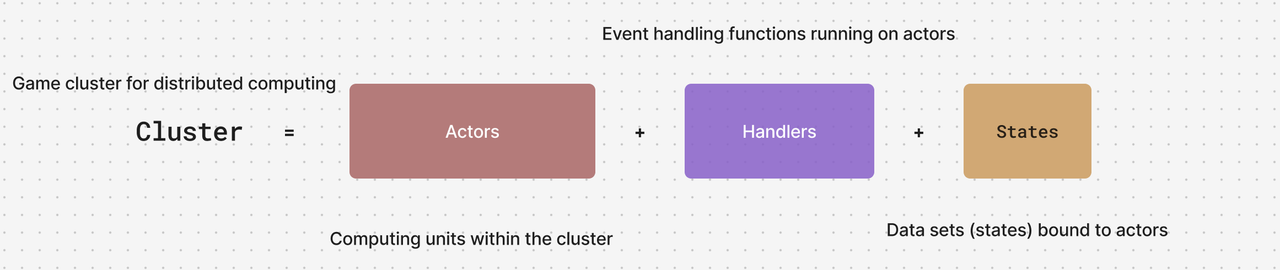
A high-performance distributed framework powered by Actor model, designed for building scalable microservices and real-time applications with ease.
- Lightweight Actor Model: Efficient Actor system based on Go goroutines, where each Actor is an independent computation unit
- Flexible Message Routing: Supports point-to-point communication, broadcasting, and wildcard routing
- Distributed Addressing: Built-in distributed address book with dynamic service discovery and load balancing
- High-Performance Communication: Efficient inter-node communication based on gRPC
- Observability: Built-in tracing and monitoring support
- Fault Tolerance: Built-in fault recovery and error handling mechanisms
- Pub/Sub: Topic-based message publishing and subscription support
- Game Servers: Ideal for handling large numbers of concurrent users and real-time communication
- IoT Applications: Managing large-scale device connections and message routing
- Microservices Architecture: Building scalable distributed service systems
- Real-time Data Processing: Handling high-concurrency data and event streams
- Distributed Computing: Supporting complex distributed computation tasks
- Easy to Use: Provides intuitive APIs, reducing the complexity of distributed system development
- High Performance: Delivers exceptional performance leveraging Go's concurrency features
- Scalability: Supports horizontal scaling to easily handle business growth
- Reliability: Built-in recovery mechanisms enhance system stability
- Development Efficiency: Offers a complete toolkit to accelerate development cycles
Install and set up a minimal working game server using the braid-cli tool
# 1. Install CLI Tool
$ go install github.com/pojol/braid-cli@latest
# 2. Generate a New Project
$ braid-cli new "you-project-name" v0.1.8
# 3. Creating .go Files from Actor Template Configurations
$ cd you-project-name/template
$ go generate
# 4. Navigate to the services directory, then try to build and run the demo
$ cd you-project-name/node
$ go run main.gouser.OnEvent("xx_event", func(ctx core.ActorContext) *actor.DefaultChain {
// use unpack middleware
unpackcfg := &middleware.MsgUnpackCfg[proto.xxx]{}
return &actor.DefaultChain{
Before: []Base.MiddlewareHandler{
middleware.MsgUnpack(unpackcfg),
},
Handler: func(ctx context.Context, msg *router.MsgWrapper) error {
realmsg, ok := unpackcfg.Msg.(*proto.xxx)
// todo ...
return nil
}
}
})m := msg.NewBuilder(context.TODO())
m.WithReqCustomFields(fields.RoomID(b.RoomID))
ctx.Call(b.ID, template.ACTOR_USER, constant.Ev_UpdateUserInfo, m.Build())Testing Robot
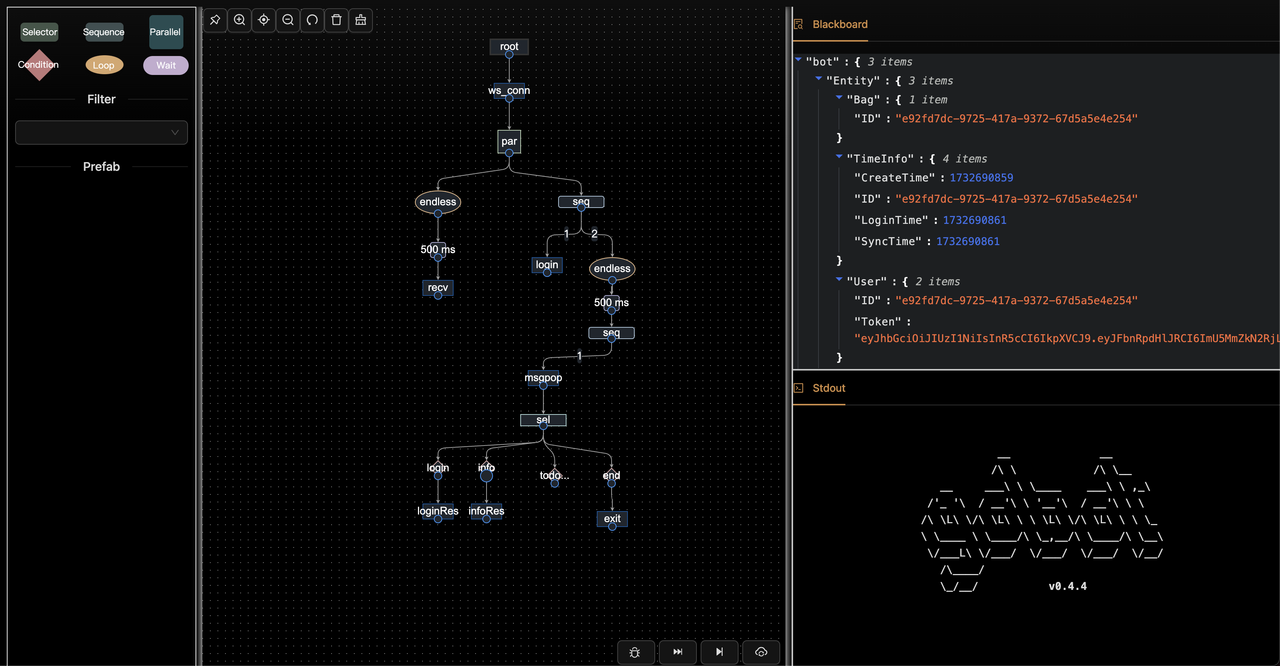
Use the project built with scaffold above
$ cd you-project-name/testbots
# 1. Launch Bot service
$ go run main.go
# 2. Download gobot editor #latest
https://github.com/pojol/gobot/releases
# 3. Launch Bot editor
$ run gobot_editor_[ver].exe or .dmg
# 4. Go to Bots tab
# 5. Click Load button to load the bot
# 6. Drag the testbot.bh file from the testbots directory to the bots page
# 7. Click bottom-left Create Bot button to create instance
# 8. Click Run to the Next button to execute the bot step by step. Monitor the bot-server interaction in the right preview windowgoos: darwin
goarch: amd64
cpu: VirtualApple @ 2.50GHz| Test Item | Node Count | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| dynamic-picker | 10 | 500 actors/s |
| call | 2 (a1 -> a2 -> b1) | 14000 calls/s |