-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 256
Consensus Module
[TOC]
Consensus module is a module to realize the consensus mechanism of blockchain, which is an important component of blockchain technology. The goal of the blockchain consensus mechanism is to make all honesty nodes maintain a consistent view of the blockchain, while satisfying two properties:
- Consistency:All honesty nodes hold exactly the same prefix portion of the blockchain.
- Validity:Information published by one honesty node will eventually be recorded by all other honesty nodes in their own blockchain.
In general, the consensus mechanism plays a role in determining who is responsible for generating new blocks and maintaining the unity of blockchain within the blockchain network.
Currently, the consensus mechanism of blockchain can be roughly divided into PoW (Proof of Work) and PoS (Proof of Stack), DPoS (Delegated Proof) and distributed consistency algorithm.
Consensus module context
Currently the consensus module in Chain33 is pluggable and supports algorithms such as Para(parallel chain consensus), PBFT,Raft,Tendermint,Ticket.
The role of the consensus module in the overall chain33 system is shown below:
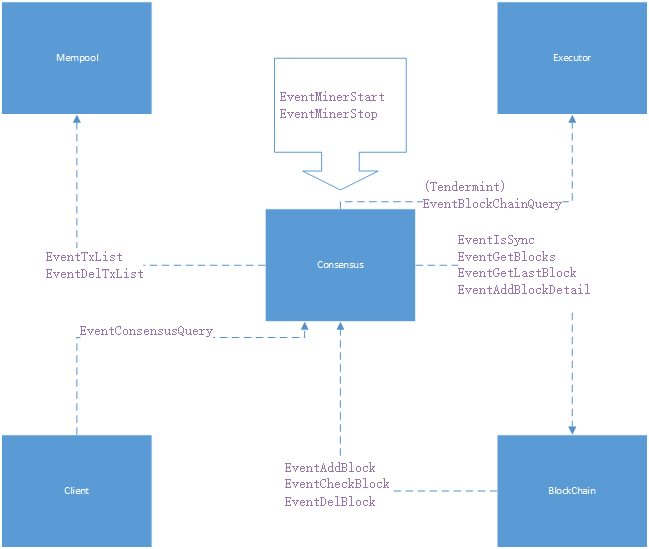
The consensus module is a bridge connecting the transaction and the block, and its role is mainly reflected in promoting the production of the block. All events emitted by the consensus module try to achieve this goal.
Note: except EventBlockChainQuery event, this event in this module only relates to the dynamic adding and removing the Validator node in Tendermint consensus
- To achieve this goal, the process is divided into the following steps:
- Synchronize block height: by sending EventIsSync event to Blockchain module, find out whether the current block height is consistent with the main chain height. If so, it can participate in the consensus process of new block. Otherwise, continue to wait for synchronization to the latest height.
- Get transaction: get the transactions that need to be packaged into the block by sending an EventTxList event to the Mempool module.
- Transaction consensus: validate the transactions to be packaged and determine which node is responsible for generating the new block.
- Generate a new block: triggered by sending an EventAddBlockDetail event to the Blockchain module.
- Remove the error transaction: triggered by sending an EventDelTxList event to the Mempool module.
Note: EventGetBlocks is used to get blocks from Blockchain module with a specified height range, EventGetLastBlock event is used to get the latest block from Blockchain module
The internal logic of the consensus module
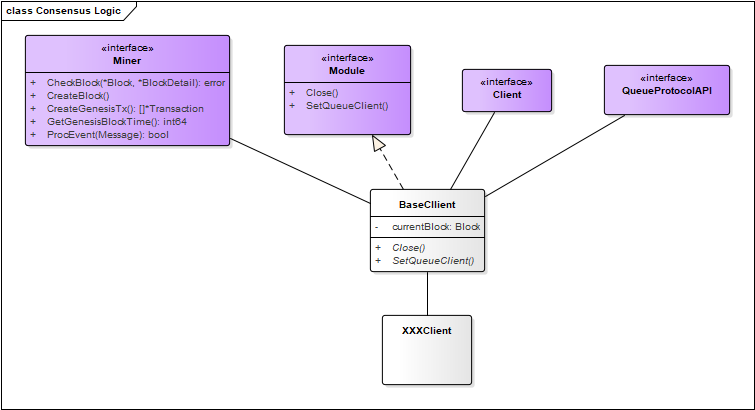
As shown in the figure above, the Consensus module implements the main logical functions: Miner() and Module().
The following sections describe the specific functions of these two interfaces.
/// Module be used for module interface
type Module interface {
//Load the Consensus module
SetQueueClient(client Client)
//Close the Consensus module and complete the cleanup
Close()
}The parameter Client of SetQueueClient interface implements the message queue Client interface. The main functions are as follows:
- Set up the message queue Client
- Initialize the local block
- Subscribe to the message and start the message loop
- Start the consensus process
type Miner interface {
//Create the transactions contained in the genesis block
CreateGenesisTx() []*types.Transaction
//Get the genesis block time
GetGenesisBlockTime() int64
//Get the transaction, package it to a new block
CreateBlock()
//Check the validity of the current block by comparing the parent block with the current block
CheckBlock(parent *types.Block, current *types.BlockDetail) error
//Handling customized events: handles customized events except those handled by BaseClient
//* Note: if you do not need to handle customized events, return false directly. Return true on successful event processing.*
ProcEvent(msg queue.Message) bool
}To introduce the secondary development process of consensus module, assume that a blockchain network with constant number of nodes adopts the following consensus rules:
- The configuration entry for each node contains the NodeId configuration, which is used to configure the unique number of the node, incrementing from 0 by 1 at a time.
