-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
1 changed file
with
105 additions
and
6 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -1,24 +1,123 @@ | ||
| # uPixels | ||
| # μPixels | ||
|
|
||
| ### RGB LED Strip controller for MicroPython micro-controllers | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ### Addressable RGB LED Strip controller for MicroPython enabled micro-controllers | ||
|
|
||
| ## Features | ||
|
|
||
| - User-Friendly - includes an user interface hosted from the micro-controller itself! | ||
| - Complete control over animations from delay time, color, brightness | ||
| - User-friendly interface hosted from the micro-controller itself! | ||
| - Completely customizable animations and user interface which is written in plain HTML/CSS/JS! | ||
| - Use with the user interface or just use the Animations API | ||
|
|
||
| - Customizable - completely customizable animations and user interface which is written in plain HTML/CSS/JS! | ||
| ### Out of the Box Animations: | ||
|
|
||
| - Modular - use with the user interface or just use the Animations API | ||
| - Rainbow | ||
| - Bounce | ||
| - Chase | ||
| - RGB Fade | ||
| - Alternating Colors | ||
| - Random Fill | ||
| - Fill from Middle | ||
| - Fill from Sides | ||
| - Fill Strip | ||
|
|
||
| ## Screenshot | ||
|
|
||
| <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/petabite/uPixels/master/images/screenshot.png" width="400"> | ||
|
|
||
| ## Requirements | ||
|
|
||
| - Micro-controller that supports MicroPython(like the NodeMCU ESP8266) | ||
| - WS2812 Individually Addressable RGB LEDs | ||
| - 3V3 to 5V Logic Level Shifter | ||
| - A regular LED(optional) | ||
| - 270 ohm resistor | ||
| - 1000 μF capacitor | ||
| - 5V Power Supply(The amperage depends on your project. Each LED draws about 60mA @ full brightness/completely white) | ||
| - Wi-Fi network for your micro-controller to connect to(if you want to use the controller interface) | ||
| - USB cable to transfer files to your micro-controller(depending on your situation) | ||
| - More info on materials: [Adafruit](https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-neopixel-uberguide), [Sparkfun](https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/ws2812-breakout-hookup-guide/all) | ||
|
|
||
| ## Dependencies | ||
| - uWeb (get it from my repo [here](https://github.com/petabite/uWeb)) | ||
| ### MicroPython Libraries: | ||
| - neopixel | ||
| - uos | ||
| - urandom | ||
| - ujson | ||
| - usocket | ||
|
|
||
| ## Schematic | ||
|
|
||
| #### The circuit diagram below depicts the setup I used to develop μPixels. | ||
|
|
||
| 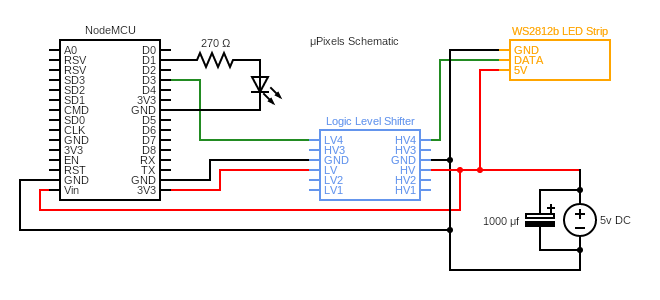 | ||
|
|
||
| ##### Some Notes: | ||
|
|
||
| - Depending on your board, you may not need the Logic Level Shifter. The NodeMCU ESP8266(which I used for testing) is a 3V3 board while the LED Strip is a 5V device so it is important that the 3V3 signal is converted to 5V so that everything works properly. | ||
| - The power supply that you will need for your project will vary depending on the number of LEDS you want to drive(Rule of thumb: Each individual LED draws about 60mA @ full brightness/completely white). Refer to these resources to decide: [Adafruit](https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-neopixel-uberguide), [Sparkfun](https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/ws2812-breakout-hookup-guide/all) | ||
| - The capacitor between the terminals of the power supply will help to smooth the supply of power when power draw changes drastically. | ||
| - It is important that all the grounds are connected together. | ||
| - It is recommended to power the LED strip directly from the power source. Don't power the strip from the board. Your board might not be able to supply the necessary current and it will blow up 💥. | ||
| - You may power the LEDs directly from the board if you only want to drive a few LEDs. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Setup | ||
| 1. Install MicroPython on your board if you have not already ([ESP8266 installation](http://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/esp8266/tutorial/intro.html#intro)) | ||
| 1. Install μWeb by following the INSTALLATION instructions on my [repo](https://github.com/petabite/uWeb#installation). | ||
| 1. Copy the μPixels project files to your board using the same method you used to copy the μWeb files. Make sure that you have transferred: | ||
| - uPixels.css | ||
| - uPixels.html | ||
| - uPixels.js | ||
| - uPixels.py | ||
| 1. Construct the circuit [above](#schematic) (or a variation of it, depending on your board). You may also follow these hookup guides: [Adafruit](https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-neopixel-uberguide), [Sparkfun](https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/ws2812-breakout-hookup-guide/all) | ||
| 1. Check out the [Quick Start](#quick-start) section for examples. | ||
| 1. Make sure you also have a boot.py for the initial setup of your board(ie: connecting to wifi) and main.py for the μPixels code. | ||
| 1. Power up your board. | ||
| 1. Navigate to your board's IP address on port 8000 to access the UI(Ex: 192.168.100.48:8000) | ||
| 1. Enjoy the light show! | ||
|
|
||
| ## Quick Start | ||
|
|
||
| #### Example application using the μPixels user interface: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` python | ||
| from uPixels import uPixels | ||
|
|
||
| pixels = uPixels(4, 30) # init a μPixels object using Pin 4 and controlling a LED strip with 30 LEDS | ||
| pixels.startServer() # start the server that hosts the UI on port 8000 | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| #### Example application using Animations API: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` python | ||
| from uPixels import uPixels | ||
|
|
||
| pixels = uPixels(4, 30) # init a μPixels object on Pin 4 that is controlling a LED strip with 30 LEDS | ||
|
|
||
| for i in range(3): | ||
| pixels.chase(ms=40, color=(100, 0, 0), direction='right') # do a chase animation with delay of 40ms, red color, going right three times. | ||
|
|
||
| pixels.randomFill(ms=150, color=None) # random fill animation with 150ms delay and random colors | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| #### See the docs below for usage of all the μPixels animations! | ||
|
|
||
| ## Documentation | ||
|
|
||
| ### Animation Methods | ||
|
|
||
| ## Tested on | ||
| - NodeMCU ESP8266 | ||
|
|
||
| ## Credits | ||
|
|
||
| - MaterializeCSS | ||
| - Google Material Design Icons | ||
| - Spectrum.js | ||
| - noUiSlider.js | ||
| - MicroPython | ||
| - jQuery | ||
| - jgarff - rpi_ws281x |