-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 140
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Merge pull request #502 from roboflow/add-inference-gpu-windows-docs
Add Inference Windows CUDA documentation
- Loading branch information
Showing
2 changed files
with
113 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,112 @@ | ||
| # Install the `inference-gpu` Python Package and NVIDIA CUDA on Windows | ||
|
|
||
| !!! warning | ||
| We strongly recommend [installing Inference with Docker on Windows](https://inference.roboflow.com/quickstart/docker/). The guide below should only be used if you are unable to use Docker on your system. | ||
|
|
||
| You can use Inference with `inference-gpu` and NVIDIA CUDA on Windows devices. | ||
|
|
||
| This guide walks through how to configure your Windows GPU setup. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Prerequisites | ||
|
|
||
| To follow this guide, you must have a Windows machine that runs either Windows 10 or Windows 11. Your machine must have an NVIDIA GPU. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Step #1: Install Python | ||
|
|
||
| Download and the latest Python 3.11.x from the [Python Windows version list](https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/). | ||
|
|
||
| Do not install the Python version from the windows store as it is not compatible with onnxruntime. | ||
|
|
||
| Click the "Windows Installer (64 Bit)" link and follow instructions to install python on the machine. | ||
|
|
||
| When the installation is finished, type `py --version` to ensure your Python installation was successful. | ||
|
|
||
| You should see a message showing your Python version. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Step #2: Install Inference GPU | ||
|
|
||
| In a powershell terminal, run: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| py -m pip install inference-gpu | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Step #3: Install CUDA Toolkit 11.8 | ||
|
|
||
