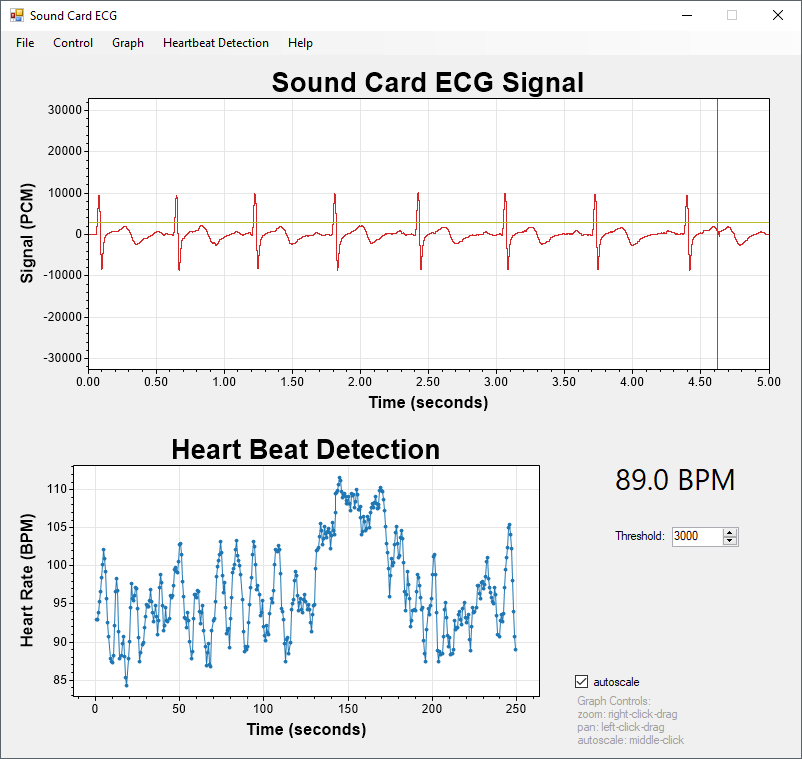
A surprisingly good ECG is possible using a single op-amp. The main idea is that you allow the simple circuit to amplify noise (mixed in with your ECG), send the noisy signal into a PC using the microphone jack of the sound card, then use Python to remove the noise in real time, revealing the ECG.
Project page: http://www.swharden.com/wp/2016-08-08-diy-ecg-with-1-op-amp/
YouTube demo: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AfirWls9Sys
Many people have found this python source code difficult to use due to its dependence on version-specific libraries. A simpler click-to-run EXE for Windows that does essentially the same thing (written in C#) is available on the Sound Card ECG project page.
| Screenshot | Video Demonstration |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Warning: This Python 2 code is obsolete. To get this software running you must install a legacy Python 2 on your system. Consider using a more modern software option like this Sound Card ECG using C#/.NET.
This software needs certain libraries like PyQt4 and numpy, so the easiest way to make sure you have versions of everything that get along is to download a pre-packaged Python distribution. This software has been tested and works with WinPython 3.5.2.1 (not the Qt5 one)
- install WinPython-64bit-3.5.2.1 (not the Qt5 one)
- download this project and modify go.bat to reflect where your python.exe is
- build the circuit, plug it into your microphone hole, and run go.bat
If you build the 1-op-amp ECG circuit and record data as a WAV file you can use a Python script like analyze.py to reduce the noise and plot the result, creating an interactive figure like this:
---