- The NodeCount configuration is contained in the configuration entry for each node to configure the total number of nodes in the network, all of which must have the same value.
- If the MOD value of the height and the number of nodes are the same as the number of a certain node, this node will be chosen to generate the new block.
Name the consensus rule NumberDecide.
The secondary development directory of the consensus module is mainly under the plugin/consensus directory. Create numberdecide folder under that directory, and create numberdecide.go and numberdecide_test.go files under that folder.
type subConfig struct {
//Genesis address
Genesis string `json:"genesis"`
//Genesis block time
GenesisBlockTime int64 `json:"genesisBlockTime"`
//NodeID
NodeId int64 `json:"nodeId"`
//Node information (IP, port number)
Nodes []string `json:"nodes"`
}Define the consensus module child configuration structure for obtaining configuration information from configuration files. The genesis address and genesis block time are used in the CreateGenesisTx() and GetGenesisBlockTime() of the Miner interface, either using the configuration in the consensus configuration or by adding a configuration to a child configuration, which is recommended.
type Client struct {
//pointer to a parent object
*drivers.BaseClient
//child config
subcfg *subConfig
}Define the Client structure that implements the Module interface.
- Modify the configuration file chain33.toml, modify name key in the [consensus] as "numberdecide".
- Add[consensus.sub.numberdecide]configuration item, add genesis,genesisBlockTime,nodeId,nodes.
- Add the init() function to numberdecide.go, add the numberdecide directory to init.go in the init folder.
[consensus]
name="numberdecide"
genesisBlockTime=1514533394
genesis="14KEKbYtKKQm4wMthSK9J4La4nAiidGozt"[consensus.sub.numberdecide]
genesis="14KEKbYtKKQm4wMthSK9J4La4nAiidGozt"
genesisBlockTime=1514534444
nodeId=0
nodes=["10.0.0.2:20181","10.0.0.3:20180","10.0.0.4:20180","10.0.0.5:20180"]
numberdecide.go
func init() {
drivers.Reg("numberdecide", New)
drivers.QueryData.Register("numberdecide", &Client{})
}
func New(cfg *types.Consensus, sub []byte) queue.Module {
c := drivers.NewBaseClient(cfg)
var subcfg subConfig
if sub != nil {
types.MustDecode(sub, &subcfg)
}
client := &Client{c, &subcfg}
c.SetChild(client)
return client
}init.go
import (
_ "github.com/33cn/plugin/plugin/consensus/para"
_ "github.com/33cn/plugin/plugin/consensus/pbft"
_ "github.com/33cn/plugin/plugin/consensus/raft"
_ "github.com/33cn/plugin/plugin/consensus/tendermint"
_ "github.com/33cn/plugin/plugin/consensus/ticket"
//Add numberdecide directory
_ "github.com/33cn/plugin/plugin/consensus/numberdecide"
)func (bc *Client) SetQueueClient(c queue.Client) {
bc.InitClient(c, func() {
//call init block
bc.InitBlock()
})
go bc.EventLoop()
//Start the consensus
go bc.startConsensus()
}
func (client *Client) Close() {
//Turn off the listening service and clear the associated storage
slog.Info("consensus numberdecide closed")
}
func (client *Client) startConsensus() {
client.connectNodes()
client.CreateBlock()
}
func (client *Client) connectNodes() {
//Create TCP services and listen to connections from other nodes
go client.listenRoutine()
for {
//Connect the nodes in the configuration file
for i:=0; i<len(client.subcfg.Nodes); i++ {
//Skip if node IP is already connected
//if ... {
// continue
//} else {
// Connect the node actively
//}
}
//Return if all nodes are connected
//if ... {
// return
//}
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
}
func (client *Client) listenRoutine() {
//Start listening and processing connections to get nodeID and node
}Because the consensus mechanism in this example is similar to solo, so the implementation of CreateGenesisTx GetGenesisBlockTime (), ProcEvent (), CheckBlock() in Miner interface are same as sole. Here won't go into details, just make a slight change to CreateBlock().
func (client *Client) CreateBlock() {
issleep := true
for {
if !client.IsMining() || !client.IsCaughtUp() {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
continue
}
if issleep {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
...
//Determine whether the mod value of the height and the number of nodes is equal to the ID of this node. If it is equal, package it; otherwise, do not package it and wait for the broadcast height update
if (lastBlock.Height + 1) % int64(len(client.subcfg.Nodes)) == client.subcfg.NodeId {
err := client.WriteBlock(lastBlock.StateHash, &newblock)
//Determine if a transaction has been deleted and such transactions are to be deleted from the mempool
if err != nil {
issleep = true
continue
}
} else {
//Check if the height has been updated
//client.checkHeightUpdate()
}
}
}hello world