| Next, we need to install CUDA Toolkit 11.8. This software will allow Inference to use CUDA. | ||
|
|
||
| [Download CUDA Toolkit](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-11-8-0-download-archive?target_os=Windows&target_arch=x86_64). | ||
|
|
||
| From the download page, choose the correct parameters for your system, and then choose "exe (Network)" and follow the link to download the toolkit. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| Open the installation file and accept all defaults in order to install the toolkit. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Step #3: Install cuDNN | ||
|
|
||
| Next, we need to install cuDNN. | ||
|
|
||
| Navigate to the [cuDNN installation page on the NVIDIA website](https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/cudnn-archive). | ||
|
|
||
| Select "cuDNN v8.7.0 (November 28th, 2022), for CUDA 11.x" | ||
|
|
||
| Choose the link for 11.x, as others will not be compatible with your CUDA version and will fail. | ||
|
|
||
| Choose "Local Installer for Windows (Zip)" and continue to download the ZIP file. You will need to sign up for an NVIDIA account in order to download the software. | ||
|
|
||
| Open the file in downloads folder, right click and choose "Extract All" to extract all files to the download folder. | ||
|
|
||
| Type ctrl+n to open a new Explorer window, and in this window navigate to `C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.8`. | ||
|
|
||
| Copy all .dll files from the bin/ folder of the cuDNN download into the bin/ folder of the CUDA toolkit: | ||
|
|
||
| 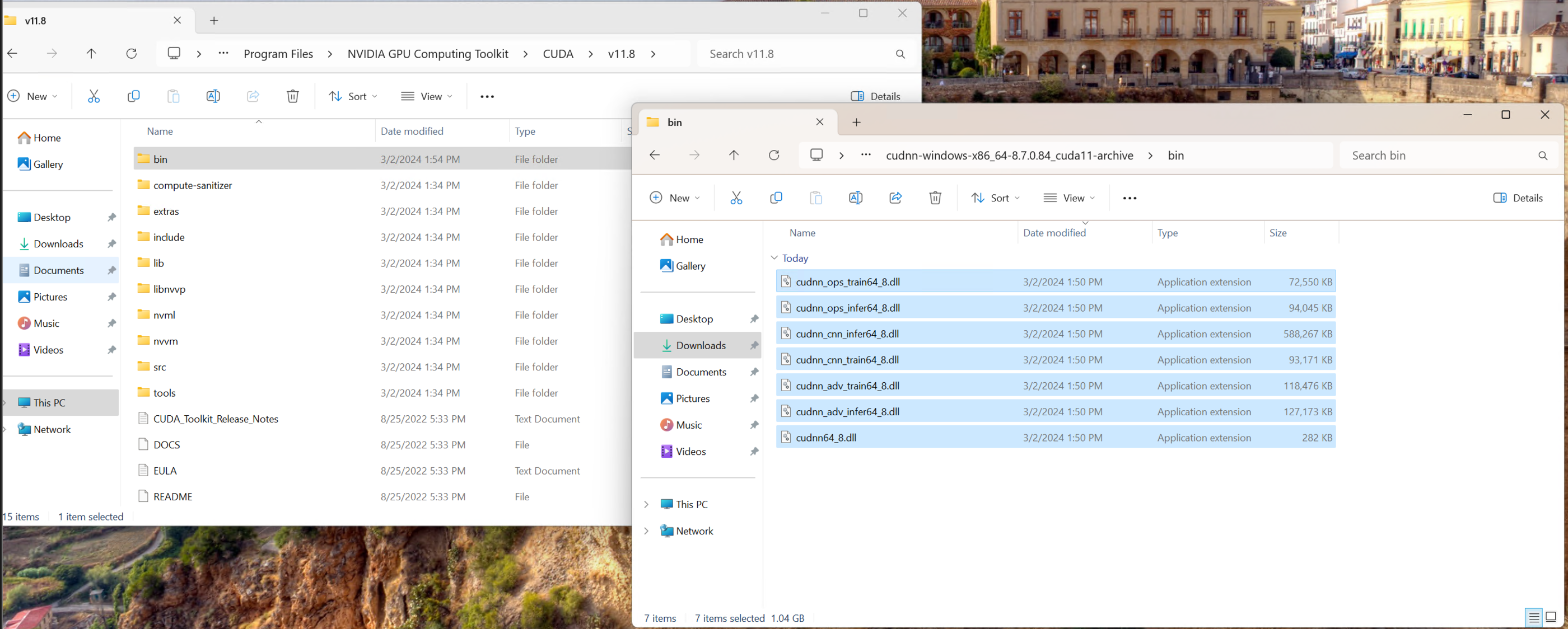 | ||
|
|
||
| Copy all .h files from the include/ folder of the cuDNN download into the include/ folder of the CUDA toolkit: | ||
|
|
||
| 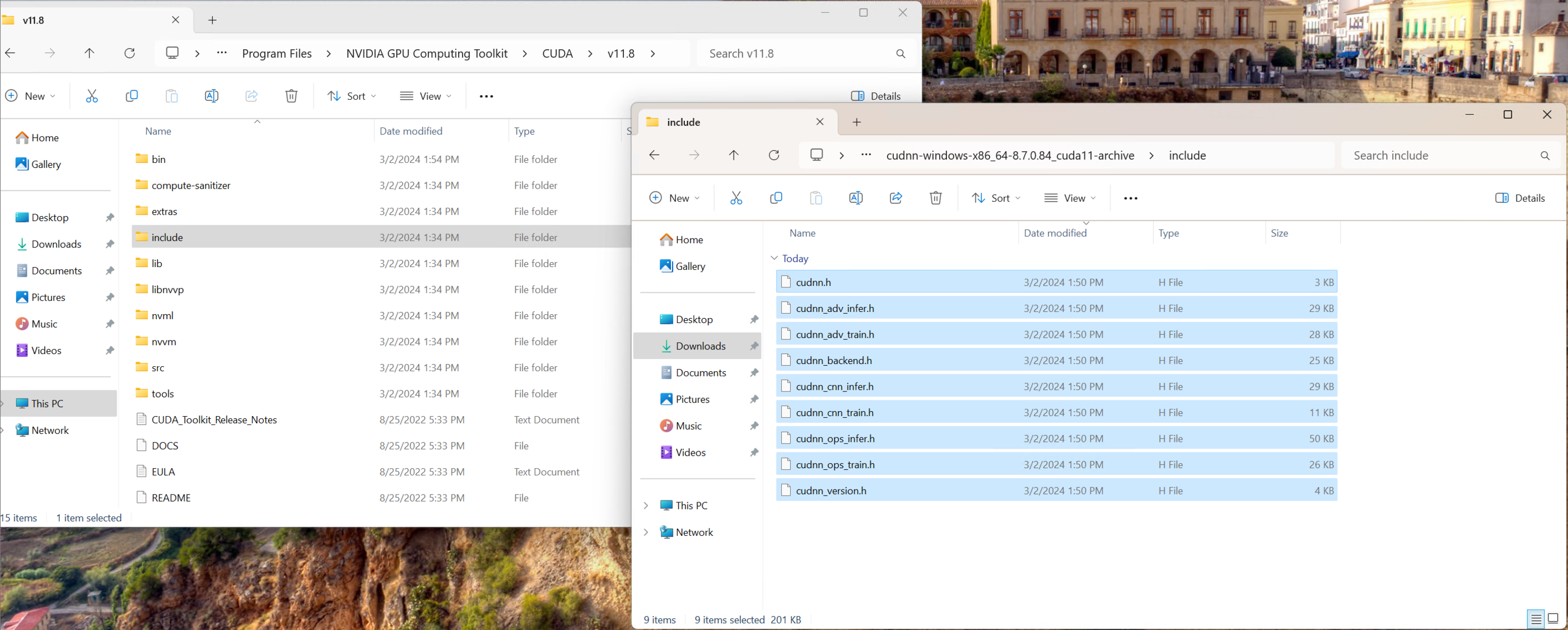 | ||
|
|
||
| Copy the x64 folder from the lib/ directory of the cuDNN download into the lib/ directory of the CUDA installation: | ||
|
|
||
| 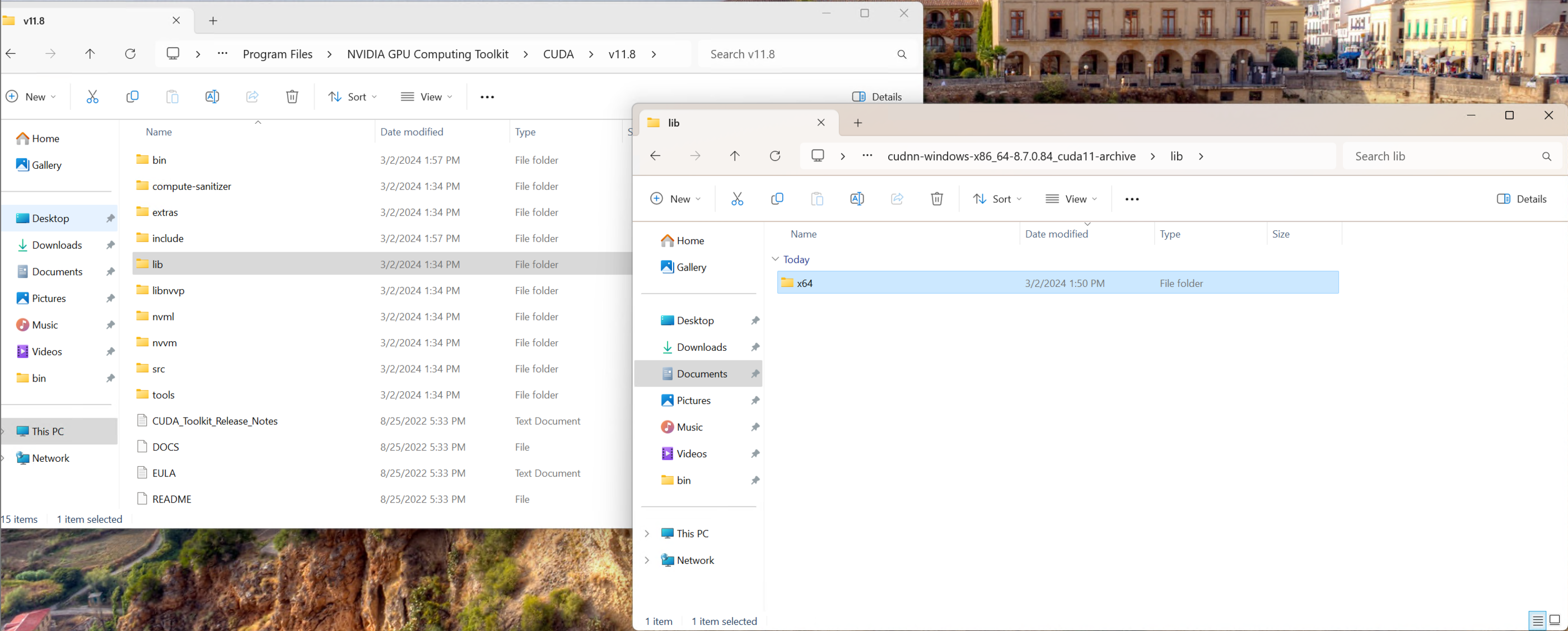 | ||
|
|
||
