JAR and Python helpers, so you can run a workload in a container similarly to a local run, as you can see in this example:
export SF=0.003
mkdir -p out_sf${SF}_bi # create output directory
docker run \
--mount type=bind,source="$(pwd)"/out_sf${SF}_bi,target=/out \
--mount type=bind,source="$(pwd)"/conf,target=/conf,readonly \
-e SPARK_CONF_DIR=/conf \
ldbc/datagen-standalone:${DATAGEN_VERSION/+/-}-${PLATFORM_VERSION} \
--parallelism 1 \
-- \
--format csv \
--scale-factor ${SF} \
--mode bi \
--generate-factorsThe standalone Docker image can be built with the provided Dockerfile. To build, execute the following command from the repository directory:
export PLATFORM_VERSION=$(sbt -batch -error 'print platformVersion')
export DATAGEN_VERSION=$(sbt -batch -error 'print version')
export DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1
docker build . --target=standalone -t ldbc/datagen-standalone:${DATAGEN_VERSION/+/-}-${PLATFORM_VERSION}The ldbc/datagen-jar image contains the assembly JAR, so it can bundled in your custom container:
FROM my-spark-image
ARG VERSION
COPY --from=ldbc/datagen-jar:${VERSION} /jar /lib/ldbc-datagen.jar
The JAR-only Docker image can be built with the provided Dockerfile. To build, execute the following command from the repository directory:
docker build . --target=jar -t ldbc/datagen-jar:${DATAGEN_VERSION/+/-}-${PLATFORM_VERSION}To release a new snapshot version on Docker Hub, run:
docker tag ldbc/datagen-jar:${DATAGEN_VERSION/+/-}-${PLATFORM_VERSION} ldbc/datagen-jar:latest
docker push ldbc/datagen-jar:${DATAGEN_VERSION/+/-}-${PLATFORM_VERSION}
docker push ldbc/datagen-jar:latest
docker tag ldbc/datagen-standalone:${DATAGEN_VERSION/+/-}-${PLATFORM_VERSION} ldbc/datagen-standalone:latest
docker push ldbc/datagen-standalone:${DATAGEN_VERSION/+/-}-${PLATFORM_VERSION}
docker push ldbc/datagen-standalone:latestTo release a new stable version, create a new Git tag (e.g. by creating a new release on GitHub), then build the Docker image and push it.
We provide scripts to run Datagen on AWS EMR. See the README in the ./tools/emr directory for details.
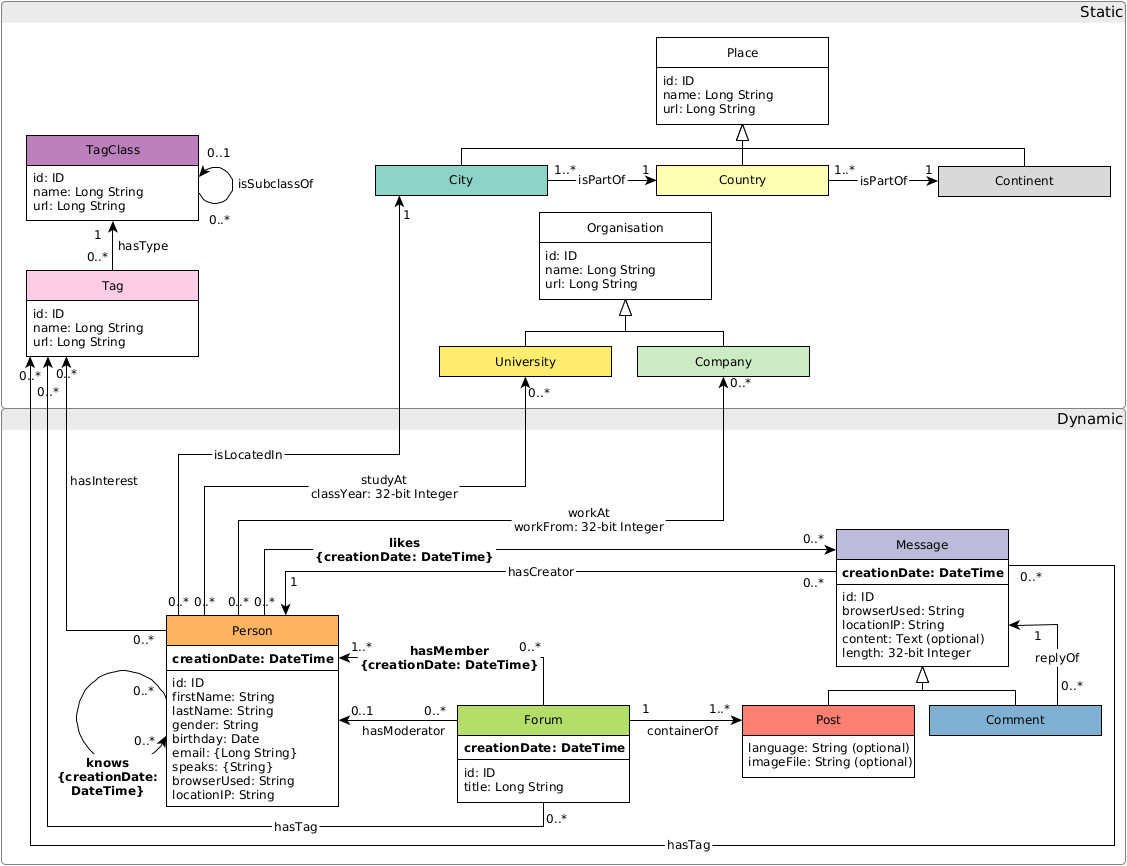
The graph schema is as follows:
- When running the tests, they might throw a
java.net.UnknownHostException: your_hostname: your_hostname: Name or service not knowncoming fromorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobSubmitter.submitJobInternal. The solution is to add an entry of your machine's hostname to the/etc/hostsfile:127.0.1.1 your_hostname. - If you are using Docker and Spark runs out of space, make sure that Docker has enough space to store its containers. To move the location of the Docker containers to a larger disk, stop Docker, edit (or create) the
/etc/docker/daemon.jsonfile and add{ "data-root": "/path/to/new/docker/data/dir" }, then sync the old folder if needed, and restart Docker. (See more detailed instructions). - If you are using a local Spark installation and run out of space in
/tmp(java.io.IOException: No space left on device), set theSPARK_LOCAL_DIRSto point to a directory with enough free space. - The Docker image may throw the following error when generating factors
java.io.FileNotFoundException: /tmp/blockmgr-.../.../temp_shuffle_... (No file descriptors available). This error occurs on Fedora 36 host machines. Changing to an Ubuntu 22.04 host machine resolves the problem. Related issue: #420.