| Right click the start menu and choose System → Advanced system settings → Environment Variables. | ||
|
|
||
| Create a new environment variable called CUDNN with the value: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.8;C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.8\bin;C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.8\include;C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.8\lib; | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Step #4: Install zlib. | ||
|
|
||
| Find the file C:\Program Files\NVIDIA Corporation\Nsight Systems 2022.4.2\host-windows-x64\zlib.dll Right click and choose "Copy". | ||
|
|
||
| Now navigate to C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.8\bin in the finder. | ||
|
|
||
| Paste the zlib.dll file into this folder and rename to zlibwapi.dll. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Step #5: Install Visual Studio 2019 C++ Runtime | ||
|
|
||
| Finally, install the Visual Studio 2019 C++ runtime ([download link](https://aka.ms/vs/17/release/vc_redist.x64.exe)). | ||
|
|
||
| Create a new file with the following contents: | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from inference import InferencePipeline | ||
| from inference.core.interfaces.stream.sinks import render_boxes | ||
|
|
||
| pipeline = InferencePipeline.init( | ||
| api_key="REPLACE API KEY", ## <- update API KEY | ||
| model_id="rock-paper-scissors-sxsw/11", | ||
| video_reference='https://media.roboflow.com/rock-paper-scissors.mp4', | ||
| on_prediction=render_boxes, | ||
| ) | ||
| pipeline.start() | ||
| pipeline.join() | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Using a text editor (we recommend Visual Studio Code), add your Roboflow API key in the string on line 5. | ||
|
|
||
| Open a PowerShell terminal in the location of the file, and type py infer.py. If the installation is successful, you should see a few frames of annotated images displayed, with no errors or warnings in the console. |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters